Popular Posts
Which Emerging Layer-1 Blockchains Should Beginners Watch?
Understanding the rapidly evolving blockchain landscape can be overwhelming for newcomers. With numerous layer-1 blockchains emerging, each promising unique features and solutions, it’s essential to identify which platforms are worth paying attention to. This guide explores some of the most promising emerging layer-1 blockchains—Polkadot, Solana, Cardano, Avalanche, and NEAR Protocol—highlighting their recent developments and potential impact on the future of blockchain technology.
What Are Layer-1 Blockchains?
Layer-1 blockchains refer to the base networks that operate independently without relying on other chains. They serve as foundational platforms for decentralized applications (dApps), cryptocurrencies, and DeFi projects. These blockchains aim to address issues such as scalability, interoperability, security, and transaction speed—key factors influencing user adoption and developer interest.
For beginners entering this space, understanding how these layer-1 solutions differ helps in making informed decisions about investments or participation in blockchain ecosystems.
Polkadot: Facilitating Blockchain Interoperability
Polkadot stands out due to its focus on interoperability—the ability of different blockchains to communicate seamlessly. Launched in May 2020 by Web3 Foundation founder Dr. Gavin Wood (also a co-founder of Ethereum), Polkadot enables diverse chains to transfer data or assets securely across networks.
Its core feature is parachains—independent parallel chains that connect through a central relay chain. This architecture allows developers to build specialized blockchains tailored for specific use cases while maintaining integration within a broader ecosystem. Additionally, Polkadot’s governance model empowers token holders with decision-making authority over network upgrades and protocol changes.
The platform's emphasis on interoperability could significantly enhance scalability by reducing fragmentation among various blockchain projects—a crucial factor for mass adoption in DeFi and enterprise applications.
Solana: High-Speed Blockchain for Decentralized Applications
Launched in March 2020 by Solana Labs, Solana aims at providing high throughput with low latency transactions suitable for demanding dApps like gaming platforms or real-time financial services. Its innovative Proof of History (PoH) consensus algorithm combines elements from Proof of Stake (PoS) with Byzantine Fault Tolerance mechanisms—allowing it to process thousands of transactions per second efficiently.
Solana has experienced rapid growth within its DeFi ecosystem; numerous decentralized exchanges (DEXs), NFT marketplaces, and lending protocols now operate on its network. Strategic partnerships with major industry players such as FTX exchange bolster its credibility further.
For users seeking fast transaction speeds at low costs—and developers aiming for scalable infrastructure—Solana presents an attractive option amidst increasing competition from Ethereum 2.0 or Cosmos-based chains.
Cardano: Focused on Security & Regulatory Compliance
Founded in 2017 by Charles Hoskinson—the co-founder of Ethereum—Cardano emphasizes security through rigorous academic research underpinning its development process. Its proof-of-stake consensus mechanism called Ouroboros is designed not only for energy efficiency but also robust security guarantees suitable for institutional use cases.
Cardano supports smart contracts via its Plutus programming language but has taken a cautious approach toward deployment compared to other platforms; this deliberate pace aims at ensuring stability before scaling further functionalities like decentralized finance or identity solutions.
A notable aspect is Cardano’s proactive stance toward regulatory compliance—a strategic move aimed at attracting institutional investors who prioritize legal clarity alongside technological robustness.
Avalanche: Modular Subnets & Fast Transactions
Avalanche launched in September 2020 with an architecture designed around customizable subnets—that are smaller independent networks operating under the main Avalanche protocol framework. This modularity allows developers flexibility when creating specialized chains optimized for particular applications like DeFi protocols or enterprise solutions while benefiting from Avalanche's high throughput capabilities.
The platform has gained traction thanks partly to partnerships with Chainlink (for oracle services) and Curve Finance (a popular stablecoin DEX). Its rapid transaction finality makes it appealing where speed matters most—for example trading environments requiring near-instant settlement times.
While competing against high-performance chains like Solana or Polkadot may pose challenges long-term scalability-wise; Avalanche’s flexible subnet model offers unique advantages suited especially well for niche deployments needing tailored blockchain environments.
NEAR Protocol: Sharding & Cloud Integration
Launched in April 2020 by NEAR Inc., NEAR Protocol employs sharding technology—a method dividing the network into smaller parts called shards—to increase capacity without sacrificing decentralization or security levels typical of proof-of-stake systems.
This design enables higher transaction throughput at lower costs while maintaining user-friendly features such as simple onboarding processes via familiar web interfaces linked directly with cloud providers like Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure.
NEAR’s ecosystem growth reflects strong developer interest driven by ease-of-use combined with scalable infrastructure capable of supporting complex dApps across sectors including gaming, social media tokens—and potentially enterprise-grade applications leveraging cloud integrations.
Its focus on accessibility makes it particularly appealing among beginners seeking scalable yet straightforward entry points into blockchain development.
Key Factors Beginners Should Consider When Watching Emerging Blockchains:
Interoperability: Platforms like Polkadot facilitate cross-chain communication essential as ecosystems grow more interconnected.
Transaction Speed & Cost: Chains such as Solana offer fast processing times ideal during periods of high demand; cost-efficiency remains critical especially when deploying multiple dApps.
Security & Governance: Platforms emphasizing secure consensus algorithms—including Cardano's formal methods—and transparent governance models tend toward stability over time.
Scalability Solutions: Technologies like sharding used by NEAR Protocol enable handling increased user activity without compromising decentralization principles.
Partnerships & Ecosystem Growth: Collaborations with established companies often accelerate development momentum—as seen across all mentioned platforms—and signal potential longevity.
Staying Ahead: How Beginners Can Keep Up With Emerging Trends
To effectively follow these emerging layer-one options:
- Regularly review official project updates via blogs or social media channels
- Participate in community forums such as Reddit or Discord groups
- Monitor industry reports from reputable sources focusing on innovation trends
- Experiment cautiously using testnets before committing significant resources
By adopting an informed approach rooted in understanding each platform's strengths—and recognizing their developmental trajectories—you can better navigate this dynamic space whether investing directly or developing new projects.
Final Thoughts
Emerging layer-one blockchains present exciting opportunities both technically and financially—but they also come with risks associated with early-stage development phases. For beginners eager to participate actively within this space—from investing wisely based on technological merits to building innovative dApps—it pays off knowing which platforms are gaining momentum today while assessing their long-term viability carefully.
Staying informed about innovations such as interoperability features from Polkadot—or high-speed capabilities offered by Solana—is key not just for making smarter choices but also contributing meaningfully towards shaping the future landscape of decentralized technology.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-23 01:13
Which emerging layer-1 blockchains should beginners watch?
Which Emerging Layer-1 Blockchains Should Beginners Watch?
Understanding the rapidly evolving blockchain landscape can be overwhelming for newcomers. With numerous layer-1 blockchains emerging, each promising unique features and solutions, it’s essential to identify which platforms are worth paying attention to. This guide explores some of the most promising emerging layer-1 blockchains—Polkadot, Solana, Cardano, Avalanche, and NEAR Protocol—highlighting their recent developments and potential impact on the future of blockchain technology.
What Are Layer-1 Blockchains?
Layer-1 blockchains refer to the base networks that operate independently without relying on other chains. They serve as foundational platforms for decentralized applications (dApps), cryptocurrencies, and DeFi projects. These blockchains aim to address issues such as scalability, interoperability, security, and transaction speed—key factors influencing user adoption and developer interest.
For beginners entering this space, understanding how these layer-1 solutions differ helps in making informed decisions about investments or participation in blockchain ecosystems.
Polkadot: Facilitating Blockchain Interoperability
Polkadot stands out due to its focus on interoperability—the ability of different blockchains to communicate seamlessly. Launched in May 2020 by Web3 Foundation founder Dr. Gavin Wood (also a co-founder of Ethereum), Polkadot enables diverse chains to transfer data or assets securely across networks.
Its core feature is parachains—independent parallel chains that connect through a central relay chain. This architecture allows developers to build specialized blockchains tailored for specific use cases while maintaining integration within a broader ecosystem. Additionally, Polkadot’s governance model empowers token holders with decision-making authority over network upgrades and protocol changes.
The platform's emphasis on interoperability could significantly enhance scalability by reducing fragmentation among various blockchain projects—a crucial factor for mass adoption in DeFi and enterprise applications.
Solana: High-Speed Blockchain for Decentralized Applications
Launched in March 2020 by Solana Labs, Solana aims at providing high throughput with low latency transactions suitable for demanding dApps like gaming platforms or real-time financial services. Its innovative Proof of History (PoH) consensus algorithm combines elements from Proof of Stake (PoS) with Byzantine Fault Tolerance mechanisms—allowing it to process thousands of transactions per second efficiently.
Solana has experienced rapid growth within its DeFi ecosystem; numerous decentralized exchanges (DEXs), NFT marketplaces, and lending protocols now operate on its network. Strategic partnerships with major industry players such as FTX exchange bolster its credibility further.
For users seeking fast transaction speeds at low costs—and developers aiming for scalable infrastructure—Solana presents an attractive option amidst increasing competition from Ethereum 2.0 or Cosmos-based chains.
Cardano: Focused on Security & Regulatory Compliance
Founded in 2017 by Charles Hoskinson—the co-founder of Ethereum—Cardano emphasizes security through rigorous academic research underpinning its development process. Its proof-of-stake consensus mechanism called Ouroboros is designed not only for energy efficiency but also robust security guarantees suitable for institutional use cases.
Cardano supports smart contracts via its Plutus programming language but has taken a cautious approach toward deployment compared to other platforms; this deliberate pace aims at ensuring stability before scaling further functionalities like decentralized finance or identity solutions.
A notable aspect is Cardano’s proactive stance toward regulatory compliance—a strategic move aimed at attracting institutional investors who prioritize legal clarity alongside technological robustness.
Avalanche: Modular Subnets & Fast Transactions
Avalanche launched in September 2020 with an architecture designed around customizable subnets—that are smaller independent networks operating under the main Avalanche protocol framework. This modularity allows developers flexibility when creating specialized chains optimized for particular applications like DeFi protocols or enterprise solutions while benefiting from Avalanche's high throughput capabilities.
The platform has gained traction thanks partly to partnerships with Chainlink (for oracle services) and Curve Finance (a popular stablecoin DEX). Its rapid transaction finality makes it appealing where speed matters most—for example trading environments requiring near-instant settlement times.
While competing against high-performance chains like Solana or Polkadot may pose challenges long-term scalability-wise; Avalanche’s flexible subnet model offers unique advantages suited especially well for niche deployments needing tailored blockchain environments.
NEAR Protocol: Sharding & Cloud Integration
Launched in April 2020 by NEAR Inc., NEAR Protocol employs sharding technology—a method dividing the network into smaller parts called shards—to increase capacity without sacrificing decentralization or security levels typical of proof-of-stake systems.
This design enables higher transaction throughput at lower costs while maintaining user-friendly features such as simple onboarding processes via familiar web interfaces linked directly with cloud providers like Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure.
NEAR’s ecosystem growth reflects strong developer interest driven by ease-of-use combined with scalable infrastructure capable of supporting complex dApps across sectors including gaming, social media tokens—and potentially enterprise-grade applications leveraging cloud integrations.
Its focus on accessibility makes it particularly appealing among beginners seeking scalable yet straightforward entry points into blockchain development.
Key Factors Beginners Should Consider When Watching Emerging Blockchains:
Interoperability: Platforms like Polkadot facilitate cross-chain communication essential as ecosystems grow more interconnected.
Transaction Speed & Cost: Chains such as Solana offer fast processing times ideal during periods of high demand; cost-efficiency remains critical especially when deploying multiple dApps.
Security & Governance: Platforms emphasizing secure consensus algorithms—including Cardano's formal methods—and transparent governance models tend toward stability over time.
Scalability Solutions: Technologies like sharding used by NEAR Protocol enable handling increased user activity without compromising decentralization principles.
Partnerships & Ecosystem Growth: Collaborations with established companies often accelerate development momentum—as seen across all mentioned platforms—and signal potential longevity.
Staying Ahead: How Beginners Can Keep Up With Emerging Trends
To effectively follow these emerging layer-one options:
- Regularly review official project updates via blogs or social media channels
- Participate in community forums such as Reddit or Discord groups
- Monitor industry reports from reputable sources focusing on innovation trends
- Experiment cautiously using testnets before committing significant resources
By adopting an informed approach rooted in understanding each platform's strengths—and recognizing their developmental trajectories—you can better navigate this dynamic space whether investing directly or developing new projects.
Final Thoughts
Emerging layer-one blockchains present exciting opportunities both technically and financially—but they also come with risks associated with early-stage development phases. For beginners eager to participate actively within this space—from investing wisely based on technological merits to building innovative dApps—it pays off knowing which platforms are gaining momentum today while assessing their long-term viability carefully.
Staying informed about innovations such as interoperability features from Polkadot—or high-speed capabilities offered by Solana—is key not just for making smarter choices but also contributing meaningfully towards shaping the future landscape of decentralized technology.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Various Countries Classify Different Types of Crypto Assets?
Understanding how different countries classify crypto assets is essential for investors, developers, and regulators navigating the rapidly evolving digital asset landscape. Each nation’s approach reflects its legal framework, economic priorities, and technological readiness. This article explores the diverse classifications adopted worldwide and highlights recent developments shaping the future of crypto regulation.
The Global Landscape of Crypto Asset Classification
Crypto assets encompass a broad spectrum of digital tokens and currencies that serve various functions—from store of value to utility within blockchain ecosystems. However, there is no universal standard for classifying these assets. Countries tend to categorize them based on their intended use, underlying technology, or regulatory concerns.
Some nations treat certain cryptocurrencies as securities due to their investment characteristics or fundraising mechanisms. Others classify them as commodities if they resemble traditional physical commodities like gold or oil in trading behavior. Still, some jurisdictions have yet to establish clear definitions, leading to regulatory ambiguity.
This patchwork creates challenges for cross-border operations but also offers opportunities for tailored regulation that aligns with local economic policies.
United States: A Mixed Approach
The United States exemplifies a complex regulatory environment where multiple agencies oversee crypto assets based on their classification. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been particularly active in identifying tokens that qualify as securities under existing laws—especially those issued through initial coin offerings (ICOs). When classified as securities, these tokens are subject to strict registration requirements designed to protect investors.
Conversely, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) views some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum as commodities—similar to gold or oil—which can be traded on regulated futures markets. This dual oversight means companies must navigate both securities law compliance and commodity regulations depending on the asset type.
At the state level, regulations such as New York's BitLicense impose licensing requirements for crypto businesses operating within specific jurisdictions. These layered rules aim to balance innovation with consumer protection but can create compliance complexities for firms operating nationwide.
Canada: Favorable Regulations with Strategic Acquisitions
Canada has positioned itself as one of North America's more welcoming environments for crypto enterprises. Its regulatory framework is characterized by clarity provided by bodies like the Canadian Securities Administrators (CSA), which issue guidelines rather than prescriptive laws—allowing flexibility while maintaining oversight.
Recent industry movements include Robinhood’s acquisition of WonderFi in May 2025—a Canadian-based platform involved in multiple acquisitions—highlighting Canada's strategic importance in global crypto markets. The country’s openness encourages innovation while ensuring investor safeguards through transparent licensing procedures.
European Union: Moving Toward Unified Regulation
The EU aims to establish comprehensive rules through its Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation set expected to come into force by 2025. MiCA seeks harmonization across member states by defining clear categories such as stablecoins, utility tokens, security tokens—and establishing licensing standards accordingly.
By creating a unified legal framework covering anti-money laundering measures and consumer protections across all member countries—including Germany France Italy—the EU hopes to foster innovation while reducing fragmentation that hampers cross-border services within Europe.
China: Strict Bans Amid Blockchain Exploration
China maintains one of the most restrictive stances toward cryptocurrencies; it has banned trading platforms entirely citing risks related to financial stability and market manipulation concerns. Despite this crackdown on trading activities involving Bitcoin or other cryptos,
the country actively promotes blockchain technology development independently from cryptocurrency speculation efforts—for example,
investments into blockchain infrastructure projects continue unabated under government guidance[not provided].
This dichotomy underscores China's focus on harnessing blockchain's potential without exposing its financial system directly via decentralized currencies or unregulated exchanges.
India: Navigating Regulatory Uncertainty
India presents an ambiguous picture regarding crypto classification due partly to ongoing legislative debates rather than concrete laws enacted so far[not provided]. While central bank authorities like RBI have expressed reservations about digital currencies’ risks—including potential misuse—they have not outright banned ownership or trading activities[not provided].
The government considers introducing legislation aimed at regulating transactions but remains cautious about fostering an environment conducive either too restrictive—or too permissive—that could impact financial stability[not provided].
Investors should monitor policy developments closely since any new bill could redefine how various types of cryptos are classified—from utility tokens used within apps—to security-like instruments raised via token sales.
Singapore: A Model for Friendly Regulation
Singapore stands out globally thanks largely due its proactive stance toward fostering industry growth alongside robust regulation[not provided]. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) issues clear guidelines covering licensing requirements for exchanges dealing with cryptocurrencies,
emphasizing AML compliance,
and consumer protection measures—all designed
to encourage responsible innovation without compromising safety standards[not provided].
This balanced approach makes Singapore an attractive hub for startups seeking a supportive yet compliant environment.
Recent Developments Shaping Classification Trends
Recent months have seen notable shifts indicating increased acceptance—or at least recognition—of certain crypto assets:
Solana ETF Approval: Bloomberg analysts estimate a 90% chance that SEC will approve a Solana-based ETF soon—a move driven partly by Solana's classification as a commodity suitable for regulated futures markets.
Market Growth: WisdomTree reported reaching $115.8 billion in assets under management at Q1 2025—a testament both to institutional interest and evolving classification frameworks supporting broader adoption.
Performance Indicators: Shares like Cantor Equity Partners II surged recently amid positive market sentiment around digital asset investments despite ongoing regulatory uncertainties elsewhere.
These developments reflect ongoing efforts worldwide towards clearer classifications facilitating mainstream acceptance while safeguarding investor interests.
Challenges from Divergent Classifications
Disparate approaches pose several risks:
Legal Confusion: Companies operating across borders face complex compliance landscapes leading potentially costly legal disputes.
Market Volatility: Regulatory uncertainty often triggers sharp price swings among traders reacting swiftly when new rules emerge.
Innovation Risks: Overly restrictive regimes may hinder technological progress; conversely,
permissive environments risk exposing consumers without adequate safeguards.
Striking an appropriate balance remains crucial amid rapid technological advancements.
Embracing Balanced Regulation
As countries refine their frameworks—for instance,
through initiatives like MiCA—the goal should be creating predictable environments where innovation thrives alongside robust protections against frauds such as scams or pump-and-dump schemes.[LSI keywords include "crypto regulation," "classification," "digital assets," "security tokens," "utility tokens," "cryptocurrency laws"]
A nuanced understanding helps stakeholders adapt strategies effectively whether they’re developing new products or investing globally.
In summary, each country's approach reflects its unique priorities—from strict bans in China versus open policies in Singapore—and influences how different types of crypto assets are classified today.[SEO keywords include “crypto asset classification,” “regulatory landscape,” “global cryptocurrency laws,” “security vs utility tokens”] Understanding these distinctions is vital not only for compliance but also unlocking opportunities within this dynamic sector.
Note: Staying informed about evolving regulations ensures better risk management and strategic planning amidst global shifts shaping the future landscape of digital finance


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 23:52
How do various countries classify different types of crypto assets?
How Do Various Countries Classify Different Types of Crypto Assets?
Understanding how different countries classify crypto assets is essential for investors, developers, and regulators navigating the rapidly evolving digital asset landscape. Each nation’s approach reflects its legal framework, economic priorities, and technological readiness. This article explores the diverse classifications adopted worldwide and highlights recent developments shaping the future of crypto regulation.
The Global Landscape of Crypto Asset Classification
Crypto assets encompass a broad spectrum of digital tokens and currencies that serve various functions—from store of value to utility within blockchain ecosystems. However, there is no universal standard for classifying these assets. Countries tend to categorize them based on their intended use, underlying technology, or regulatory concerns.
Some nations treat certain cryptocurrencies as securities due to their investment characteristics or fundraising mechanisms. Others classify them as commodities if they resemble traditional physical commodities like gold or oil in trading behavior. Still, some jurisdictions have yet to establish clear definitions, leading to regulatory ambiguity.
This patchwork creates challenges for cross-border operations but also offers opportunities for tailored regulation that aligns with local economic policies.
United States: A Mixed Approach
The United States exemplifies a complex regulatory environment where multiple agencies oversee crypto assets based on their classification. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been particularly active in identifying tokens that qualify as securities under existing laws—especially those issued through initial coin offerings (ICOs). When classified as securities, these tokens are subject to strict registration requirements designed to protect investors.
Conversely, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) views some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum as commodities—similar to gold or oil—which can be traded on regulated futures markets. This dual oversight means companies must navigate both securities law compliance and commodity regulations depending on the asset type.
At the state level, regulations such as New York's BitLicense impose licensing requirements for crypto businesses operating within specific jurisdictions. These layered rules aim to balance innovation with consumer protection but can create compliance complexities for firms operating nationwide.
Canada: Favorable Regulations with Strategic Acquisitions
Canada has positioned itself as one of North America's more welcoming environments for crypto enterprises. Its regulatory framework is characterized by clarity provided by bodies like the Canadian Securities Administrators (CSA), which issue guidelines rather than prescriptive laws—allowing flexibility while maintaining oversight.
Recent industry movements include Robinhood’s acquisition of WonderFi in May 2025—a Canadian-based platform involved in multiple acquisitions—highlighting Canada's strategic importance in global crypto markets. The country’s openness encourages innovation while ensuring investor safeguards through transparent licensing procedures.
European Union: Moving Toward Unified Regulation
The EU aims to establish comprehensive rules through its Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation set expected to come into force by 2025. MiCA seeks harmonization across member states by defining clear categories such as stablecoins, utility tokens, security tokens—and establishing licensing standards accordingly.
By creating a unified legal framework covering anti-money laundering measures and consumer protections across all member countries—including Germany France Italy—the EU hopes to foster innovation while reducing fragmentation that hampers cross-border services within Europe.
China: Strict Bans Amid Blockchain Exploration
China maintains one of the most restrictive stances toward cryptocurrencies; it has banned trading platforms entirely citing risks related to financial stability and market manipulation concerns. Despite this crackdown on trading activities involving Bitcoin or other cryptos,
the country actively promotes blockchain technology development independently from cryptocurrency speculation efforts—for example,
investments into blockchain infrastructure projects continue unabated under government guidance[not provided].
This dichotomy underscores China's focus on harnessing blockchain's potential without exposing its financial system directly via decentralized currencies or unregulated exchanges.
India: Navigating Regulatory Uncertainty
India presents an ambiguous picture regarding crypto classification due partly to ongoing legislative debates rather than concrete laws enacted so far[not provided]. While central bank authorities like RBI have expressed reservations about digital currencies’ risks—including potential misuse—they have not outright banned ownership or trading activities[not provided].
The government considers introducing legislation aimed at regulating transactions but remains cautious about fostering an environment conducive either too restrictive—or too permissive—that could impact financial stability[not provided].
Investors should monitor policy developments closely since any new bill could redefine how various types of cryptos are classified—from utility tokens used within apps—to security-like instruments raised via token sales.
Singapore: A Model for Friendly Regulation
Singapore stands out globally thanks largely due its proactive stance toward fostering industry growth alongside robust regulation[not provided]. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) issues clear guidelines covering licensing requirements for exchanges dealing with cryptocurrencies,
emphasizing AML compliance,
and consumer protection measures—all designed
to encourage responsible innovation without compromising safety standards[not provided].
This balanced approach makes Singapore an attractive hub for startups seeking a supportive yet compliant environment.
Recent Developments Shaping Classification Trends
Recent months have seen notable shifts indicating increased acceptance—or at least recognition—of certain crypto assets:
Solana ETF Approval: Bloomberg analysts estimate a 90% chance that SEC will approve a Solana-based ETF soon—a move driven partly by Solana's classification as a commodity suitable for regulated futures markets.
Market Growth: WisdomTree reported reaching $115.8 billion in assets under management at Q1 2025—a testament both to institutional interest and evolving classification frameworks supporting broader adoption.
Performance Indicators: Shares like Cantor Equity Partners II surged recently amid positive market sentiment around digital asset investments despite ongoing regulatory uncertainties elsewhere.
These developments reflect ongoing efforts worldwide towards clearer classifications facilitating mainstream acceptance while safeguarding investor interests.
Challenges from Divergent Classifications
Disparate approaches pose several risks:
Legal Confusion: Companies operating across borders face complex compliance landscapes leading potentially costly legal disputes.
Market Volatility: Regulatory uncertainty often triggers sharp price swings among traders reacting swiftly when new rules emerge.
Innovation Risks: Overly restrictive regimes may hinder technological progress; conversely,
permissive environments risk exposing consumers without adequate safeguards.
Striking an appropriate balance remains crucial amid rapid technological advancements.
Embracing Balanced Regulation
As countries refine their frameworks—for instance,
through initiatives like MiCA—the goal should be creating predictable environments where innovation thrives alongside robust protections against frauds such as scams or pump-and-dump schemes.[LSI keywords include "crypto regulation," "classification," "digital assets," "security tokens," "utility tokens," "cryptocurrency laws"]
A nuanced understanding helps stakeholders adapt strategies effectively whether they’re developing new products or investing globally.
In summary, each country's approach reflects its unique priorities—from strict bans in China versus open policies in Singapore—and influences how different types of crypto assets are classified today.[SEO keywords include “crypto asset classification,” “regulatory landscape,” “global cryptocurrency laws,” “security vs utility tokens”] Understanding these distinctions is vital not only for compliance but also unlocking opportunities within this dynamic sector.
Note: Staying informed about evolving regulations ensures better risk management and strategic planning amidst global shifts shaping the future landscape of digital finance
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Common Services and Platforms in the DeFi Ecosystem
The decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem has revolutionized traditional financial services by leveraging blockchain technology to create open, transparent, and permissionless platforms. As DeFi continues to grow rapidly, understanding its core services and key platforms is essential for users, investors, and developers alike. This article explores the most common offerings within DeFi, providing a comprehensive overview of how these components work together to shape the future of finance.
What Are DeFi Services?
DeFi services encompass a broad range of financial activities that operate without centralized intermediaries like banks or brokerages. Instead, smart contracts—self-executing code stored on blockchains—automate transactions and enforce rules transparently. These services aim to democratize access to financial tools by making them accessible globally and removing barriers such as geographic restrictions or credit checks.
The primary categories include lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), yield farming protocols, stablecoins, and prediction markets. Each serves a specific purpose but often integrates with others within the ecosystem to provide seamless user experiences.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms
Lending protocols are among the earliest innovations in DeFi that mirror traditional banking functions but operate in a decentralized manner. They enable users to lend their crypto assets out for interest or borrow against collateral without involving banks or other intermediaries.
Aave is one of the most prominent examples; it allows users to lend various cryptocurrencies while earning interest or borrow assets at variable rates based on market conditions. Its flexible features include flash loans—unsecured loans executed within a single transaction—which have opened new possibilities for arbitrageurs and developers.
Similarly, Compound offers an algorithmic money market where supply rates fluctuate depending on supply-demand dynamics. Users can earn interest by supplying assets or take out loans using their crypto holdings as collateral.
MakerDAO, distinct from pure lending platforms, provides stability through its governance model that issues DAI—a decentralized stablecoin pegged 1:1 with USD. Users can lock collateral into Maker vaults to generate DAI tokens used across various DeFi applications.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges facilitate peer-to-peer trading directly from user wallets without relying on centralized order books or custodianship of funds. They use automated market makers (AMMs), which rely on liquidity pools instead of traditional order matching systems.
Uniswap, arguably the most popular DEX globally, exemplifies this model with its simple interface allowing anyone to swap tokens instantly via liquidity pools funded by other users who earn fees proportional to their contribution’s size.
Other notable DEXs include SushiSwap, which originated as a fork of Uniswap but added community-driven features like staking rewards for liquidity providers; it has gained significant traction due partly due to its governance token SUSHI.
Curve Finance specializes in stablecoin trading with low slippage thanks to optimized algorithms tailored for assets pegged closely together—ideal for traders seeking minimal price impact when swapping USDC for USDT or similar pairs.
Yield Farming & Liquidity Provision
Yield farming involves providing liquidity—depositing tokens into protocols—to earn returns often higher than traditional savings accounts but accompanied by increased risk levels such as impermanent loss or smart contract vulnerabilities.
Platforms like Yearn.finance aggregate multiple yield opportunities across different protocols automatically optimizing yields based on current conditions. Users deposit tokens into Yearn vaults that deploy funds into various strategies aiming at maximizing returns while managing risks effectively.
SushiSwap also offers yield farming options through its liquidity pools where participants stake pairs like ETH/USDT earning transaction fees plus additional incentives via SUSHI tokens—a process incentivizing active participation in maintaining healthy markets within the ecosystem.
Stablecoins: The Cornerstone Assets
Stablecoins are digital assets designed explicitly for stability—they maintain peg values close enough that they serve as reliable mediums of exchange within DeFi environments rather than volatile cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC).
- DAI, created by MakerDAO’s protocol using overcollateralized crypto assets such as ETH; it maintains decentralization while offering stability.
- USDC, issued jointly by Circle Financial and Coinbase; widely adopted due to regulatory compliance.
- Tether (USDT) remains one of the most traded stablecoins despite ongoing debates about transparency because of its extensive adoption across exchanges worldwide.
These coins underpin many DeFi activities—from trading pairs on DEXs—and serve as safe havens during volatile periods when traders seek refuge from price swings elsewhere in crypto markets.
Prediction Markets & Oracles
Prediction markets allow participants betting on future events’ outcomes—for example election results—or even sports scores—all conducted securely via blockchain-based smart contracts ensuring transparency around odds-setting processes.
Platforms like Augur enable users not only bet but also create custom markets covering diverse topics ranging from politics' outcomes till economic indicators’ movements—all settled automatically once event results are verified externally through oracle feeds provided primarily by Chainlink's network infrastructure.
Oracles play an essential role here—they bridge real-world data with blockchain environments ensuring accurate information feeds necessary for fair settlement processes in prediction markets.
Recent Trends Shaping Core Platforms
Over recent years, regulatory scrutiny has intensified globally—with agencies like SEC scrutinizing certain projects suspected of unregistered securities issuance—and this has prompted many platforms toward increased transparency standards including audits and compliance measures aimed at safeguarding investor interests while maintaining decentralization principles effectively balancing innovation versus regulation adherence.
Security remains paramount amid frequent high-profile hacks exposing vulnerabilities inherent in complex smart contracts architectures leading developers investing heavily into security audits alongside bug bounty programs designed explicitly toward identifying potential flaws before exploitation occurs.
Market volatility continues influencing platform operations significantly; sharp price swings impact liquidity levels adversely affecting yields especially during downturn phases which may lead some investors toward more conservative strategies involving stable asset holdings rather than high-risk yield farming endeavors.
Risks & Future Outlook
While these core services form robust pillars supporting DeFi’s growth trajectory today—including innovative products such as flash loans—the space faces challenges ahead:
- Regulatory actions could tighten restrictions impacting service availability.
- Security improvements require continuous investment amidst evolving threat landscapes.
- Market volatility necessitates developing mechanisms capable of stabilizing ecosystems against sudden shocks.
Despite these hurdles, ongoing technological advancements coupled with increasing institutional interest suggest promising prospects if stakeholders prioritize security enhancements alongside clear regulatory frameworks fostering sustainable growth.
Navigating Key Components Within The DeFi Ecosystem
Understanding common services offered within de-fi helps both newcomers navigate this complex landscape efficiently while enabling experienced participants optimize their strategies responsibly. From lending protocols offering passive income streams through borrowing mechanisms facilitating capital efficiency—to decentralized exchanges democratizing trade access—the diversity ensures broad utility aligned with user needs.
By staying informed about developments across these core areas—including emerging trends such as integrated insurance solutions or cross-chain interoperability—users can better position themselves amidst rapid innovation shaping tomorrow's financial landscape.
This overview aims not only at informing readers about prevalent de-fi platforms but also emphasizes responsible participation rooted in awareness about risks involved.


kai
2025-05-22 19:56
What are some common services or platforms found within the DeFi ecosystem?
Common Services and Platforms in the DeFi Ecosystem
The decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem has revolutionized traditional financial services by leveraging blockchain technology to create open, transparent, and permissionless platforms. As DeFi continues to grow rapidly, understanding its core services and key platforms is essential for users, investors, and developers alike. This article explores the most common offerings within DeFi, providing a comprehensive overview of how these components work together to shape the future of finance.
What Are DeFi Services?
DeFi services encompass a broad range of financial activities that operate without centralized intermediaries like banks or brokerages. Instead, smart contracts—self-executing code stored on blockchains—automate transactions and enforce rules transparently. These services aim to democratize access to financial tools by making them accessible globally and removing barriers such as geographic restrictions or credit checks.
The primary categories include lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), yield farming protocols, stablecoins, and prediction markets. Each serves a specific purpose but often integrates with others within the ecosystem to provide seamless user experiences.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms
Lending protocols are among the earliest innovations in DeFi that mirror traditional banking functions but operate in a decentralized manner. They enable users to lend their crypto assets out for interest or borrow against collateral without involving banks or other intermediaries.
Aave is one of the most prominent examples; it allows users to lend various cryptocurrencies while earning interest or borrow assets at variable rates based on market conditions. Its flexible features include flash loans—unsecured loans executed within a single transaction—which have opened new possibilities for arbitrageurs and developers.
Similarly, Compound offers an algorithmic money market where supply rates fluctuate depending on supply-demand dynamics. Users can earn interest by supplying assets or take out loans using their crypto holdings as collateral.
MakerDAO, distinct from pure lending platforms, provides stability through its governance model that issues DAI—a decentralized stablecoin pegged 1:1 with USD. Users can lock collateral into Maker vaults to generate DAI tokens used across various DeFi applications.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges facilitate peer-to-peer trading directly from user wallets without relying on centralized order books or custodianship of funds. They use automated market makers (AMMs), which rely on liquidity pools instead of traditional order matching systems.
Uniswap, arguably the most popular DEX globally, exemplifies this model with its simple interface allowing anyone to swap tokens instantly via liquidity pools funded by other users who earn fees proportional to their contribution’s size.
Other notable DEXs include SushiSwap, which originated as a fork of Uniswap but added community-driven features like staking rewards for liquidity providers; it has gained significant traction due partly due to its governance token SUSHI.
Curve Finance specializes in stablecoin trading with low slippage thanks to optimized algorithms tailored for assets pegged closely together—ideal for traders seeking minimal price impact when swapping USDC for USDT or similar pairs.
Yield Farming & Liquidity Provision
Yield farming involves providing liquidity—depositing tokens into protocols—to earn returns often higher than traditional savings accounts but accompanied by increased risk levels such as impermanent loss or smart contract vulnerabilities.
Platforms like Yearn.finance aggregate multiple yield opportunities across different protocols automatically optimizing yields based on current conditions. Users deposit tokens into Yearn vaults that deploy funds into various strategies aiming at maximizing returns while managing risks effectively.
SushiSwap also offers yield farming options through its liquidity pools where participants stake pairs like ETH/USDT earning transaction fees plus additional incentives via SUSHI tokens—a process incentivizing active participation in maintaining healthy markets within the ecosystem.
Stablecoins: The Cornerstone Assets
Stablecoins are digital assets designed explicitly for stability—they maintain peg values close enough that they serve as reliable mediums of exchange within DeFi environments rather than volatile cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC).
- DAI, created by MakerDAO’s protocol using overcollateralized crypto assets such as ETH; it maintains decentralization while offering stability.
- USDC, issued jointly by Circle Financial and Coinbase; widely adopted due to regulatory compliance.
- Tether (USDT) remains one of the most traded stablecoins despite ongoing debates about transparency because of its extensive adoption across exchanges worldwide.
These coins underpin many DeFi activities—from trading pairs on DEXs—and serve as safe havens during volatile periods when traders seek refuge from price swings elsewhere in crypto markets.
Prediction Markets & Oracles
Prediction markets allow participants betting on future events’ outcomes—for example election results—or even sports scores—all conducted securely via blockchain-based smart contracts ensuring transparency around odds-setting processes.
Platforms like Augur enable users not only bet but also create custom markets covering diverse topics ranging from politics' outcomes till economic indicators’ movements—all settled automatically once event results are verified externally through oracle feeds provided primarily by Chainlink's network infrastructure.
Oracles play an essential role here—they bridge real-world data with blockchain environments ensuring accurate information feeds necessary for fair settlement processes in prediction markets.
Recent Trends Shaping Core Platforms
Over recent years, regulatory scrutiny has intensified globally—with agencies like SEC scrutinizing certain projects suspected of unregistered securities issuance—and this has prompted many platforms toward increased transparency standards including audits and compliance measures aimed at safeguarding investor interests while maintaining decentralization principles effectively balancing innovation versus regulation adherence.
Security remains paramount amid frequent high-profile hacks exposing vulnerabilities inherent in complex smart contracts architectures leading developers investing heavily into security audits alongside bug bounty programs designed explicitly toward identifying potential flaws before exploitation occurs.
Market volatility continues influencing platform operations significantly; sharp price swings impact liquidity levels adversely affecting yields especially during downturn phases which may lead some investors toward more conservative strategies involving stable asset holdings rather than high-risk yield farming endeavors.
Risks & Future Outlook
While these core services form robust pillars supporting DeFi’s growth trajectory today—including innovative products such as flash loans—the space faces challenges ahead:
- Regulatory actions could tighten restrictions impacting service availability.
- Security improvements require continuous investment amidst evolving threat landscapes.
- Market volatility necessitates developing mechanisms capable of stabilizing ecosystems against sudden shocks.
Despite these hurdles, ongoing technological advancements coupled with increasing institutional interest suggest promising prospects if stakeholders prioritize security enhancements alongside clear regulatory frameworks fostering sustainable growth.
Navigating Key Components Within The DeFi Ecosystem
Understanding common services offered within de-fi helps both newcomers navigate this complex landscape efficiently while enabling experienced participants optimize their strategies responsibly. From lending protocols offering passive income streams through borrowing mechanisms facilitating capital efficiency—to decentralized exchanges democratizing trade access—the diversity ensures broad utility aligned with user needs.
By staying informed about developments across these core areas—including emerging trends such as integrated insurance solutions or cross-chain interoperability—users can better position themselves amidst rapid innovation shaping tomorrow's financial landscape.
This overview aims not only at informing readers about prevalent de-fi platforms but also emphasizes responsible participation rooted in awareness about risks involved.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are the Potential Tax Implications of Buying, Selling, or Trading Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency has transformed from a niche digital asset into a mainstream investment option. As more individuals and institutions participate in buying, selling, and trading cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, understanding the tax implications becomes increasingly important. This article explores the key tax considerations investors should be aware of to stay compliant and optimize their strategies.
How Are Cryptocurrencies Classified for Tax Purposes?
One of the foundational aspects affecting cryptocurrency taxation is how authorities classify these assets. In the United States, for example, the IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property rather than currency. This classification means that any gains or losses from transactions are subject to capital gains tax rules similar to those applied to stocks or real estate.
This property classification impacts how investors report transactions—whether they buy, sell, trade between different cryptocurrencies, or receive crypto as payment for goods or services. It also influences whether gains are taxed at short-term rates (for holdings less than a year) or long-term rates (for holdings over a year). Understanding this classification helps investors plan their trades more strategically to manage potential tax liabilities.
Reporting Requirements for Cryptocurrency Transactions
Accurate record-keeping is crucial due to strict reporting obligations imposed by tax authorities like the IRS. Investors must report all cryptocurrency activities on their annual tax returns — including purchases, sales, exchanges between different cryptocurrencies, staking rewards, mining income—and even receiving crypto as payment.
Many taxpayers overlook smaller transactions but failing to report them can lead to audits and penalties. To simplify compliance efforts:
- Use dedicated cryptocurrency tracking tools
- Maintain detailed records of dates and amounts
- Keep documentation of wallet addresses involved in each transaction
These practices ensure transparency and help prevent issues during audits while enabling precise calculation of taxable gains or deductible losses.
How Do Capital Gains Taxes Apply to Cryptocurrency Trades?
Capital gains taxes are central when it comes to trading cryptocurrencies. The rate depends on how long an investor holds an asset before selling:
- Short-term capital gains apply if held for one year or less; taxed at ordinary income rates which can be higher.
- Long-term capital gains apply if held longer than one year; typically taxed at lower rates such as 15% or 20%.
For example: If you buy Bitcoin today and sell it within six months at a profit—this gain will be taxed at your regular income rate. Conversely: Holding that same Bitcoin for over a year before selling could result in significant tax savings due to favorable long-term capital gain rates.
Tax-loss harvesting strategies can also offset taxable gains by realizing losses on other investments—a tactic increasingly used by crypto traders seeking efficiency in their portfolios.
Impact of Wash Sale Rules on Crypto Trading Strategies
The wash sale rule prevents taxpayers from claiming a loss if they purchase "substantially identical" securities within 30 days before or after selling them at a loss. While originally designed for stocks and securities markets—its application extends into cryptocurrency trading in some jurisdictions like the U.S., especially after recent regulatory clarifications.
This rule complicates strategies such as tax-loss harvesting because traders cannot immediately repurchase assets they've sold at a loss without losing that deduction temporarily. Investors need careful planning around timing trades around this rule’s constraints so they don’t inadvertently disallow deductions while maintaining market exposure.
International Variations in Cryptocurrency Tax Laws
Global differences significantly influence how investors approach crypto taxation:
- In countries like the UK, cryptocurrencies are considered assets subjecting them primarily to capital gains taxes.
- Countries such as Singapore do not impose capital gains taxes on cryptocurrencies but may have other reporting requirements.
Other nations might treat certain activities differently—for instance: mining profits could be classified as income rather than capital gain—and some jurisdictions impose VAT/GST on specific transactions involving digital currencies.
Understanding local laws is essential because non-compliance can lead not only to penalties but also legal complications across borders where investments might involve multiple jurisdictions with differing rules.
Recent Developments Shaping Crypto Tax Policies
Regulatory bodies worldwide have been working toward clearer guidelines amid rising market activity:
Regulatory Clarity & Guidance
Recent years have seen agencies issue guidance documents addressing forks (when new coins emerge from existing ones),irdrops (free distributions), staking rewards,and other complex scenarios affecting taxable events—all aimed at reducing ambiguity surrounding crypto taxation policies .
Advances in Tax Reporting Tools
Technology has played an instrumental role; specialized software now allows seamless integration with exchanges/wallets providing comprehensive transaction histories . These tools help investors accurately calculate liabilities without manual errors , reducing risks associated with misreporting .
Market Volatility & Its Effects
Cryptocurrency markets remain highly volatile—with rapid price swings impacting realized profits/losses significantly within short periods . Such fluctuations necessitate proactive planning regarding estimated taxes , especially when large swings occur unexpectedly .
Upcoming Events & Risks
Events like share unlocks—for example , Grayscale Solana Trust's scheduled unlocks—can trigger increased trading volume leading up-to these dates . Investors should anticipate potential market impacts which may affect both pricesand resultingtax obligations .
Why Proper Record-Keeping Is Critical
Given complex regulations—including international variations—and evolving guidance investing in cryptos demands meticulous documentation:
- Transaction timestamps
- Purchase/sale prices
- Wallet addresses involved 4.. Corresponding exchange statements
Maintaining detailed records ensures compliance during audits while enabling accurate calculation of taxable events—saving time,money,and avoiding penalties down-the-line .
Staying informed about current regulations coupled with diligent record management empowers investors not only legally but financially too — helping navigate this dynamic landscape effectively while optimizing overall investment outcomes.


kai
2025-05-22 19:07
What are the potential tax implications of buying, selling, or trading cryptocurrency?
What Are the Potential Tax Implications of Buying, Selling, or Trading Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency has transformed from a niche digital asset into a mainstream investment option. As more individuals and institutions participate in buying, selling, and trading cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, understanding the tax implications becomes increasingly important. This article explores the key tax considerations investors should be aware of to stay compliant and optimize their strategies.
How Are Cryptocurrencies Classified for Tax Purposes?
One of the foundational aspects affecting cryptocurrency taxation is how authorities classify these assets. In the United States, for example, the IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property rather than currency. This classification means that any gains or losses from transactions are subject to capital gains tax rules similar to those applied to stocks or real estate.
This property classification impacts how investors report transactions—whether they buy, sell, trade between different cryptocurrencies, or receive crypto as payment for goods or services. It also influences whether gains are taxed at short-term rates (for holdings less than a year) or long-term rates (for holdings over a year). Understanding this classification helps investors plan their trades more strategically to manage potential tax liabilities.
Reporting Requirements for Cryptocurrency Transactions
Accurate record-keeping is crucial due to strict reporting obligations imposed by tax authorities like the IRS. Investors must report all cryptocurrency activities on their annual tax returns — including purchases, sales, exchanges between different cryptocurrencies, staking rewards, mining income—and even receiving crypto as payment.
Many taxpayers overlook smaller transactions but failing to report them can lead to audits and penalties. To simplify compliance efforts:
- Use dedicated cryptocurrency tracking tools
- Maintain detailed records of dates and amounts
- Keep documentation of wallet addresses involved in each transaction
These practices ensure transparency and help prevent issues during audits while enabling precise calculation of taxable gains or deductible losses.
How Do Capital Gains Taxes Apply to Cryptocurrency Trades?
Capital gains taxes are central when it comes to trading cryptocurrencies. The rate depends on how long an investor holds an asset before selling:
- Short-term capital gains apply if held for one year or less; taxed at ordinary income rates which can be higher.
- Long-term capital gains apply if held longer than one year; typically taxed at lower rates such as 15% or 20%.
For example: If you buy Bitcoin today and sell it within six months at a profit—this gain will be taxed at your regular income rate. Conversely: Holding that same Bitcoin for over a year before selling could result in significant tax savings due to favorable long-term capital gain rates.
Tax-loss harvesting strategies can also offset taxable gains by realizing losses on other investments—a tactic increasingly used by crypto traders seeking efficiency in their portfolios.
Impact of Wash Sale Rules on Crypto Trading Strategies
The wash sale rule prevents taxpayers from claiming a loss if they purchase "substantially identical" securities within 30 days before or after selling them at a loss. While originally designed for stocks and securities markets—its application extends into cryptocurrency trading in some jurisdictions like the U.S., especially after recent regulatory clarifications.
This rule complicates strategies such as tax-loss harvesting because traders cannot immediately repurchase assets they've sold at a loss without losing that deduction temporarily. Investors need careful planning around timing trades around this rule’s constraints so they don’t inadvertently disallow deductions while maintaining market exposure.
International Variations in Cryptocurrency Tax Laws
Global differences significantly influence how investors approach crypto taxation:
- In countries like the UK, cryptocurrencies are considered assets subjecting them primarily to capital gains taxes.
- Countries such as Singapore do not impose capital gains taxes on cryptocurrencies but may have other reporting requirements.
Other nations might treat certain activities differently—for instance: mining profits could be classified as income rather than capital gain—and some jurisdictions impose VAT/GST on specific transactions involving digital currencies.
Understanding local laws is essential because non-compliance can lead not only to penalties but also legal complications across borders where investments might involve multiple jurisdictions with differing rules.
Recent Developments Shaping Crypto Tax Policies
Regulatory bodies worldwide have been working toward clearer guidelines amid rising market activity:
Regulatory Clarity & Guidance
Recent years have seen agencies issue guidance documents addressing forks (when new coins emerge from existing ones),irdrops (free distributions), staking rewards,and other complex scenarios affecting taxable events—all aimed at reducing ambiguity surrounding crypto taxation policies .
Advances in Tax Reporting Tools
Technology has played an instrumental role; specialized software now allows seamless integration with exchanges/wallets providing comprehensive transaction histories . These tools help investors accurately calculate liabilities without manual errors , reducing risks associated with misreporting .
Market Volatility & Its Effects
Cryptocurrency markets remain highly volatile—with rapid price swings impacting realized profits/losses significantly within short periods . Such fluctuations necessitate proactive planning regarding estimated taxes , especially when large swings occur unexpectedly .
Upcoming Events & Risks
Events like share unlocks—for example , Grayscale Solana Trust's scheduled unlocks—can trigger increased trading volume leading up-to these dates . Investors should anticipate potential market impacts which may affect both pricesand resultingtax obligations .
Why Proper Record-Keeping Is Critical
Given complex regulations—including international variations—and evolving guidance investing in cryptos demands meticulous documentation:
- Transaction timestamps
- Purchase/sale prices
- Wallet addresses involved 4.. Corresponding exchange statements
Maintaining detailed records ensures compliance during audits while enabling accurate calculation of taxable events—saving time,money,and avoiding penalties down-the-line .
Staying informed about current regulations coupled with diligent record management empowers investors not only legally but financially too — helping navigate this dynamic landscape effectively while optimizing overall investment outcomes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Assess the Security of a New Cryptocurrency Project
When considering investing in or using a new cryptocurrency project, understanding its security posture is essential. The rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technology and digital assets has brought about innovative solutions but also exposed projects to various vulnerabilities. A thorough security assessment helps protect your investments and ensures the project adheres to best practices for safeguarding user funds and data.
Why Security Matters in Cryptocurrency Projects
Cryptocurrency projects are attractive targets for hackers due to their decentralized nature and the potential for significant financial gains. High-profile hacks have resulted in millions of dollars lost, eroding trust within the community. For investors, users, and developers alike, evaluating security measures is crucial before engaging with any new project. Proper assessment not only minimizes risks but also signals that a project values transparency and responsibility.
Key Aspects to Evaluate When Assessing Security
Smart Contract Security
Smart contracts form the backbone of many blockchain applications; however, they are prone to coding errors that can be exploited. To evaluate their security:
- Code Review: Examine the smart contract code for vulnerabilities using tools like Etherscan or Solidity analyzers. Look out for common issues such as reentrancy attacks or integer overflows.
- Third-Party Audits: Verify whether reputable cybersecurity firms have audited the smart contracts. Audits provide an independent review that can uncover hidden flaws.
- Open Source Transparency: Open-source code allows community members and experts to review and identify potential issues proactively.
Wallet Security Measures
Wallet management is critical since wallets store private keys that control access to funds:
- Multi-Signature Wallets: These require multiple approvals before executing transactions, reducing single-point failure risks.
- Cold Storage Solutions: Funds stored offline (cold storage) are less vulnerable to online hacking attempts.
- Key Management Practices: Secure handling of private keys—such as hardware wallets or encrypted storage—ensures better protection against theft.
Decentralized Application (dApp) Safety
Security extends beyond smart contracts into front-end interfaces and back-end infrastructure:
- Front-End Vulnerability Checks: Use tools like OWASP ZAP to scan web interfaces for common vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Back-End Infrastructure Protections: Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular patching protocols.
- User Authentication Protocols: Strong authentication mechanisms prevent unauthorized access; multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security.
Evaluating Team Experience & Community Engagement
The expertise of a project's team significantly influences its ability to address security challenges effectively:
- An experienced development team with prior success in blockchain projects demonstrates competence in managing complex security issues.
Community involvement further enhances security through bug bounty programs where external researchers report vulnerabilities responsibly. Active communities often participate in discussions around ongoing improvements or alert developers about potential threats promptly.
Regulatory Compliance & Legal Standing
Adherence to legal standards reduces risks related to regulatory actions:
- Ensure compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures if applicable.
Licensing from relevant authorities indicates legitimacy; certifications related specifically to financial services add credibility while aligning with industry standards.
Transparency & Documentation Quality
Clear documentation fosters trust among users by providing insights into development processes:
- Well-written whitepapers should detail technical architecture alongside planned updates on patches or fixes addressing known vulnerabilities.
Transparency regarding development milestones reassures stakeholders about ongoing efforts toward maintaining robust security practices.
Bug Bounty Programs & Penetration Testing Initiatives
Proactive vulnerability identification involves inviting external experts through bug bounty programs offering rewards for discovering flaws responsibly:
Regular penetration testing simulates real-world attack scenarios—identifying weaknesses before malicious actors do—and should be conducted periodically by reputable cybersecurity firms.
Reputation Within Cryptocurrency Community
A project's standing among peers offers indirect clues about its commitment toward safety:
Positive reviews from trusted sources combined with active participation during audits suggest reliability; conversely, unresolved past breaches may raise red flags needing deeper investigation.
Recent Trends Shaping Cryptocurrency Security
The industry has seen notable developments aimed at strengthening defenses:
- Increased emphasis on comprehensive audits by specialized firms enhances overall safety standards across projects.
- Growing regulatory clarity guides teams toward implementing compliant features like AML/KYC measures early on.
- Advances in detection tools enable faster identification of emerging threats—helping prevent exploits proactively.
- Community-driven initiatives such as bug bounty programs foster collaborative efforts between developers and white-hat hackers worldwide—a vital component given open-source transparency's importance amid rising cyber threats.
Risks Associated With Inadequate Security Measures
Failing secure practices can lead directly or indirectly to severe consequences:
Financial Losses: Hackers exploiting weak points may drain user wallets leading up substantial monetary damages both personally—and reputationally—for projects involved.*
Reputation Damage: Trust once broken is hard—or impossible—to restore; breaches often result in diminished user confidence which hampers future growth.*
Legal Repercussions: Non-compliance with regulations could trigger fines or shutdown orders from authorities.*
Community Backlash: The crypto community tends towards vigilance; publicized breaches often lead users abandoning affected platforms altogether.*
Ensuring You Make Informed Decisions About New Crypto Projects
Assessing a cryptocurrency project's security isn't just about checking boxes—it requires understanding how different components work together within broader industry standards while remaining vigilant against evolving threats. Focus on transparent documentation, verified audits, active community engagement via bug bounties—all indicators pointing toward strong foundational practices designed not only for current safety but also adaptability against future challenges.
By applying these evaluation strategies diligently, investors can better navigate this complex environment—making smarter choices rooted in solid technical assessments rather than hype alone—and contribute positively towards building safer blockchain ecosystems globally.
Keywords: cryptocurrency security assessment | smart contract audit | wallet protection | dApp vulnerability testing | blockchain project evaluation | crypto community reviews | cybersecurity best practices


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 18:08
How can I assess the security of a new cryptocurrency project?
How to Assess the Security of a New Cryptocurrency Project
When considering investing in or using a new cryptocurrency project, understanding its security posture is essential. The rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technology and digital assets has brought about innovative solutions but also exposed projects to various vulnerabilities. A thorough security assessment helps protect your investments and ensures the project adheres to best practices for safeguarding user funds and data.
Why Security Matters in Cryptocurrency Projects
Cryptocurrency projects are attractive targets for hackers due to their decentralized nature and the potential for significant financial gains. High-profile hacks have resulted in millions of dollars lost, eroding trust within the community. For investors, users, and developers alike, evaluating security measures is crucial before engaging with any new project. Proper assessment not only minimizes risks but also signals that a project values transparency and responsibility.
Key Aspects to Evaluate When Assessing Security
Smart Contract Security
Smart contracts form the backbone of many blockchain applications; however, they are prone to coding errors that can be exploited. To evaluate their security:
- Code Review: Examine the smart contract code for vulnerabilities using tools like Etherscan or Solidity analyzers. Look out for common issues such as reentrancy attacks or integer overflows.
- Third-Party Audits: Verify whether reputable cybersecurity firms have audited the smart contracts. Audits provide an independent review that can uncover hidden flaws.
- Open Source Transparency: Open-source code allows community members and experts to review and identify potential issues proactively.
Wallet Security Measures
Wallet management is critical since wallets store private keys that control access to funds:
- Multi-Signature Wallets: These require multiple approvals before executing transactions, reducing single-point failure risks.
- Cold Storage Solutions: Funds stored offline (cold storage) are less vulnerable to online hacking attempts.
- Key Management Practices: Secure handling of private keys—such as hardware wallets or encrypted storage—ensures better protection against theft.
Decentralized Application (dApp) Safety
Security extends beyond smart contracts into front-end interfaces and back-end infrastructure:
- Front-End Vulnerability Checks: Use tools like OWASP ZAP to scan web interfaces for common vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Back-End Infrastructure Protections: Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular patching protocols.
- User Authentication Protocols: Strong authentication mechanisms prevent unauthorized access; multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security.
Evaluating Team Experience & Community Engagement
The expertise of a project's team significantly influences its ability to address security challenges effectively:
- An experienced development team with prior success in blockchain projects demonstrates competence in managing complex security issues.
Community involvement further enhances security through bug bounty programs where external researchers report vulnerabilities responsibly. Active communities often participate in discussions around ongoing improvements or alert developers about potential threats promptly.
Regulatory Compliance & Legal Standing
Adherence to legal standards reduces risks related to regulatory actions:
- Ensure compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures if applicable.
Licensing from relevant authorities indicates legitimacy; certifications related specifically to financial services add credibility while aligning with industry standards.
Transparency & Documentation Quality
Clear documentation fosters trust among users by providing insights into development processes:
- Well-written whitepapers should detail technical architecture alongside planned updates on patches or fixes addressing known vulnerabilities.
Transparency regarding development milestones reassures stakeholders about ongoing efforts toward maintaining robust security practices.
Bug Bounty Programs & Penetration Testing Initiatives
Proactive vulnerability identification involves inviting external experts through bug bounty programs offering rewards for discovering flaws responsibly:
Regular penetration testing simulates real-world attack scenarios—identifying weaknesses before malicious actors do—and should be conducted periodically by reputable cybersecurity firms.
Reputation Within Cryptocurrency Community
A project's standing among peers offers indirect clues about its commitment toward safety:
Positive reviews from trusted sources combined with active participation during audits suggest reliability; conversely, unresolved past breaches may raise red flags needing deeper investigation.
Recent Trends Shaping Cryptocurrency Security
The industry has seen notable developments aimed at strengthening defenses:
- Increased emphasis on comprehensive audits by specialized firms enhances overall safety standards across projects.
- Growing regulatory clarity guides teams toward implementing compliant features like AML/KYC measures early on.
- Advances in detection tools enable faster identification of emerging threats—helping prevent exploits proactively.
- Community-driven initiatives such as bug bounty programs foster collaborative efforts between developers and white-hat hackers worldwide—a vital component given open-source transparency's importance amid rising cyber threats.
Risks Associated With Inadequate Security Measures
Failing secure practices can lead directly or indirectly to severe consequences:
Financial Losses: Hackers exploiting weak points may drain user wallets leading up substantial monetary damages both personally—and reputationally—for projects involved.*
Reputation Damage: Trust once broken is hard—or impossible—to restore; breaches often result in diminished user confidence which hampers future growth.*
Legal Repercussions: Non-compliance with regulations could trigger fines or shutdown orders from authorities.*
Community Backlash: The crypto community tends towards vigilance; publicized breaches often lead users abandoning affected platforms altogether.*
Ensuring You Make Informed Decisions About New Crypto Projects
Assessing a cryptocurrency project's security isn't just about checking boxes—it requires understanding how different components work together within broader industry standards while remaining vigilant against evolving threats. Focus on transparent documentation, verified audits, active community engagement via bug bounties—all indicators pointing toward strong foundational practices designed not only for current safety but also adaptability against future challenges.
By applying these evaluation strategies diligently, investors can better navigate this complex environment—making smarter choices rooted in solid technical assessments rather than hype alone—and contribute positively towards building safer blockchain ecosystems globally.
Keywords: cryptocurrency security assessment | smart contract audit | wallet protection | dApp vulnerability testing | blockchain project evaluation | crypto community reviews | cybersecurity best practices
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Why Limited Supply Matters for Cryptocurrencies
Understanding the significance of limited supply in cryptocurrencies is essential for anyone interested in digital assets, whether you're an investor, developer, or simply curious about how these innovative financial tools work. The concept of limited supply is not just a technical feature; it fundamentally influences the value, security, and long-term viability of cryptocurrencies.
The Role of Blockchain Technology in Enforcing Supply Limits
Most cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain technology—a decentralized ledger that records all transactions transparently and securely. This technology enables the implementation of fixed or capped supplies through smart contracts or protocol rules embedded within the blockchain. For example, Bitcoin’s protocol explicitly limits its total supply to 21 million coins. This predetermined cap ensures that no central authority can increase the total number of bitcoins in circulation, maintaining scarcity over time.
This scarcity is crucial because it creates a predictable environment where supply cannot be arbitrarily inflated. Unlike traditional fiat currencies controlled by central banks—where money printing can lead to inflation—cryptocurrencies with fixed supplies are designed to prevent such devaluation mechanisms from undermining their value.
Fixed vs. Variable Supply: How Different Cryptos Manage Scarcity
Cryptocurrencies differ significantly in how they handle their supply:
Fixed Supply Coins: Bitcoin exemplifies this approach with its hard cap at 21 million coins. Once mined, no more bitcoins will ever be created. This fixed limit fosters scarcity and often leads to increased demand as more coins are mined or become available on secondary markets.
Variable or Capped Supply Coins: Ethereum initially had an uncapped issuance model but has moved toward mechanisms like EIP-1559 that introduce fee burns and potential caps on issuance over time. These adjustments aim to balance network security needs with controlling inflationary pressures.
Such differences influence investor perceptions and market dynamics profoundly since scarcity directly impacts perceived value and investment attractiveness.
Why Scarcity Helps Control Inflation
Inflation erodes purchasing power when a currency's supply increases faster than demand. Traditional fiat currencies are susceptible because governments can print money at will—leading to inflation if not managed carefully.
Cryptocurrencies with limited supplies inherently resist this problem by design; their total quantity cannot be increased beyond set limits (or only under predefined conditions). As a result, each coin retains its relative value better over time compared to inflation-prone fiat currencies, making them attractive stores of value for investors seeking long-term growth potential.
Limited Supply Enhances Security Through Scarcity
The rarity associated with capped cryptocurrencies also contributes indirectly to network security. Because scarce tokens tend to have higher market values, they become more attractive targets for theft by malicious actors seeking significant gains through hacking exchanges or wallets holding large amounts of these assets.
This heightened risk incentivizes stronger security measures across platforms handling such tokens—benefiting overall ecosystem robustness—and discourages malicious activities due to the high stakes involved when dealing with valuable digital assets.
Investor Attraction Due To Scarcity
Many investors view limited-supply cryptocurrencies as "digital gold" because their scarcity mimics precious metals like gold which have historically preserved wealth over centuries. The anticipation that demand will outpace supply often drives prices upward as new investors enter markets expecting appreciation driven by finite availability rather than arbitrary monetary expansion policies seen elsewhere.
Regulatory Perspectives on Fixed-Supply Digital Assets
Regulators tend favor cryptocurrencies with clear caps because they align more closely with traditional monetary principles—they do not facilitate unchecked money creation nor pose risks associated with hyperinflation scenarios common in some fiat systems during economic crises or mismanagements.
As regulatory clarity improves globally—including frameworks around initial coin offerings (ICOs), securities classification, and anti-money laundering measures—the perception around fixed-supply tokens remains positive among policymakers aiming for stability within crypto markets while fostering innovation responsibly.
Recent Developments Shaping Limited Supply Dynamics
Several recent events highlight how managing cryptocurrency supply continues evolving:
Bitcoin Halving Events: Approximately every four years, Bitcoin undergoes halving—a process reducing miners’ rewards by half—which effectively cuts new bitcoin issuance rate in half again and again until maximum cap is reached around 2140. Historically, these halvings have led to significant price increases due to reduced new supply entering circulation while demand remains steady or grows.
Ethereum’s Transition Toward Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Moving from proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism allows Ethereum developers greater control over Ether’s emission rate via staking protocols and fee burning mechanisms introduced through upgrades like EIP-1559—all aimed at managing token issuance sustainably.
Emerging Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Governments exploring CBDCs consider implementing digital versions of national currencies possibly featuring predefined caps aligned with monetary policy goals—potentially influencing global liquidity management strategies while addressing issues related to transparency and traceability.
Potential Challenges Linked To Limited Cryptocurrency Supplies
While scarcity offers many benefits—including price stability prospects—it also introduces certain risks:
- Market Volatility – When perceived scarcity drives prices up rapidly during bull runs but declines sharply during downturns; this volatility can deter mainstream adoption.
- Regulatory Risks – Governments may impose restrictions if they perceive scarce cryptos threaten financial stability or facilitate illicit activities.
- Technological Changes – Innovations such as alternative consensus algorithms could alter existing tokenomics models unexpectedly—for example, introducing new ways for tokens’ supplies being adjusted dynamically rather than remaining strictly capped.
Tracking Future Trends In Cryptocurrency Supply Management
As blockchain technology advances further—with innovations like layer-two solutions improving scalability—the way cryptocurrency supplies are managed may evolve significantly:
New protocols might introduce dynamic adjustment features allowing flexible control over circulating quantities based on economic conditions.
Increased integration between traditional finance systems via tokenized assets could lead regulators worldwide developing clearer standards governing maximum supplies.
Continued development around stablecoins backed by reserves might blur lines between fixed-supply cryptos versus those tied directly into real-world assets.
Understanding why limited supply matters helps clarify why certain cryptocurrencies hold intrinsic appeal beyond mere speculation—they embody principles rooted in scarcity akin to precious metals but enhanced through technological safeguards provided by blockchain networks.
By appreciating these factors—from technical design choices through market implications—you gain deeper insights into what makes scarce digital assets compelling investments today—and what future developments might shape their trajectory within global finance ecosystems


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 14:47
Why is a limited supply important for certain cryptocurrencies?
Why Limited Supply Matters for Cryptocurrencies
Understanding the significance of limited supply in cryptocurrencies is essential for anyone interested in digital assets, whether you're an investor, developer, or simply curious about how these innovative financial tools work. The concept of limited supply is not just a technical feature; it fundamentally influences the value, security, and long-term viability of cryptocurrencies.
The Role of Blockchain Technology in Enforcing Supply Limits
Most cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain technology—a decentralized ledger that records all transactions transparently and securely. This technology enables the implementation of fixed or capped supplies through smart contracts or protocol rules embedded within the blockchain. For example, Bitcoin’s protocol explicitly limits its total supply to 21 million coins. This predetermined cap ensures that no central authority can increase the total number of bitcoins in circulation, maintaining scarcity over time.
This scarcity is crucial because it creates a predictable environment where supply cannot be arbitrarily inflated. Unlike traditional fiat currencies controlled by central banks—where money printing can lead to inflation—cryptocurrencies with fixed supplies are designed to prevent such devaluation mechanisms from undermining their value.
Fixed vs. Variable Supply: How Different Cryptos Manage Scarcity
Cryptocurrencies differ significantly in how they handle their supply:
Fixed Supply Coins: Bitcoin exemplifies this approach with its hard cap at 21 million coins. Once mined, no more bitcoins will ever be created. This fixed limit fosters scarcity and often leads to increased demand as more coins are mined or become available on secondary markets.
Variable or Capped Supply Coins: Ethereum initially had an uncapped issuance model but has moved toward mechanisms like EIP-1559 that introduce fee burns and potential caps on issuance over time. These adjustments aim to balance network security needs with controlling inflationary pressures.
Such differences influence investor perceptions and market dynamics profoundly since scarcity directly impacts perceived value and investment attractiveness.
Why Scarcity Helps Control Inflation
Inflation erodes purchasing power when a currency's supply increases faster than demand. Traditional fiat currencies are susceptible because governments can print money at will—leading to inflation if not managed carefully.
Cryptocurrencies with limited supplies inherently resist this problem by design; their total quantity cannot be increased beyond set limits (or only under predefined conditions). As a result, each coin retains its relative value better over time compared to inflation-prone fiat currencies, making them attractive stores of value for investors seeking long-term growth potential.
Limited Supply Enhances Security Through Scarcity
The rarity associated with capped cryptocurrencies also contributes indirectly to network security. Because scarce tokens tend to have higher market values, they become more attractive targets for theft by malicious actors seeking significant gains through hacking exchanges or wallets holding large amounts of these assets.
This heightened risk incentivizes stronger security measures across platforms handling such tokens—benefiting overall ecosystem robustness—and discourages malicious activities due to the high stakes involved when dealing with valuable digital assets.
Investor Attraction Due To Scarcity
Many investors view limited-supply cryptocurrencies as "digital gold" because their scarcity mimics precious metals like gold which have historically preserved wealth over centuries. The anticipation that demand will outpace supply often drives prices upward as new investors enter markets expecting appreciation driven by finite availability rather than arbitrary monetary expansion policies seen elsewhere.
Regulatory Perspectives on Fixed-Supply Digital Assets
Regulators tend favor cryptocurrencies with clear caps because they align more closely with traditional monetary principles—they do not facilitate unchecked money creation nor pose risks associated with hyperinflation scenarios common in some fiat systems during economic crises or mismanagements.
As regulatory clarity improves globally—including frameworks around initial coin offerings (ICOs), securities classification, and anti-money laundering measures—the perception around fixed-supply tokens remains positive among policymakers aiming for stability within crypto markets while fostering innovation responsibly.
Recent Developments Shaping Limited Supply Dynamics
Several recent events highlight how managing cryptocurrency supply continues evolving:
Bitcoin Halving Events: Approximately every four years, Bitcoin undergoes halving—a process reducing miners’ rewards by half—which effectively cuts new bitcoin issuance rate in half again and again until maximum cap is reached around 2140. Historically, these halvings have led to significant price increases due to reduced new supply entering circulation while demand remains steady or grows.
Ethereum’s Transition Toward Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Moving from proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism allows Ethereum developers greater control over Ether’s emission rate via staking protocols and fee burning mechanisms introduced through upgrades like EIP-1559—all aimed at managing token issuance sustainably.
Emerging Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Governments exploring CBDCs consider implementing digital versions of national currencies possibly featuring predefined caps aligned with monetary policy goals—potentially influencing global liquidity management strategies while addressing issues related to transparency and traceability.
Potential Challenges Linked To Limited Cryptocurrency Supplies
While scarcity offers many benefits—including price stability prospects—it also introduces certain risks:
- Market Volatility – When perceived scarcity drives prices up rapidly during bull runs but declines sharply during downturns; this volatility can deter mainstream adoption.
- Regulatory Risks – Governments may impose restrictions if they perceive scarce cryptos threaten financial stability or facilitate illicit activities.
- Technological Changes – Innovations such as alternative consensus algorithms could alter existing tokenomics models unexpectedly—for example, introducing new ways for tokens’ supplies being adjusted dynamically rather than remaining strictly capped.
Tracking Future Trends In Cryptocurrency Supply Management
As blockchain technology advances further—with innovations like layer-two solutions improving scalability—the way cryptocurrency supplies are managed may evolve significantly:
New protocols might introduce dynamic adjustment features allowing flexible control over circulating quantities based on economic conditions.
Increased integration between traditional finance systems via tokenized assets could lead regulators worldwide developing clearer standards governing maximum supplies.
Continued development around stablecoins backed by reserves might blur lines between fixed-supply cryptos versus those tied directly into real-world assets.
Understanding why limited supply matters helps clarify why certain cryptocurrencies hold intrinsic appeal beyond mere speculation—they embody principles rooted in scarcity akin to precious metals but enhanced through technological safeguards provided by blockchain networks.
By appreciating these factors—from technical design choices through market implications—you gain deeper insights into what makes scarce digital assets compelling investments today—and what future developments might shape their trajectory within global finance ecosystems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Utility NFTs Differ from Purely Collectible NFTs?
Understanding the distinctions between different types of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is essential as the digital asset market continues to expand. While many are familiar with NFTs as digital collectibles, a newer category known as utility NFTs is gaining prominence. This article explores how utility NFTs differ from purely collectible ones, providing clarity on their functions, benefits, and recent trends.
What Are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)?
NFTs are unique digital assets stored on a blockchain that verify ownership and authenticity of a specific item. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are interchangeable and fungible, each NFT is one-of-a-kind. This uniqueness makes them ideal for representing digital art, music, virtual items in gaming environments, or other creative works.
The blockchain technology underpinning NFTs ensures transparency in ownership history and scarcity—key factors driving their value. As a result, they have become popular among artists, collectors, gamers, and investors seeking verifiable ownership of digital assets.
Characteristics of Purely Collectible NFTs
Purely collectible NFTs primarily serve aesthetic or sentimental purposes. They often take the form of digital art pieces or exclusive music tracks created by renowned artists or musicians. These tokens are bought for their rarity and potential future value rather than functional benefits.
Marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible facilitate trading these collectibles globally. The demand has surged significantly over recent years; some artworks have sold for millions of dollars at auction houses like Christie's or Sotheby's in NFT form.
Investors often purchase collectible NFTs with the hope that their value will appreciate over time so they can resell at a profit later on—a practice similar to traditional art collecting but within the digital realm.
What Are Utility NFTs?
In contrast to purely aesthetic-focused tokens, utility NFTs provide tangible benefits beyond mere ownership acknowledgment. They grant holders access to exclusive content such as early product releases or special events; offer voting rights within decentralized communities; or represent stakes in projects—effectively functioning as membership cards with added privileges.
These tokens foster deeper engagement by creating interactive experiences around an asset rather than just owning it visually. For example:
- Access Rights: Holding certain utility NFTs might unlock VIP access to concerts or virtual events.
- Participation: Some enable voting on project development decisions within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
- Ownership Stakes: Certain utility tokens symbolize partial ownership in startups or community-driven initiatives.
This functional aspect encourages ongoing participation from holders while adding real-world value aligned with technological innovation trends like blockchain-based governance systems.
Recent Trends Shaping Utility vs Collectibles
The evolving landscape highlights several key developments:
Gaming & Virtual Worlds
Platforms such as Decentraland and The Sandbox leverage utility NFT models extensively by allowing users to buy land parcels and assets that confer gameplay advantages—like building virtual spaces—or grant access rights within immersive environments.
Social Media & Community Engagement
Social platforms increasingly integrate utility features through NFT-based memberships—for instance: Discord servers offering exclusive channels accessible only via holding specific tokens—enhancing user loyalty through tangible perks rather than simple visual collectibles.
DeFi Integration & Financial Benefits
Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols now incorporate utility aspects into NFT offerings by enabling interest accruals on holdings or dividend distributions tied directly to token ownership—adding financial incentives alongside community participation elements.
Challenges Facing Utility vs Collectible NFT Markets
Despite rapid growth across both categories, several hurdles remain:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks surrounding NFT classification vary across jurisdictions; questions about intellectual property rights management persist.
Market Volatility: Prices for both collectible and utility-based tokens can fluctuate wildly due to speculation rather than intrinsic value.
Scalability Concerns: Blockchain infrastructure still faces challenges related to transaction speed and costs—which could hinder mass adoption if not addressed effectively.
How To Identify Value in Different Types of NFTs
When evaluating whether an NFT is primarily collectible or offers genuine utility:
- Check if it grants access: Does owning this token unlock services?
- Review community involvement: Is there active participation enabled through this token?
- Consider project backing: Does it represent an investment stake?
- Analyze provenance: Is its origin linked directly with creators’ reputation?
Understanding these factors helps buyers make informed decisions aligned with personal goals—whether investing for appreciation potential via collectibles—or seeking ongoing benefits through utilities.
The Future Outlook for Utility vs Collectibles
As blockchain technology matures further—with improvements in scalability solutions like Layer 2 protocols—the scope for more sophisticated use cases expands significantly for both categories but especially so for utility-focused applications that blend social engagement with financial incentives.
Emerging sectors such as metaverse development suggest that utilities embedded into virtual environments will become increasingly integral—not just enhancing user experience but also creating sustainable economic models around these assets.
By recognizing the fundamental differences between purely collectible non-fungible tokens and those offering practical functionalities—and staying aware of current trends—you can better navigate this rapidly evolving space tailored toward your interests whether artistic appreciation versus active participation within communities driven by blockchain innovations.


Lo
2025-05-22 11:45
How do utility NFTs differ from purely collectible NFTs?
How Do Utility NFTs Differ from Purely Collectible NFTs?
Understanding the distinctions between different types of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is essential as the digital asset market continues to expand. While many are familiar with NFTs as digital collectibles, a newer category known as utility NFTs is gaining prominence. This article explores how utility NFTs differ from purely collectible ones, providing clarity on their functions, benefits, and recent trends.
What Are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)?
NFTs are unique digital assets stored on a blockchain that verify ownership and authenticity of a specific item. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are interchangeable and fungible, each NFT is one-of-a-kind. This uniqueness makes them ideal for representing digital art, music, virtual items in gaming environments, or other creative works.
The blockchain technology underpinning NFTs ensures transparency in ownership history and scarcity—key factors driving their value. As a result, they have become popular among artists, collectors, gamers, and investors seeking verifiable ownership of digital assets.
Characteristics of Purely Collectible NFTs
Purely collectible NFTs primarily serve aesthetic or sentimental purposes. They often take the form of digital art pieces or exclusive music tracks created by renowned artists or musicians. These tokens are bought for their rarity and potential future value rather than functional benefits.
Marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible facilitate trading these collectibles globally. The demand has surged significantly over recent years; some artworks have sold for millions of dollars at auction houses like Christie's or Sotheby's in NFT form.
Investors often purchase collectible NFTs with the hope that their value will appreciate over time so they can resell at a profit later on—a practice similar to traditional art collecting but within the digital realm.
What Are Utility NFTs?
In contrast to purely aesthetic-focused tokens, utility NFTs provide tangible benefits beyond mere ownership acknowledgment. They grant holders access to exclusive content such as early product releases or special events; offer voting rights within decentralized communities; or represent stakes in projects—effectively functioning as membership cards with added privileges.
These tokens foster deeper engagement by creating interactive experiences around an asset rather than just owning it visually. For example:
- Access Rights: Holding certain utility NFTs might unlock VIP access to concerts or virtual events.
- Participation: Some enable voting on project development decisions within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
- Ownership Stakes: Certain utility tokens symbolize partial ownership in startups or community-driven initiatives.
This functional aspect encourages ongoing participation from holders while adding real-world value aligned with technological innovation trends like blockchain-based governance systems.
Recent Trends Shaping Utility vs Collectibles
The evolving landscape highlights several key developments:
Gaming & Virtual Worlds
Platforms such as Decentraland and The Sandbox leverage utility NFT models extensively by allowing users to buy land parcels and assets that confer gameplay advantages—like building virtual spaces—or grant access rights within immersive environments.
Social Media & Community Engagement
Social platforms increasingly integrate utility features through NFT-based memberships—for instance: Discord servers offering exclusive channels accessible only via holding specific tokens—enhancing user loyalty through tangible perks rather than simple visual collectibles.
DeFi Integration & Financial Benefits
Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols now incorporate utility aspects into NFT offerings by enabling interest accruals on holdings or dividend distributions tied directly to token ownership—adding financial incentives alongside community participation elements.
Challenges Facing Utility vs Collectible NFT Markets
Despite rapid growth across both categories, several hurdles remain:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks surrounding NFT classification vary across jurisdictions; questions about intellectual property rights management persist.
Market Volatility: Prices for both collectible and utility-based tokens can fluctuate wildly due to speculation rather than intrinsic value.
Scalability Concerns: Blockchain infrastructure still faces challenges related to transaction speed and costs—which could hinder mass adoption if not addressed effectively.
How To Identify Value in Different Types of NFTs
When evaluating whether an NFT is primarily collectible or offers genuine utility:
- Check if it grants access: Does owning this token unlock services?
- Review community involvement: Is there active participation enabled through this token?
- Consider project backing: Does it represent an investment stake?
- Analyze provenance: Is its origin linked directly with creators’ reputation?
Understanding these factors helps buyers make informed decisions aligned with personal goals—whether investing for appreciation potential via collectibles—or seeking ongoing benefits through utilities.
The Future Outlook for Utility vs Collectibles
As blockchain technology matures further—with improvements in scalability solutions like Layer 2 protocols—the scope for more sophisticated use cases expands significantly for both categories but especially so for utility-focused applications that blend social engagement with financial incentives.
Emerging sectors such as metaverse development suggest that utilities embedded into virtual environments will become increasingly integral—not just enhancing user experience but also creating sustainable economic models around these assets.
By recognizing the fundamental differences between purely collectible non-fungible tokens and those offering practical functionalities—and staying aware of current trends—you can better navigate this rapidly evolving space tailored toward your interests whether artistic appreciation versus active participation within communities driven by blockchain innovations.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Are Creator Royalties Enforced in the NFT Ecosystem?
Understanding how creator royalties are enforced in the NFT ecosystem is crucial for artists, collectors, and marketplace operators alike. As NFTs continue to revolutionize digital ownership and art sales, ensuring that creators receive fair compensation through automatic royalty payments has become a key concern. This article explores the mechanisms behind enforcing creator royalties, highlighting technological solutions, legal considerations, and industry practices.
What Are Creator Royalties in NFTs?
Creator royalties are a percentage of an NFT’s sale price that goes directly to the original artist or creator whenever their work is resold on secondary markets. Similar to traditional art royalties—where artists earn from subsequent sales—NFT creator royalties aim to provide ongoing revenue streams for digital creators. These percentages typically range from 5% to 10%, though they can be higher or lower depending on individual agreements.
The core idea is straightforward: when an NFT changes hands multiple times across different platforms or owners, the original artist continues to benefit financially. This system incentivizes creators by offering potential long-term earnings beyond their initial sale.
How Blockchain Technology Facilitates Royalty Enforcement
Blockchain technology underpins most NFTs and plays a vital role in enforcing royalty payments. Platforms like Ethereum store NFTs as unique tokens with transparent transaction histories recorded immutably on the blockchain. This transparency allows anyone to verify ownership history and transaction details at any time.
Smart contracts—self-executing code embedded within blockchain transactions—are central to automating royalty enforcement. When an NFT is sold via a marketplace supporting royalties, these smart contracts automatically deduct a predetermined percentage of the sale price and transfer it directly into the creator’s wallet without manual intervention.
This automation reduces reliance on trust-based agreements or third-party enforcement mechanisms; instead, it leverages blockchain's inherent security features for reliable execution of royalty terms.
Role of Popular Marketplaces in Enforcing Royalties
Major NFT marketplaces such as OpenSea and Rarible have integrated features that enable creators to set their preferred royalty rates during minting or listing processes:
OpenSea: In 2023, OpenSea updated its policies allowing creators full control over setting secondary sale royalties for each collection they list. The platform enforces these rates through smart contract interactions during transactions.
Rarible: Rarible introduced dynamic royalty settings where artists can adjust their rates based on factors like sale price or other criteria. Their platform also supports programmable royalties via customizable smart contracts.
These marketplaces act as intermediaries that facilitate enforceable payments by embedding royalty logic into transaction protocols supported by blockchain standards such as ERC-721 (for non-fungible tokens) and ERC-1155 (multi-token standard).
However, enforcement depends heavily on whether marketplaces honor these settings consistently across all transactions—a challenge given differing policies among platforms.
Challenges Due to Lack of Standardization
One significant obstacle in enforcing creator royalties stems from inconsistent standards across various platforms:
- Some marketplaces honor setroyalty percentages strictly.
- Others may ignore them entirely if not embedded properly within smart contracts.
This inconsistency leads to confusion among buyers who might expect certain fees but encounter situations where sellers bypass or disable automatic payments—a practice sometimes called "royalty bypassing" or "resale loopholes."
Furthermore, some platforms do not support programmable royalties at all—or only partially enforce them—making universal enforcement difficult without industry-wide standardization efforts.
Legal Considerations Surrounding Royalty Enforcement
While technically feasible through smart contracts and blockchain transparency, legal issues complicate enforcement:
Contractual Nature: Many argue that automated royalities should be legally binding contractual obligations; however,
Terms of Service vs Contract Law: Some dispute whether marketplace policies constitute legally enforceable agreements versus mere terms of service.
Jurisdictional Variability: Different countries have varying laws regarding digital assets’ contractual enforceability which adds complexity when disputes arise over unpaid royalties.
Ongoing discussions focus on establishing clearer legal frameworks that recognize automated smart contract obligations related to intellectual property rights within digital ecosystems.
Recent Industry Developments Supporting Enforcement
The industry has seen notable advancements aimed at strengthening royaltiy enforcement:
OpenSea’s Policy Update (2023) – Allowed creators greater control over setting secondary sale commissions directly linked with underlying smart contracts.
Rarible’s Dynamic Royalties – Enabled flexible rate adjustments based on specific conditions like resale value thresholds.
Emergence of DAO Governance Models – Decentralized Autonomous Organizations are being proposed as governance bodies overseeing collective management of funds—including enforcing rules around creator compensation—to promote fairness across communities.
These developments reflect growing recognition within the community about protecting artists' rights while leveraging technological innovations for better compliance management.
Industry Support & Community Engagement
Major marketplaces actively promote tools enabling easy setup and management of royalty payments:
- User-friendly interfaces allow artists without technical expertise to embed desired rates during minting processes.
- Community forums foster discussions about fair compensation practices—and many advocate increasing default rates or improving transparency around payment flows.
This engagement helps build trust between creators and buyers while encouraging adoption of best practices aligned with evolving standards for fair remuneration.
Future Directions Toward Standardized Enforcement
Looking ahead, several initiatives aim toward creating uniformity:
- Developing cross-platform standards using common protocols such as EIP (Ethereum Improvement Proposals) related specifically to royalty enforcement
- Establishing regulatory frameworks recognizing automated payment commitments
- Promoting industry-wide agreements among major players ensuring consistent adherence
Technological advancements will likely lead toward more sophisticated solutions—for example:
- Blockchain interoperability allowing seamless tracking across multiple chains
- Smart contract templates designed explicitly for enforceable copyright terms
Such innovations could significantly reduce disputes related to unpaid dues while reinforcing trustworthiness within this rapidly expanding market segment.
Final Thoughts
Enforcing creator royalties effectively remains a multifaceted challenge involving technological innovation, legal clarity, market cooperation—and active community participation. While current systems leverage blockchain's transparency coupled with programmable smart contracts successfully in many cases—including leading marketplaces—the lack of universal standardization continues posing hurdles worldwide.
As adoption grows alongside ongoing regulatory discussions and technological improvements — including decentralized governance models — we can expect more robust mechanisms ensuring fair compensation for digital artists moving forward.
By understanding these dynamics, artists, collectors, marketplace operators, and regulators can better navigate this evolving landscape—ensuring creativity remains rewarded fairly amid rapid innovation.*


kai
2025-05-22 11:39
How are creator royalties enforced in the NFT ecosystem?
How Are Creator Royalties Enforced in the NFT Ecosystem?
Understanding how creator royalties are enforced in the NFT ecosystem is crucial for artists, collectors, and marketplace operators alike. As NFTs continue to revolutionize digital ownership and art sales, ensuring that creators receive fair compensation through automatic royalty payments has become a key concern. This article explores the mechanisms behind enforcing creator royalties, highlighting technological solutions, legal considerations, and industry practices.
What Are Creator Royalties in NFTs?
Creator royalties are a percentage of an NFT’s sale price that goes directly to the original artist or creator whenever their work is resold on secondary markets. Similar to traditional art royalties—where artists earn from subsequent sales—NFT creator royalties aim to provide ongoing revenue streams for digital creators. These percentages typically range from 5% to 10%, though they can be higher or lower depending on individual agreements.
The core idea is straightforward: when an NFT changes hands multiple times across different platforms or owners, the original artist continues to benefit financially. This system incentivizes creators by offering potential long-term earnings beyond their initial sale.
How Blockchain Technology Facilitates Royalty Enforcement
Blockchain technology underpins most NFTs and plays a vital role in enforcing royalty payments. Platforms like Ethereum store NFTs as unique tokens with transparent transaction histories recorded immutably on the blockchain. This transparency allows anyone to verify ownership history and transaction details at any time.
Smart contracts—self-executing code embedded within blockchain transactions—are central to automating royalty enforcement. When an NFT is sold via a marketplace supporting royalties, these smart contracts automatically deduct a predetermined percentage of the sale price and transfer it directly into the creator’s wallet without manual intervention.
This automation reduces reliance on trust-based agreements or third-party enforcement mechanisms; instead, it leverages blockchain's inherent security features for reliable execution of royalty terms.
Role of Popular Marketplaces in Enforcing Royalties
Major NFT marketplaces such as OpenSea and Rarible have integrated features that enable creators to set their preferred royalty rates during minting or listing processes:
OpenSea: In 2023, OpenSea updated its policies allowing creators full control over setting secondary sale royalties for each collection they list. The platform enforces these rates through smart contract interactions during transactions.
Rarible: Rarible introduced dynamic royalty settings where artists can adjust their rates based on factors like sale price or other criteria. Their platform also supports programmable royalties via customizable smart contracts.
These marketplaces act as intermediaries that facilitate enforceable payments by embedding royalty logic into transaction protocols supported by blockchain standards such as ERC-721 (for non-fungible tokens) and ERC-1155 (multi-token standard).
However, enforcement depends heavily on whether marketplaces honor these settings consistently across all transactions—a challenge given differing policies among platforms.
Challenges Due to Lack of Standardization
One significant obstacle in enforcing creator royalties stems from inconsistent standards across various platforms:
- Some marketplaces honor setroyalty percentages strictly.
- Others may ignore them entirely if not embedded properly within smart contracts.
This inconsistency leads to confusion among buyers who might expect certain fees but encounter situations where sellers bypass or disable automatic payments—a practice sometimes called "royalty bypassing" or "resale loopholes."
Furthermore, some platforms do not support programmable royalties at all—or only partially enforce them—making universal enforcement difficult without industry-wide standardization efforts.
Legal Considerations Surrounding Royalty Enforcement
While technically feasible through smart contracts and blockchain transparency, legal issues complicate enforcement:
Contractual Nature: Many argue that automated royalities should be legally binding contractual obligations; however,
Terms of Service vs Contract Law: Some dispute whether marketplace policies constitute legally enforceable agreements versus mere terms of service.
Jurisdictional Variability: Different countries have varying laws regarding digital assets’ contractual enforceability which adds complexity when disputes arise over unpaid royalties.
Ongoing discussions focus on establishing clearer legal frameworks that recognize automated smart contract obligations related to intellectual property rights within digital ecosystems.
Recent Industry Developments Supporting Enforcement
The industry has seen notable advancements aimed at strengthening royaltiy enforcement:
OpenSea’s Policy Update (2023) – Allowed creators greater control over setting secondary sale commissions directly linked with underlying smart contracts.
Rarible’s Dynamic Royalties – Enabled flexible rate adjustments based on specific conditions like resale value thresholds.
Emergence of DAO Governance Models – Decentralized Autonomous Organizations are being proposed as governance bodies overseeing collective management of funds—including enforcing rules around creator compensation—to promote fairness across communities.
These developments reflect growing recognition within the community about protecting artists' rights while leveraging technological innovations for better compliance management.
Industry Support & Community Engagement
Major marketplaces actively promote tools enabling easy setup and management of royalty payments:
- User-friendly interfaces allow artists without technical expertise to embed desired rates during minting processes.
- Community forums foster discussions about fair compensation practices—and many advocate increasing default rates or improving transparency around payment flows.
This engagement helps build trust between creators and buyers while encouraging adoption of best practices aligned with evolving standards for fair remuneration.
Future Directions Toward Standardized Enforcement
Looking ahead, several initiatives aim toward creating uniformity:
- Developing cross-platform standards using common protocols such as EIP (Ethereum Improvement Proposals) related specifically to royalty enforcement
- Establishing regulatory frameworks recognizing automated payment commitments
- Promoting industry-wide agreements among major players ensuring consistent adherence
Technological advancements will likely lead toward more sophisticated solutions—for example:
- Blockchain interoperability allowing seamless tracking across multiple chains
- Smart contract templates designed explicitly for enforceable copyright terms
Such innovations could significantly reduce disputes related to unpaid dues while reinforcing trustworthiness within this rapidly expanding market segment.
Final Thoughts
Enforcing creator royalties effectively remains a multifaceted challenge involving technological innovation, legal clarity, market cooperation—and active community participation. While current systems leverage blockchain's transparency coupled with programmable smart contracts successfully in many cases—including leading marketplaces—the lack of universal standardization continues posing hurdles worldwide.
As adoption grows alongside ongoing regulatory discussions and technological improvements — including decentralized governance models — we can expect more robust mechanisms ensuring fair compensation for digital artists moving forward.
By understanding these dynamics, artists, collectors, marketplace operators, and regulators can better navigate this evolving landscape—ensuring creativity remains rewarded fairly amid rapid innovation.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Evaluate the Security Measures of a Cryptocurrency Project
Understanding how to assess the security of a cryptocurrency project is essential for investors, developers, and users alike. With the increasing complexity of blockchain systems and the rising number of cyber threats, evaluating security measures helps ensure that your assets and data are protected. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of key factors to consider when analyzing a project's security posture.
Understanding Blockchain Security Fundamentals
At its core, blockchain technology offers inherent security features through decentralization. Transactions are recorded across multiple nodes, making tampering difficult without controlling a majority of the network's computational power or stake. Different consensus algorithms influence this security level significantly.
Proof of Work (PoW): Used by Bitcoin, PoW requires miners to solve complex puzzles before adding new blocks. This process makes attacks like double-spending costly and resource-intensive but consumes significant energy.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Employed by projects like Ethereum 2.0, PoS selects validators based on their stake in the network. While more energy-efficient than PoW, it introduces different vulnerabilities such as "nothing at stake" attacks if not properly mitigated.
When evaluating a project’s blockchain infrastructure, examine which consensus mechanism it uses and how well it defends against common threats like 51% attacks or chain reorganizations.
Assessing Smart Contract Security
Smart contracts automate transactions and enforce rules without intermediaries but can be vulnerable if not properly coded or tested. The infamous DAO hack in 2016 exposed critical flaws in smart contract design—leading to substantial financial losses.
To evaluate smart contract security:
- Code Audits: Check whether independent audits have been conducted by reputable firms.
- Testing Practices: Determine if thorough testing procedures—including formal verification—are implemented.
- Open Source Transparency: Open-source code allows community review that can uncover vulnerabilities early.
- Bug Bounty Programs: Active bug bounty initiatives encourage external researchers to identify issues proactively.
Given that smart contract exploits can lead to significant financial damage—as seen with incidents involving DeFi protocols—rigorous development practices are non-negotiable indicators of strong security measures.
Analyzing User Protection Against Phishing & Social Engineering
While technical defenses are vital, user awareness plays an equally important role in overall system security. Phishing scams often target individual users through fake websites or malicious links designed to steal private keys or login credentials.
Effective projects implement:
- Clear communication about phishing risks
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Secure wallet integrations
Additionally, educating users about social engineering tactics helps prevent manipulation attempts aimed at compromising accounts or sensitive information.
Reviewing Regulatory Compliance & Legal Safeguards
Regulatory environments vary globally; some jurisdictions impose strict requirements on cryptocurrency projects while others adopt more lenient policies. Projects adhering closely to legal standards demonstrate commitment toward transparency and risk management—a positive indicator for investors concerned about compliance-related vulnerabilities or legal sanctions that could undermine project stability.
Assess whether the project complies with relevant regulations such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), and securities laws where applicable.
Importance of Regular Auditing & Penetration Testing
Continuous assessment is crucial because new vulnerabilities emerge over time as technology evolves. Regular code audits performed by third-party cybersecurity firms help identify weaknesses before malicious actors do so themselves. Penetration testing simulates real-world attack scenarios on both blockchain infrastructure and associated applications like wallets or dApps—providing insights into potential entry points for hackers.
Check whether ongoing auditing processes are documented publicly; transparent practices reflect proactive risk management strategies essential for maintaining trustworthiness within the community.
Community Involvement & Open Source Development
Open-source codebases foster transparency since anyone can review contributions for potential flaws or malicious code snippets. Many successful projects leverage community involvement through forums, developer groups, bug bounty programs—and these collaborative efforts often lead to faster identification and resolution of vulnerabilities compared with closed systems alone.
Key Indicators:
- Active development repositories
- Publicly available audit reports
- Engagement metrics from bug bounty platforms
Community-driven approaches enhance overall resilience against emerging threats while building confidence among stakeholders who rely on open scrutiny rather than proprietary secrecy alone.
Recent Trends & Challenges in Cryptocurrency Security
The rapid growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) has introduced new attack vectors requiring specialized attention from developers:
Notable Incidents:
- DAO Hack (2016): Exploited a recursive call vulnerability leading to $50 million loss.
- Parity Wallet Breach (2017): A flawed multisig wallet caused $30 million worth of Ether being frozen.
- Compound Protocol Exploit (2020): An attacker drained approximately $80 million via flash loan manipulation.
- Uniswap V2 Flash Loan Attack: Around $25 million was drained due to inadequate safeguards against flash loans' rapid borrowing capabilities.
These events underscore ongoing challenges such as ensuring robust protocol design against complex attack methods like flash loans—a technique allowing attackers instant access large sums without collateral during short periods.
Regulatory Impact:
Governments worldwide increasingly scrutinize unregulated crypto activities; actions taken by agencies such as SEC highlight risks related not only to technical flaws but also compliance failures which could result in legal penalties affecting project viability.
By thoroughly examining these aspects—from underlying blockchain mechanics through community engagement—you gain deeper insight into how well-positioned a cryptocurrency project is regarding its defenses against cyber threats today—and tomorrow's evolving landscape.
Final Thoughts on Evaluating Crypto Project Security Measures
Prioritizing comprehensive assessments ensures you’re making informed decisions rooted in understanding both technological safeguards and operational transparency within any crypto ecosystem you consider engaging with—or investing in—that aligns with best practices for safeguarding digital assets amid an ever-changing threat environment


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 06:28
How can I evaluate the security measures of a specific cryptocurrency project?
How to Evaluate the Security Measures of a Cryptocurrency Project
Understanding how to assess the security of a cryptocurrency project is essential for investors, developers, and users alike. With the increasing complexity of blockchain systems and the rising number of cyber threats, evaluating security measures helps ensure that your assets and data are protected. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of key factors to consider when analyzing a project's security posture.
Understanding Blockchain Security Fundamentals
At its core, blockchain technology offers inherent security features through decentralization. Transactions are recorded across multiple nodes, making tampering difficult without controlling a majority of the network's computational power or stake. Different consensus algorithms influence this security level significantly.
Proof of Work (PoW): Used by Bitcoin, PoW requires miners to solve complex puzzles before adding new blocks. This process makes attacks like double-spending costly and resource-intensive but consumes significant energy.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Employed by projects like Ethereum 2.0, PoS selects validators based on their stake in the network. While more energy-efficient than PoW, it introduces different vulnerabilities such as "nothing at stake" attacks if not properly mitigated.
When evaluating a project’s blockchain infrastructure, examine which consensus mechanism it uses and how well it defends against common threats like 51% attacks or chain reorganizations.
Assessing Smart Contract Security
Smart contracts automate transactions and enforce rules without intermediaries but can be vulnerable if not properly coded or tested. The infamous DAO hack in 2016 exposed critical flaws in smart contract design—leading to substantial financial losses.
To evaluate smart contract security:
- Code Audits: Check whether independent audits have been conducted by reputable firms.
- Testing Practices: Determine if thorough testing procedures—including formal verification—are implemented.
- Open Source Transparency: Open-source code allows community review that can uncover vulnerabilities early.
- Bug Bounty Programs: Active bug bounty initiatives encourage external researchers to identify issues proactively.
Given that smart contract exploits can lead to significant financial damage—as seen with incidents involving DeFi protocols—rigorous development practices are non-negotiable indicators of strong security measures.
Analyzing User Protection Against Phishing & Social Engineering
While technical defenses are vital, user awareness plays an equally important role in overall system security. Phishing scams often target individual users through fake websites or malicious links designed to steal private keys or login credentials.
Effective projects implement:
- Clear communication about phishing risks
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Secure wallet integrations
Additionally, educating users about social engineering tactics helps prevent manipulation attempts aimed at compromising accounts or sensitive information.
Reviewing Regulatory Compliance & Legal Safeguards
Regulatory environments vary globally; some jurisdictions impose strict requirements on cryptocurrency projects while others adopt more lenient policies. Projects adhering closely to legal standards demonstrate commitment toward transparency and risk management—a positive indicator for investors concerned about compliance-related vulnerabilities or legal sanctions that could undermine project stability.
Assess whether the project complies with relevant regulations such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), and securities laws where applicable.
Importance of Regular Auditing & Penetration Testing
Continuous assessment is crucial because new vulnerabilities emerge over time as technology evolves. Regular code audits performed by third-party cybersecurity firms help identify weaknesses before malicious actors do so themselves. Penetration testing simulates real-world attack scenarios on both blockchain infrastructure and associated applications like wallets or dApps—providing insights into potential entry points for hackers.
Check whether ongoing auditing processes are documented publicly; transparent practices reflect proactive risk management strategies essential for maintaining trustworthiness within the community.
Community Involvement & Open Source Development
Open-source codebases foster transparency since anyone can review contributions for potential flaws or malicious code snippets. Many successful projects leverage community involvement through forums, developer groups, bug bounty programs—and these collaborative efforts often lead to faster identification and resolution of vulnerabilities compared with closed systems alone.
Key Indicators:
- Active development repositories
- Publicly available audit reports
- Engagement metrics from bug bounty platforms
Community-driven approaches enhance overall resilience against emerging threats while building confidence among stakeholders who rely on open scrutiny rather than proprietary secrecy alone.
Recent Trends & Challenges in Cryptocurrency Security
The rapid growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) has introduced new attack vectors requiring specialized attention from developers:
Notable Incidents:
- DAO Hack (2016): Exploited a recursive call vulnerability leading to $50 million loss.
- Parity Wallet Breach (2017): A flawed multisig wallet caused $30 million worth of Ether being frozen.
- Compound Protocol Exploit (2020): An attacker drained approximately $80 million via flash loan manipulation.
- Uniswap V2 Flash Loan Attack: Around $25 million was drained due to inadequate safeguards against flash loans' rapid borrowing capabilities.
These events underscore ongoing challenges such as ensuring robust protocol design against complex attack methods like flash loans—a technique allowing attackers instant access large sums without collateral during short periods.
Regulatory Impact:
Governments worldwide increasingly scrutinize unregulated crypto activities; actions taken by agencies such as SEC highlight risks related not only to technical flaws but also compliance failures which could result in legal penalties affecting project viability.
By thoroughly examining these aspects—from underlying blockchain mechanics through community engagement—you gain deeper insight into how well-positioned a cryptocurrency project is regarding its defenses against cyber threats today—and tomorrow's evolving landscape.
Final Thoughts on Evaluating Crypto Project Security Measures
Prioritizing comprehensive assessments ensures you’re making informed decisions rooted in understanding both technological safeguards and operational transparency within any crypto ecosystem you consider engaging with—or investing in—that aligns with best practices for safeguarding digital assets amid an ever-changing threat environment
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Can I Convert My Cryptocurrency Back Into Traditional Fiat Currency?
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the way we think about money, offering decentralized and digital alternatives to traditional currencies. However, one of the most common questions among users and investors is whether they can convert their crypto holdings back into fiat currency—such as USD, EUR, or JPY—and how this process works. This article provides a comprehensive overview of cryptocurrency-to-fiat conversions, covering methods, challenges, recent developments, and best practices to ensure secure and efficient transactions.
Understanding Cryptocurrency and Fiat Currency
Before diving into conversion options, it’s essential to understand what cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies are. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets secured by cryptography that operate on decentralized blockchain networks. Bitcoin remains the most prominent example but is just one among over 5,000 different cryptocurrencies available today.
In contrast, fiat currencies are government-issued legal tender with no intrinsic value but backed by national authorities. Examples include the US dollar (USD), euro (EUR), yen (JPY), among others. These currencies are widely accepted for everyday transactions across borders.
Why Do People Convert Cryptocurrency to Fiat?
Converting crypto into fiat currency serves multiple purposes:
- Realizing Profits: Investors often buy cryptocurrencies at lower prices with plans to sell later when prices increase.
- Daily Spending: For routine expenses like groceries or bills that require traditional money.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many financial institutions mandate transactions in fiat for legal reasons.
- Liquidity Needs: Accessing cash quickly for emergencies or other financial commitments.
Understanding these motivations helps clarify why seamless conversion options are vital within the broader ecosystem of digital finance.
Methods for Converting Cryptocurrency to Fiat
There are several practical ways users can convert their cryptocurrencies into traditional money:
1. Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Exchanges such as Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Bitstamp provide user-friendly platforms where you can sell your crypto holdings directly for fiat currency. These platforms typically support various cryptocurrencies and offer real-time market rates.
Advantages:
- High liquidity
- Multiple supported coins
- Easy-to-use interfaces
Disadvantages:
- Transaction fees vary depending on platform
- Potential security risks if accounts aren’t properly secured
2. Digital Wallets with Conversion Features
Some digital wallets like MetaMask or Trust Wallet now incorporate features allowing users to swap tokens directly within their apps before transferring funds elsewhere or withdrawing as cash through linked services.
3. Crypto ATMs (Bitcoin ATMs)
Crypto ATMs enable in-person exchanges where you can insert cryptocurrency—either via a wallet QR code or card—and receive cash instantly in return.
Pros:
- Immediate access to physical cash
- No need for bank account linkage in some cases
Cons:
- Limited availability geographically
- Higher transaction fees compared to online exchanges
4. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Services
For large-volume conversions beyond typical exchange limits or when seeking privacy/security assurances—OTC desks facilitate direct trades between buyers and sellers outside public markets.
Fees Associated With Conversion Processes
Converting cryptocurrency isn’t free; various fees impact your net proceeds:
| Type of Fee | Description |
|---|---|
| Exchange Fees | Charged per transaction; varies by platform |
| Withdrawal Fees | Costs associated with transferring funds from exchange/wallet |
| Network Fees | Blockchain transaction costs paid by users during transfers |
Being aware of these charges helps optimize your conversion strategy — choosing platforms with competitive rates can significantly affect overall profitability.
Security Risks During Conversion
While converting crypto offers liquidity benefits, it also introduces certain risks:
Market Volatility: Prices fluctuate rapidly; timing your sale is crucial.Security Breaches: Hacks targeting exchanges have occurred historically; using reputable platforms enhances safety.Regulatory Changes: New laws may restrict certain conversions or impose additional compliance measures.Technical Failures: System outages or network issues could delay transactions leading to potential losses if market conditions change suddenly.
Implementing strong security practices—including two-factor authentication (2FA) and keeping software updated—is essential when managing conversions securely.
Recent Trends Impacting Crypto-to-Fiat Conversions
Recent years have seen notable developments influencing how easily users convert crypto assets:
Regulatory Clarity Enhances Confidence
In 2022 onwards, regulatory bodies like the U.S Securities & Exchange Commission began clarifying rules around cryptocurrencies’ legal status—affecting how exchanges operate across jurisdictions which impacts user access points for converting assets legally compliant manner[1].
Technological Innovations Improve Efficiency
Advancements such as AI integration in payment systems streamline transaction processes while reducing fraud risk[1]. For instance:
- Stripe’s new AI foundation model aims at bridging traditional banking systems with blockchain payments,
- Faster settlement times,
- Lower fees,
making conversions more accessible even during volatile market periods[1].
The Impact of Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets remain highly volatile; sudden price swings mean timing your sale carefully is critical if you want favorable rates without incurring losses—a challenge especially relevant during rapid bull runs or downturns[1].
Future Outlook
By 2025+, innovations like integrated payment rails combining both traditional finance infrastructure and blockchain technology will likely make converting crypto into fiat more seamless than ever before[1]. Enhanced regulatory clarity combined with technological progress promises safer environments for retail investors seeking liquidity solutions efficiently.
Best Practices When Converting Crypto To Fiat
To maximize benefits while minimizing risks:
- Use reputable exchanges known for security standards,
- Monitor market conditions closely before executing large trades,
- Be aware of all applicable fees upfront,
- Enable strong account security measures,
- Stay informed about evolving regulations affecting your jurisdiction,
Adopting these practices ensures smoother experiences regardless of whether you're a casual user or an active trader seeking quick liquidity solutions.
Navigating the landscape of cryptocurrency-to-fiat conversion involves understanding available methods alongside associated risks and recent technological trends that influence ease-of-use today. As adoption continues expanding globally amidst evolving regulations—and innovations making processes faster—the ability to convert digital assets into tangible cash remains a cornerstone feature supporting mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies worldwide.
References
[1] Based on data up until October 2023 regarding technological advancements like Stripe's AI models integrating payments systems alongside regulatory shifts impacting cryptocurrency markets globally.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 05:25
Can I convert my cryptocurrency back into traditional fiat currency?
Can I Convert My Cryptocurrency Back Into Traditional Fiat Currency?
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the way we think about money, offering decentralized and digital alternatives to traditional currencies. However, one of the most common questions among users and investors is whether they can convert their crypto holdings back into fiat currency—such as USD, EUR, or JPY—and how this process works. This article provides a comprehensive overview of cryptocurrency-to-fiat conversions, covering methods, challenges, recent developments, and best practices to ensure secure and efficient transactions.
Understanding Cryptocurrency and Fiat Currency
Before diving into conversion options, it’s essential to understand what cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies are. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets secured by cryptography that operate on decentralized blockchain networks. Bitcoin remains the most prominent example but is just one among over 5,000 different cryptocurrencies available today.
In contrast, fiat currencies are government-issued legal tender with no intrinsic value but backed by national authorities. Examples include the US dollar (USD), euro (EUR), yen (JPY), among others. These currencies are widely accepted for everyday transactions across borders.
Why Do People Convert Cryptocurrency to Fiat?
Converting crypto into fiat currency serves multiple purposes:
- Realizing Profits: Investors often buy cryptocurrencies at lower prices with plans to sell later when prices increase.
- Daily Spending: For routine expenses like groceries or bills that require traditional money.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many financial institutions mandate transactions in fiat for legal reasons.
- Liquidity Needs: Accessing cash quickly for emergencies or other financial commitments.
Understanding these motivations helps clarify why seamless conversion options are vital within the broader ecosystem of digital finance.
Methods for Converting Cryptocurrency to Fiat
There are several practical ways users can convert their cryptocurrencies into traditional money:
1. Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Exchanges such as Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Bitstamp provide user-friendly platforms where you can sell your crypto holdings directly for fiat currency. These platforms typically support various cryptocurrencies and offer real-time market rates.
Advantages:
- High liquidity
- Multiple supported coins
- Easy-to-use interfaces
Disadvantages:
- Transaction fees vary depending on platform
- Potential security risks if accounts aren’t properly secured
2. Digital Wallets with Conversion Features
Some digital wallets like MetaMask or Trust Wallet now incorporate features allowing users to swap tokens directly within their apps before transferring funds elsewhere or withdrawing as cash through linked services.
3. Crypto ATMs (Bitcoin ATMs)
Crypto ATMs enable in-person exchanges where you can insert cryptocurrency—either via a wallet QR code or card—and receive cash instantly in return.
Pros:
- Immediate access to physical cash
- No need for bank account linkage in some cases
Cons:
- Limited availability geographically
- Higher transaction fees compared to online exchanges
4. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Services
For large-volume conversions beyond typical exchange limits or when seeking privacy/security assurances—OTC desks facilitate direct trades between buyers and sellers outside public markets.
Fees Associated With Conversion Processes
Converting cryptocurrency isn’t free; various fees impact your net proceeds:
| Type of Fee | Description |
|---|---|
| Exchange Fees | Charged per transaction; varies by platform |
| Withdrawal Fees | Costs associated with transferring funds from exchange/wallet |
| Network Fees | Blockchain transaction costs paid by users during transfers |
Being aware of these charges helps optimize your conversion strategy — choosing platforms with competitive rates can significantly affect overall profitability.
Security Risks During Conversion
While converting crypto offers liquidity benefits, it also introduces certain risks:
Market Volatility: Prices fluctuate rapidly; timing your sale is crucial.Security Breaches: Hacks targeting exchanges have occurred historically; using reputable platforms enhances safety.Regulatory Changes: New laws may restrict certain conversions or impose additional compliance measures.Technical Failures: System outages or network issues could delay transactions leading to potential losses if market conditions change suddenly.
Implementing strong security practices—including two-factor authentication (2FA) and keeping software updated—is essential when managing conversions securely.
Recent Trends Impacting Crypto-to-Fiat Conversions
Recent years have seen notable developments influencing how easily users convert crypto assets:
Regulatory Clarity Enhances Confidence
In 2022 onwards, regulatory bodies like the U.S Securities & Exchange Commission began clarifying rules around cryptocurrencies’ legal status—affecting how exchanges operate across jurisdictions which impacts user access points for converting assets legally compliant manner[1].
Technological Innovations Improve Efficiency
Advancements such as AI integration in payment systems streamline transaction processes while reducing fraud risk[1]. For instance:
- Stripe’s new AI foundation model aims at bridging traditional banking systems with blockchain payments,
- Faster settlement times,
- Lower fees,
making conversions more accessible even during volatile market periods[1].
The Impact of Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets remain highly volatile; sudden price swings mean timing your sale carefully is critical if you want favorable rates without incurring losses—a challenge especially relevant during rapid bull runs or downturns[1].
Future Outlook
By 2025+, innovations like integrated payment rails combining both traditional finance infrastructure and blockchain technology will likely make converting crypto into fiat more seamless than ever before[1]. Enhanced regulatory clarity combined with technological progress promises safer environments for retail investors seeking liquidity solutions efficiently.
Best Practices When Converting Crypto To Fiat
To maximize benefits while minimizing risks:
- Use reputable exchanges known for security standards,
- Monitor market conditions closely before executing large trades,
- Be aware of all applicable fees upfront,
- Enable strong account security measures,
- Stay informed about evolving regulations affecting your jurisdiction,
Adopting these practices ensures smoother experiences regardless of whether you're a casual user or an active trader seeking quick liquidity solutions.
Navigating the landscape of cryptocurrency-to-fiat conversion involves understanding available methods alongside associated risks and recent technological trends that influence ease-of-use today. As adoption continues expanding globally amidst evolving regulations—and innovations making processes faster—the ability to convert digital assets into tangible cash remains a cornerstone feature supporting mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies worldwide.
References
[1] Based on data up until October 2023 regarding technological advancements like Stripe's AI models integrating payments systems alongside regulatory shifts impacting cryptocurrency markets globally.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Buy Your First Cryptocurrency: A Step-by-Step Guide
Getting started with cryptocurrency can seem daunting at first, especially for beginners unfamiliar with digital assets. However, the process of acquiring your first cryptocurrency is more straightforward than many think. By understanding the key steps involved and following best practices, you can confidently enter the world of digital currencies and begin your investment journey.
Choosing a Reliable Cryptocurrency Exchange
The foundation of buying cryptocurrency begins with selecting a reputable exchange platform. An exchange acts as a marketplace where you can buy, sell, and trade various cryptocurrencies. For beginners, user-friendly interfaces and strong security features are essential factors to consider.
Popular options include Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken—each offering intuitive platforms suitable for newcomers. These exchanges typically support multiple payment methods such as bank transfers, credit/debit cards, or PayPal. When choosing an exchange, verify its licensing status in your country and review user feedback to ensure reliability.
Creating Your Account Safely
Once you've selected an appropriate exchange platform, creating an account is usually straightforward but requires some verification steps to comply with regulatory standards (KYC procedures). You'll need to provide basic personal information like your name, email address, phone number—and sometimes additional identification documents such as a driver’s license or passport.
Secure account creation involves setting a strong password and enabling two-factor authentication (2FA). This extra layer of security helps protect your account from unauthorized access—a crucial consideration given the financial value stored in digital wallets.
Funding Your Account Through Deposits
After successfully setting up your account, you'll need to deposit funds into it before making any purchases. Most exchanges support traditional payment methods including bank transfers (ACH), credit/debit cards—which are often instant—or third-party services like PayPal in some regions.
Deposit limits vary depending on the platform and verification level; higher limits generally require additional identity checks. It’s advisable to start with small amounts until you're comfortable navigating the process securely.
Purchasing Your First Cryptocurrency
With funds available in your exchange account—whether fiat currency or stablecoins—you’re ready to buy cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), or other altcoins that interest you. The purchase process typically involves selecting the desired crypto asset and specifying either:
- The amount of money you want to spend
- The amount of cryptocurrency you wish to acquire
Most platforms offer simple “Buy” buttons along with real-time price data for informed decision-making. Keep in mind that transaction fees may apply depending on the payment method used; reviewing fee structures beforehand helps optimize costs.
Securing Your Digital Assets Properly
Once you've purchased cryptocurrencies through an exchange platform—often stored temporarily within their custodial wallets—it’s vital to transfer them into secure storage solutions tailored for long-term holding or active trading.
Digital wallets come in two main types:
Software Wallets: Applications like MetaMask (for Ethereum) or Exodus provide convenient access while maintaining control over private keys.
Hardware Wallets: Devices such as Ledger Nano S/X offer enhanced security by storing private keys offline—ideal for safeguarding larger holdings against hacking attempts.
Always enable security features like two-factor authentication on wallet accounts if available—and avoid leaving large sums on exchanges due to potential vulnerabilities associated with centralized platforms.
Recent Trends Impacting Cryptocurrency Acquisition
The landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies continues evolving rapidly due to technological innovations and regulatory developments worldwide. Governments are increasingly implementing regulations aimed at protecting investors while preventing illicit activities; this includes clarifying rules around initial coin offerings (ICOs) and securities classifications which influence how new investors engage with crypto markets safely.
Technological advancements have led toward more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake (PoS), reducing environmental concerns linked historically with mining-intensive coins like Bitcoin. These improvements aim not only at sustainability but also at increasing transaction speeds—a critical factor when purchasing assets during volatile market conditions.
Risks Every New Investor Should Be Aware Of
While entering cryptocurrency markets offers exciting opportunities—including potential high returns—it also carries significant risks that must be understood upfront:
Security Threats: Hacks targeting exchanges or wallets remain common; always use secure passwords combined with 2FA.
Market Volatility: Prices can fluctuate wildly within short periods driven by news events or market sentiment; never invest more than you’re willing—or able—to lose.
Environmental Concerns: Mining certain coins consumes vast amounts of electricity contributing negatively toward climate change.
Scams & Fraudulent Schemes: From fake ICOs promising quick profits to phishing attacks stealing login credentials—due diligence is essential before investing.
Navigating Future Developments in Digital Currency Investment
As regulations tighten globally alongside ongoing technological progress—including faster blockchain networks—the way individuals acquire cryptocurrencies will continue changing dynamically. Staying informed through reputable sources ensures you're aware of legal updates affecting ownership rights or tax obligations related directly back to investments made via exchanges.
Additionally—and perhaps most importantly—educating yourself about different types of digital assets beyond just Bitcoin expands investment opportunities while diversifying risk exposure across various sectors within blockchain technology.
By following these structured steps—from choosing trustworthy platforms through securing assets—you establish a solid foundation for entering cryptocurrency markets responsibly. Remember that continuous learning about recent trends—as well as understanding inherent risks—is key when navigating this fast-paced environment effectively over time.
Keywords: how to buy cryptocurrency | beginner's guide crypto | best crypto exchanges | secure crypto storage | investing in digital currencies


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 04:59
What is the most straightforward way to acquire my first cryptocurrency?
How to Buy Your First Cryptocurrency: A Step-by-Step Guide
Getting started with cryptocurrency can seem daunting at first, especially for beginners unfamiliar with digital assets. However, the process of acquiring your first cryptocurrency is more straightforward than many think. By understanding the key steps involved and following best practices, you can confidently enter the world of digital currencies and begin your investment journey.
Choosing a Reliable Cryptocurrency Exchange
The foundation of buying cryptocurrency begins with selecting a reputable exchange platform. An exchange acts as a marketplace where you can buy, sell, and trade various cryptocurrencies. For beginners, user-friendly interfaces and strong security features are essential factors to consider.
Popular options include Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken—each offering intuitive platforms suitable for newcomers. These exchanges typically support multiple payment methods such as bank transfers, credit/debit cards, or PayPal. When choosing an exchange, verify its licensing status in your country and review user feedback to ensure reliability.
Creating Your Account Safely
Once you've selected an appropriate exchange platform, creating an account is usually straightforward but requires some verification steps to comply with regulatory standards (KYC procedures). You'll need to provide basic personal information like your name, email address, phone number—and sometimes additional identification documents such as a driver’s license or passport.
Secure account creation involves setting a strong password and enabling two-factor authentication (2FA). This extra layer of security helps protect your account from unauthorized access—a crucial consideration given the financial value stored in digital wallets.
Funding Your Account Through Deposits
After successfully setting up your account, you'll need to deposit funds into it before making any purchases. Most exchanges support traditional payment methods including bank transfers (ACH), credit/debit cards—which are often instant—or third-party services like PayPal in some regions.
Deposit limits vary depending on the platform and verification level; higher limits generally require additional identity checks. It’s advisable to start with small amounts until you're comfortable navigating the process securely.
Purchasing Your First Cryptocurrency
With funds available in your exchange account—whether fiat currency or stablecoins—you’re ready to buy cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), or other altcoins that interest you. The purchase process typically involves selecting the desired crypto asset and specifying either:
- The amount of money you want to spend
- The amount of cryptocurrency you wish to acquire
Most platforms offer simple “Buy” buttons along with real-time price data for informed decision-making. Keep in mind that transaction fees may apply depending on the payment method used; reviewing fee structures beforehand helps optimize costs.
Securing Your Digital Assets Properly
Once you've purchased cryptocurrencies through an exchange platform—often stored temporarily within their custodial wallets—it’s vital to transfer them into secure storage solutions tailored for long-term holding or active trading.
Digital wallets come in two main types:
Software Wallets: Applications like MetaMask (for Ethereum) or Exodus provide convenient access while maintaining control over private keys.
Hardware Wallets: Devices such as Ledger Nano S/X offer enhanced security by storing private keys offline—ideal for safeguarding larger holdings against hacking attempts.
Always enable security features like two-factor authentication on wallet accounts if available—and avoid leaving large sums on exchanges due to potential vulnerabilities associated with centralized platforms.
Recent Trends Impacting Cryptocurrency Acquisition
The landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies continues evolving rapidly due to technological innovations and regulatory developments worldwide. Governments are increasingly implementing regulations aimed at protecting investors while preventing illicit activities; this includes clarifying rules around initial coin offerings (ICOs) and securities classifications which influence how new investors engage with crypto markets safely.
Technological advancements have led toward more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake (PoS), reducing environmental concerns linked historically with mining-intensive coins like Bitcoin. These improvements aim not only at sustainability but also at increasing transaction speeds—a critical factor when purchasing assets during volatile market conditions.
Risks Every New Investor Should Be Aware Of
While entering cryptocurrency markets offers exciting opportunities—including potential high returns—it also carries significant risks that must be understood upfront:
Security Threats: Hacks targeting exchanges or wallets remain common; always use secure passwords combined with 2FA.
Market Volatility: Prices can fluctuate wildly within short periods driven by news events or market sentiment; never invest more than you’re willing—or able—to lose.
Environmental Concerns: Mining certain coins consumes vast amounts of electricity contributing negatively toward climate change.
Scams & Fraudulent Schemes: From fake ICOs promising quick profits to phishing attacks stealing login credentials—due diligence is essential before investing.
Navigating Future Developments in Digital Currency Investment
As regulations tighten globally alongside ongoing technological progress—including faster blockchain networks—the way individuals acquire cryptocurrencies will continue changing dynamically. Staying informed through reputable sources ensures you're aware of legal updates affecting ownership rights or tax obligations related directly back to investments made via exchanges.
Additionally—and perhaps most importantly—educating yourself about different types of digital assets beyond just Bitcoin expands investment opportunities while diversifying risk exposure across various sectors within blockchain technology.
By following these structured steps—from choosing trustworthy platforms through securing assets—you establish a solid foundation for entering cryptocurrency markets responsibly. Remember that continuous learning about recent trends—as well as understanding inherent risks—is key when navigating this fast-paced environment effectively over time.
Keywords: how to buy cryptocurrency | beginner's guide crypto | best crypto exchanges | secure crypto storage | investing in digital currencies
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Market Ratios in Valuation: P/E and EV/EBITDA Explained
Understanding how investors evaluate the worth of a company is essential for making informed investment decisions. Among the most widely used tools in this process are market ratios, particularly the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio and Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) ratio. These metrics serve as foundational indicators that help assess whether a company's stock or overall valuation is reasonable relative to its earnings and financial health.
What Are P/E and EV/EBITDA Ratios?
The P/E ratio measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company's earnings per share (EPS). It is calculated by dividing the current stock price by EPS. For example, if a stock trades at $100 per share and its EPS is $5, then its P/E ratio would be 20. This means investors are paying 20 times the company's earnings for each share, which can reflect expectations about future growth or perceived risk.
In contrast, the EV/EBITDA ratio offers a broader perspective on valuation by considering enterprise value — which includes market capitalization plus debt minus cash — relative to EBITDA, an indicator of operating profitability before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. This metric helps compare companies regardless of their capital structure since it normalizes differences such as debt levels or cash reserves.
Why These Ratios Matter in Valuation
Both ratios provide insights into whether a company might be overvalued or undervalued compared to industry peers or historical averages. The P/E ratio tends to be more popular among equity investors focusing on stock prices relative to earnings growth prospects. Meanwhile, EV/EBITDA offers advantages when comparing companies with different debt levels because it accounts for leverage effects that can distort other valuation metrics.
Historically speaking, these ratios have been integral parts of financial analysis since their inception—P/E dating back over a century—and gained prominence with the rise of sophisticated investment strategies like private equity during the late 20th century. Today they remain relevant not only in traditional markets but also increasingly influence emerging sectors such as cryptocurrencies.
Recent Trends and Developments
In recent years, market ratios have adapted alongside evolving financial landscapes. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored their importance amid heightened volatility; many analysts relied heavily on these metrics when reassessing valuations amidst economic uncertainty. As markets recovered post-pandemic, fluctuations in P/E and EV/EBITDA reflected changing investor sentiment about growth prospects across industries.
Furthermore, there's been an increasing integration of Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) factors into valuation models—leading some firms to adjust traditional ratios accordingly. ESG-adjusted P/E ratios now aim to incorporate sustainability considerations that could impact long-term profitability or risk profiles.
Additionally, while these ratios originated within traditional finance domains—public equities—they are now being explored within private equity transactions where they assist in evaluating target companies' worth efficiently before acquisition deals close.
Market Ratios Across Industries
Industry-specific benchmarks significantly influence what constitutes a "normal" P/E or EV/EBITDA multiple:
- Technology Sector: Typically exhibits higher P/E ratios due to rapid growth expectations.
- Utilities & Consumer Staples: Usually have lower multiples reflecting stable but slower-growing businesses.
- Financials & Capital-Intensive Industries: Often show varied multiples depending on leverage levels; EV/EBITDA helps normalize comparisons here.
Investors should always compare these metrics against industry averages rather than absolute numbers alone because context matters greatly when interpreting valuation signals.
Limitations and Cautions
Despite their usefulness—these ratios aren't foolproof indicators:
- Earnings Manipulation: Earnings figures can sometimes be manipulated through accounting practices leading to misleadingly high or low P/E values.
- Growth Expectations: High P/E may reflect optimistic future growth rather than current undervaluation.
- Debt Levels: While EV/EBITDA adjusts for leverage effects better than other measures like Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S), it still doesn't capture all risks associated with high debt loads.
- Crypto Market Challenges: Applying traditional valuations like P/E or EV/EBITDA directly onto cryptocurrencies remains problematic due to their fundamentally different nature—many lack earnings altogether—and regulatory uncertainties affecting crypto assets' valuations.
Emerging Trends Impacting Market Ratios
The ongoing evolution toward integrating ESG factors influences how analysts interpret these metrics today:
- Companies demonstrating strong sustainability practices often enjoy premium valuations.
- Investors increasingly scrutinize non-financial factors alongside traditional data points when assessing long-term viability.
Moreover, technological advancements enable more nuanced analysis tools that combine multiple financial metrics—including market sentiment indicators—to produce comprehensive valuation models suited for both conventional stocks and alternative assets like digital currencies.
Applying Market Ratios Effectively
To maximize insights from these tools:
- Always benchmark against industry averages rather than relying solely on absolute figures.
- Use multiple ratios together—for instance combining PE with PEG (Price-to-Earnings Growth)—to get clearer pictures about growth potential versus value status.
- Consider qualitative factors such as management quality or macroeconomic trends influencing earnings forecasts beyond numerical data alone.
Staying Informed About Market Dynamics
Investors should keep abreast of recent developments affecting valuation multiples:
- Economic shifts impacting interest rates can alter discount rates used implicitly in valuations
- Regulatory changes especially relevant within crypto markets
- Broader macroeconomic conditions influencing corporate profitability
By understanding both core principles behind key market ratios like P/E and EV/EBITDA—and recognizing their limitations—you'll be better equipped to interpret company valuations accurately across diverse sectors including emerging asset classes such as cryptocurrencies.
How Do Market Ratios Inform Investment Decisions?
Ultimately, market ratios serve as vital benchmarks guiding buy-sell decisions based on perceived fair value versus current prices—a critical component for both individual investors aiming at portfolio optimization and institutional players managing large-scale investments carefully aligned with risk appetite.
Keywords: Market Ratios , Valuation Metrics , Price-to-Earnings Ratio , Enterprise Value EBITDA , Company Valuation , Investment Analysis , Financial Metrics , Industry Benchmarks , Crypto Asset Valuation


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-19 14:05
How do market ratios like P/E and EV/EBITDA inform valuation?
Market Ratios in Valuation: P/E and EV/EBITDA Explained
Understanding how investors evaluate the worth of a company is essential for making informed investment decisions. Among the most widely used tools in this process are market ratios, particularly the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio and Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) ratio. These metrics serve as foundational indicators that help assess whether a company's stock or overall valuation is reasonable relative to its earnings and financial health.
What Are P/E and EV/EBITDA Ratios?
The P/E ratio measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company's earnings per share (EPS). It is calculated by dividing the current stock price by EPS. For example, if a stock trades at $100 per share and its EPS is $5, then its P/E ratio would be 20. This means investors are paying 20 times the company's earnings for each share, which can reflect expectations about future growth or perceived risk.
In contrast, the EV/EBITDA ratio offers a broader perspective on valuation by considering enterprise value — which includes market capitalization plus debt minus cash — relative to EBITDA, an indicator of operating profitability before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. This metric helps compare companies regardless of their capital structure since it normalizes differences such as debt levels or cash reserves.
Why These Ratios Matter in Valuation
Both ratios provide insights into whether a company might be overvalued or undervalued compared to industry peers or historical averages. The P/E ratio tends to be more popular among equity investors focusing on stock prices relative to earnings growth prospects. Meanwhile, EV/EBITDA offers advantages when comparing companies with different debt levels because it accounts for leverage effects that can distort other valuation metrics.
Historically speaking, these ratios have been integral parts of financial analysis since their inception—P/E dating back over a century—and gained prominence with the rise of sophisticated investment strategies like private equity during the late 20th century. Today they remain relevant not only in traditional markets but also increasingly influence emerging sectors such as cryptocurrencies.
Recent Trends and Developments
In recent years, market ratios have adapted alongside evolving financial landscapes. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored their importance amid heightened volatility; many analysts relied heavily on these metrics when reassessing valuations amidst economic uncertainty. As markets recovered post-pandemic, fluctuations in P/E and EV/EBITDA reflected changing investor sentiment about growth prospects across industries.
Furthermore, there's been an increasing integration of Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) factors into valuation models—leading some firms to adjust traditional ratios accordingly. ESG-adjusted P/E ratios now aim to incorporate sustainability considerations that could impact long-term profitability or risk profiles.
Additionally, while these ratios originated within traditional finance domains—public equities—they are now being explored within private equity transactions where they assist in evaluating target companies' worth efficiently before acquisition deals close.
Market Ratios Across Industries
Industry-specific benchmarks significantly influence what constitutes a "normal" P/E or EV/EBITDA multiple:
- Technology Sector: Typically exhibits higher P/E ratios due to rapid growth expectations.
- Utilities & Consumer Staples: Usually have lower multiples reflecting stable but slower-growing businesses.
- Financials & Capital-Intensive Industries: Often show varied multiples depending on leverage levels; EV/EBITDA helps normalize comparisons here.
Investors should always compare these metrics against industry averages rather than absolute numbers alone because context matters greatly when interpreting valuation signals.
Limitations and Cautions
Despite their usefulness—these ratios aren't foolproof indicators:
- Earnings Manipulation: Earnings figures can sometimes be manipulated through accounting practices leading to misleadingly high or low P/E values.
- Growth Expectations: High P/E may reflect optimistic future growth rather than current undervaluation.
- Debt Levels: While EV/EBITDA adjusts for leverage effects better than other measures like Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S), it still doesn't capture all risks associated with high debt loads.
- Crypto Market Challenges: Applying traditional valuations like P/E or EV/EBITDA directly onto cryptocurrencies remains problematic due to their fundamentally different nature—many lack earnings altogether—and regulatory uncertainties affecting crypto assets' valuations.
Emerging Trends Impacting Market Ratios
The ongoing evolution toward integrating ESG factors influences how analysts interpret these metrics today:
- Companies demonstrating strong sustainability practices often enjoy premium valuations.
- Investors increasingly scrutinize non-financial factors alongside traditional data points when assessing long-term viability.
Moreover, technological advancements enable more nuanced analysis tools that combine multiple financial metrics—including market sentiment indicators—to produce comprehensive valuation models suited for both conventional stocks and alternative assets like digital currencies.
Applying Market Ratios Effectively
To maximize insights from these tools:
- Always benchmark against industry averages rather than relying solely on absolute figures.
- Use multiple ratios together—for instance combining PE with PEG (Price-to-Earnings Growth)—to get clearer pictures about growth potential versus value status.
- Consider qualitative factors such as management quality or macroeconomic trends influencing earnings forecasts beyond numerical data alone.
Staying Informed About Market Dynamics
Investors should keep abreast of recent developments affecting valuation multiples:
- Economic shifts impacting interest rates can alter discount rates used implicitly in valuations
- Regulatory changes especially relevant within crypto markets
- Broader macroeconomic conditions influencing corporate profitability
By understanding both core principles behind key market ratios like P/E and EV/EBITDA—and recognizing their limitations—you'll be better equipped to interpret company valuations accurately across diverse sectors including emerging asset classes such as cryptocurrencies.
How Do Market Ratios Inform Investment Decisions?
Ultimately, market ratios serve as vital benchmarks guiding buy-sell decisions based on perceived fair value versus current prices—a critical component for both individual investors aiming at portfolio optimization and institutional players managing large-scale investments carefully aligned with risk appetite.
Keywords: Market Ratios , Valuation Metrics , Price-to-Earnings Ratio , Enterprise Value EBITDA , Company Valuation , Investment Analysis , Financial Metrics , Industry Benchmarks , Crypto Asset Valuation
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding Valuation Ratios in Financial Analysis
Valuation ratios are fundamental tools used by investors, analysts, and financial professionals to assess the intrinsic value of a company or asset. These ratios help interpret a company's financial health, profitability, and growth potential by comparing market prices to various financial metrics. While traditionally applied within stock markets and corporate finance, understanding valuation ratios is increasingly relevant in the context of cryptocurrencies and digital assets.
Key Valuation Ratios and Their Formulas
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio is one of the most widely recognized valuation metrics in traditional finance. It measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings generated by a company. The formula is straightforward:
P/E = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share (EPS)
A high P/E ratio often indicates that investors expect higher future earnings growth from the company, whereas a lower P/E might suggest undervaluation or lower growth prospects. For example, if a stock trades at $100 per share with an EPS of $5, its P/E ratio would be 20.
In cryptocurrency markets, however, this metric isn't directly applicable because digital assets typically do not generate earnings like traditional companies do. Instead, alternative indicators such as market capitalization relative to transaction volume or price-to-market-cap ratios serve as proxies for assessing market sentiment and valuation.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The P/B ratio compares a company's current market price to its book value—the net asset value recorded on its balance sheet:
P/B = Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share
A low P/B ratio can signal that the stock may be undervalued relative to its assets; conversely, a high P/B might indicate overvaluation or high growth expectations embedded in the stock price.
In crypto markets where companies have no tangible book values like physical assets or equity statements—especially decentralized projects—the concept shifts towards evaluating metrics such as market capitalization relative to circulating supply or network value versus transaction volume.
Dividend Yield
This metric shows how much income an investor receives from dividends relative to the current share price:
Dividend Yield = Annual Dividend Payment per Share / Current Stock Price
It’s particularly useful for income-focused investors seeking steady cash flows from their investments. However, most cryptocurrencies do not pay dividends; instead, some DeFi tokens offer yields through staking protocols or liquidity provision rewards which serve similar purposes but require different analytical approaches.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
This ratio indicates how leveraged a company is by comparing total debt against shareholders' equity:
Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
Higher ratios imply greater leverage and potentially higher risk if debt levels become unsustainable during downturns. In crypto contexts where traditional debt isn’t common—though leveraged trading exists—analysts look at borrowing levels within lending platforms or margin trading activities as analogous indicators of leverage risk.
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE measures profitability relative to shareholder investment:
ROE = Net Income / Total Equity
It reflects management’s efficiency in generating profits from shareholders’ funds. Since most cryptocurrencies lack equity structures akin to corporations—being decentralized networks rather than entities with shareholders—the direct application is limited; instead, ROI metrics tailored for crypto investments are more prevalent here.
Current Ratio
This liquidity measure compares current assets against current liabilities:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
A higher ratio suggests better short-term financial health and liquidity position—a critical factor for businesses but less directly relevant in crypto markets where liquidity is assessed via trading volumes rather than balance sheet items.
Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio
The P/S ratio evaluates how much investors are willing to pay based on sales figures:
P/S Ratio = Market Price per Share / Sales per Share
It's especially useful when companies have negative earnings but positive sales figures. In cryptocurrency terms? Metrics like network activity compared with market cap—or transaction volume versus valuation—serve similar roles in gauging economic activity within blockchain ecosystems.
Recent Trends Impacting Valuation Metrics in Crypto Markets
With rapid technological advancements and evolving regulatory landscapes shaping digital asset valuations today’s analysis incorporates new dimensions beyond traditional formulas. The rise of DeFi has introduced innovative metrics such as yield farming returns—and liquidity pool sizes—that provide insights into project sustainability beyond simple price movements.
Furthermore, increased institutional participation has brought more standardized evaluation techniques into play—including applying familiar financial ratios—but adapting them carefully due to differences between centralized corporate structures versus decentralized networks without conventional balance sheets or income statements.
Regulatory clarity remains crucial: clearer guidelines can lead toward more reliable application of these ratios while reducing speculative excesses that often inflate valuations artificially—a concern especially pertinent given recent volatility spikes across crypto markets driven by hype cycles rather than fundamentals.
Challenges & Risks When Applying Traditional Ratios To Cryptocurrencies
Applying classic valuation formulas directly onto cryptocurrencies presents unique challenges because many foundational assumptions don’t hold true outside traditional business models. For instance:
- Cryptocurrencies generally lack tangible assets reflected on balance sheets.
- Many tokens operate without generating profits.
- Liquidity dynamics differ significantly from those seen with stocks.
Moreover:
- High volatility can distort perceived valuations.
- Lack of standardization across different projects complicates comparative analysis.
Despite these hurdles — understanding these limitations helps prevent misinterpretation while emphasizing context-specific adjustments necessary when analyzing digital assets effectively.
Emerging Developments Shaping Cryptocurrency Valuations
Recent years have seen significant innovations influencing how we evaluate cryptos:
- DeFi Metrics: Yield farming rates — which reflect returns earned through staking tokens — along with liquidity pool sizes provide alternative ways for assessing project viability.
- Institutional Adoption: As large players enter space using familiar tools like discounted cash flow models alongside traditional valuation ratios fosters greater transparency.
- Market Volatility & Sentiment: Rapid swings necessitate combining quantitative analysis with sentiment indicators derived from social media trends and news flow for comprehensive assessment.
Managing Risks Through Financial Analysis
Given inherent risks—including regulatory uncertainty—and potential overvaluation concerns highlighted during bull runs—it’s vital that investors employ robust risk management strategies grounded in sound financial analysis principles:
- Use multiple valuation methods together rather than relying solely on one metric
- Stay updated on regulatory developments impacting token classifications
- Monitor macroeconomic factors influencing both fiat currencies and digital assets
By integrating these practices into your investment approach you enhance decision-making confidence amid volatile conditions.
Understanding key valuation ratios provides essential insights whether you're analyzing stocks or navigating complex cryptocurrency markets today’s landscape demands adaptability combined with rigorous research standards rooted in established principles yet flexible enough for emerging trends—and always aligned with user intent seeking clarity about fundamental evaluation methods across diverse asset classes


Lo
2025-05-19 08:59
What are the formulas and interpretations for key valuation ratios?
Understanding Valuation Ratios in Financial Analysis
Valuation ratios are fundamental tools used by investors, analysts, and financial professionals to assess the intrinsic value of a company or asset. These ratios help interpret a company's financial health, profitability, and growth potential by comparing market prices to various financial metrics. While traditionally applied within stock markets and corporate finance, understanding valuation ratios is increasingly relevant in the context of cryptocurrencies and digital assets.
Key Valuation Ratios and Their Formulas
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio is one of the most widely recognized valuation metrics in traditional finance. It measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings generated by a company. The formula is straightforward:
P/E = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share (EPS)
A high P/E ratio often indicates that investors expect higher future earnings growth from the company, whereas a lower P/E might suggest undervaluation or lower growth prospects. For example, if a stock trades at $100 per share with an EPS of $5, its P/E ratio would be 20.
In cryptocurrency markets, however, this metric isn't directly applicable because digital assets typically do not generate earnings like traditional companies do. Instead, alternative indicators such as market capitalization relative to transaction volume or price-to-market-cap ratios serve as proxies for assessing market sentiment and valuation.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The P/B ratio compares a company's current market price to its book value—the net asset value recorded on its balance sheet:
P/B = Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share
A low P/B ratio can signal that the stock may be undervalued relative to its assets; conversely, a high P/B might indicate overvaluation or high growth expectations embedded in the stock price.
In crypto markets where companies have no tangible book values like physical assets or equity statements—especially decentralized projects—the concept shifts towards evaluating metrics such as market capitalization relative to circulating supply or network value versus transaction volume.
Dividend Yield
This metric shows how much income an investor receives from dividends relative to the current share price:
Dividend Yield = Annual Dividend Payment per Share / Current Stock Price
It’s particularly useful for income-focused investors seeking steady cash flows from their investments. However, most cryptocurrencies do not pay dividends; instead, some DeFi tokens offer yields through staking protocols or liquidity provision rewards which serve similar purposes but require different analytical approaches.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
This ratio indicates how leveraged a company is by comparing total debt against shareholders' equity:
Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
Higher ratios imply greater leverage and potentially higher risk if debt levels become unsustainable during downturns. In crypto contexts where traditional debt isn’t common—though leveraged trading exists—analysts look at borrowing levels within lending platforms or margin trading activities as analogous indicators of leverage risk.
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE measures profitability relative to shareholder investment:
ROE = Net Income / Total Equity
It reflects management’s efficiency in generating profits from shareholders’ funds. Since most cryptocurrencies lack equity structures akin to corporations—being decentralized networks rather than entities with shareholders—the direct application is limited; instead, ROI metrics tailored for crypto investments are more prevalent here.
Current Ratio
This liquidity measure compares current assets against current liabilities:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
A higher ratio suggests better short-term financial health and liquidity position—a critical factor for businesses but less directly relevant in crypto markets where liquidity is assessed via trading volumes rather than balance sheet items.
Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio
The P/S ratio evaluates how much investors are willing to pay based on sales figures:
P/S Ratio = Market Price per Share / Sales per Share
It's especially useful when companies have negative earnings but positive sales figures. In cryptocurrency terms? Metrics like network activity compared with market cap—or transaction volume versus valuation—serve similar roles in gauging economic activity within blockchain ecosystems.
Recent Trends Impacting Valuation Metrics in Crypto Markets
With rapid technological advancements and evolving regulatory landscapes shaping digital asset valuations today’s analysis incorporates new dimensions beyond traditional formulas. The rise of DeFi has introduced innovative metrics such as yield farming returns—and liquidity pool sizes—that provide insights into project sustainability beyond simple price movements.
Furthermore, increased institutional participation has brought more standardized evaluation techniques into play—including applying familiar financial ratios—but adapting them carefully due to differences between centralized corporate structures versus decentralized networks without conventional balance sheets or income statements.
Regulatory clarity remains crucial: clearer guidelines can lead toward more reliable application of these ratios while reducing speculative excesses that often inflate valuations artificially—a concern especially pertinent given recent volatility spikes across crypto markets driven by hype cycles rather than fundamentals.
Challenges & Risks When Applying Traditional Ratios To Cryptocurrencies
Applying classic valuation formulas directly onto cryptocurrencies presents unique challenges because many foundational assumptions don’t hold true outside traditional business models. For instance:
- Cryptocurrencies generally lack tangible assets reflected on balance sheets.
- Many tokens operate without generating profits.
- Liquidity dynamics differ significantly from those seen with stocks.
Moreover:
- High volatility can distort perceived valuations.
- Lack of standardization across different projects complicates comparative analysis.
Despite these hurdles — understanding these limitations helps prevent misinterpretation while emphasizing context-specific adjustments necessary when analyzing digital assets effectively.
Emerging Developments Shaping Cryptocurrency Valuations
Recent years have seen significant innovations influencing how we evaluate cryptos:
- DeFi Metrics: Yield farming rates — which reflect returns earned through staking tokens — along with liquidity pool sizes provide alternative ways for assessing project viability.
- Institutional Adoption: As large players enter space using familiar tools like discounted cash flow models alongside traditional valuation ratios fosters greater transparency.
- Market Volatility & Sentiment: Rapid swings necessitate combining quantitative analysis with sentiment indicators derived from social media trends and news flow for comprehensive assessment.
Managing Risks Through Financial Analysis
Given inherent risks—including regulatory uncertainty—and potential overvaluation concerns highlighted during bull runs—it’s vital that investors employ robust risk management strategies grounded in sound financial analysis principles:
- Use multiple valuation methods together rather than relying solely on one metric
- Stay updated on regulatory developments impacting token classifications
- Monitor macroeconomic factors influencing both fiat currencies and digital assets
By integrating these practices into your investment approach you enhance decision-making confidence amid volatile conditions.
Understanding key valuation ratios provides essential insights whether you're analyzing stocks or navigating complex cryptocurrency markets today’s landscape demands adaptability combined with rigorous research standards rooted in established principles yet flexible enough for emerging trends—and always aligned with user intent seeking clarity about fundamental evaluation methods across diverse asset classes
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Role Does Dark Pool Print Data Play in Technical Analysis?
Understanding Dark Pool Print Data
Dark pool print data refers to the information generated from trades executed within dark pools—private trading venues where large investors, such as institutions and hedge funds, can buy or sell significant amounts of assets without revealing their intentions to the broader market. Unlike public exchanges, dark pools do not display order books openly, making their activity less transparent but highly influential. The "print" in this context indicates the actual transaction data that appears post-trade, providing insights into large-volume trades that might otherwise remain hidden.
In cryptocurrency markets, dark pools have gained prominence as traders seek anonymity for sizable transactions. These platforms allow institutional players to execute large orders discreetly, minimizing market impact and avoiding price slippage. As a result, analyzing dark pool print data has become an essential part of technical analysis for traders aiming to understand underlying market sentiment and potential future movements.
The Significance of Dark Pool Data in Market Sentiment
One of the primary reasons traders focus on dark pool print data is its ability to reflect real-time market sentiment beyond what is visible on public exchanges. Large trades executed in these private venues often indicate significant buying or selling pressure from institutional investors who prefer discretion. When analysts observe a surge in buy-side prints within dark pools, it may signal accumulating bullish momentum ahead of a price rally.
Conversely, an increase in sell-side activity can suggest impending downward movement or profit-taking by major players. By monitoring these patterns over time—such as volume spikes or repeated large transactions—traders can gauge whether overall market sentiment leans bullish or bearish even before price action becomes apparent publicly.
Impact on Price Movements and Market Dynamics
Dark pool transactions can influence cryptocurrency prices subtly yet substantially. Since these trades are often substantial in size but not immediately visible on mainstream charts, they may cause hidden shifts that precede noticeable price changes on public exchanges.
For example:
- Large buy orders executed quietly could lead to upward price pressure once they leak into public markets.
- Conversely, significant sell-offs might be absorbed within dark pools temporarily suppressing volatility until the activity spills over publicly.
This dynamic creates a layer of complexity for technical analysts who aim to interpret true supply-demand conditions accurately. Recognizing patterns within dark pool prints helps traders anticipate potential breakouts or reversals before they manifest visibly on traditional charts.
Enhancing Risk Management Strategies
Incorporating dark pool print analysis into trading strategies enhances risk management by providing early signals about underlying market moves that are not yet reflected publicly. For instance:
- Detecting increased selling activity behind closed doors allows traders to tighten stop-loss levels.
- Spotting accumulation phases through persistent buying prints could encourage position building with controlled risk exposure.
By understanding these hidden activities alongside conventional technical indicators like moving averages and RSI (Relative Strength Index), traders develop more comprehensive views of potential trend shifts—reducing surprises caused by unanticipated large trades slipping under standard radar.
Advancements Facilitating Dark Pool Analysis
Recent technological developments have significantly improved access and interpretation of dark pool data:
- Transparency Initiatives: Some crypto exchanges now disclose more detailed information about their internal dark pools—a move driven partly by regulatory pressures aimed at increasing overall transparency.
- Analytics Tools: Sophisticated software leveraging machine learning algorithms enables analysts to sift through vast datasets efficiently—identifying meaningful patterns amid noise.
- Market Integration: As traditional financial practices merge with crypto markets, methodologies used for analyzing institutional activities are increasingly adapted for digital assets—including tracking anonymized trade flows across multiple platforms simultaneously.
These advancements empower both retail and professional traders with better tools for incorporating deep-layered insights into their decision-making processes.
Potential Risks and Ethical Considerations
While analyzing dark pool print data offers valuable advantages, it also presents certain risks:
- Market Manipulation: Large anonymous trades could be part of schemes designed intentionally to mislead other participants about true supply-demand dynamics.
- Regulatory Challenges: Increasing scrutiny from regulators aims at curbing unfair practices; stricter rules may limit access or impose restrictions on how this data is collected and used.
- Security Concerns: Sensitive trade information falling into malicious hands could facilitate insider trading or fraud if improperly secured.
Ethically speaking, using such confidential information responsibly is crucial; exploiting non-public trade details without disclosure raises questions about fairness and legality within financial markets.
Emerging Trends Shaping Future Use
The landscape surrounding dark pool print data continues evolving rapidly due to several key factors:
- Greater transparency initiatives led by regulators aim at reducing opacity while maintaining fair trading environments.
- The integration of advanced analytics tools makes it easier than ever for individual investors—and especially institutional ones—to interpret complex datasets effectively.
- Growing adoption across crypto exchanges signifies recognition that understanding behind-the-scenes activities enhances overall market integrity when managed properly.
How Traders Can Leverage Dark Pool Data Effectively
To maximize benefits from analyzing dark pool prints:
- Combine with Traditional Indicators – Use alongside volume analysis tools like OBV (On-Balance Volume) or MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence).
- Monitor Patterns Over Time – Look for consistent increases/decreases indicating sustained accumulation/distribution phases rather than one-off spikes.
- Stay Updated With Regulatory Changes – Be aware of legal frameworks affecting access rights which might impact your analytical capabilities.4.. Use Reliable Analytics Platforms – Invest in reputable software capable of processing vast datasets accurately while filtering out false signals.
Final Thoughts
Dark pool print data has become an integral component in modern technical analysis within cryptocurrency markets due to its ability to reveal hidden trader intentions behind major transactions. Its role extends beyond mere speculation; it provides critical insights into underlying sentiment shifts that precede visible price movements—a valuable advantage when navigating volatile digital asset landscapes.
As technology advances and regulatory environments evolve towards greater transparency without compromising privacy rights, the utility derived from this type of data will likely grow further — empowering informed decision-making while emphasizing responsible use aligned with ethical standards.


Lo
2025-05-14 18:48
What role does dark pool print data play in technical analysis?
What Role Does Dark Pool Print Data Play in Technical Analysis?
Understanding Dark Pool Print Data
Dark pool print data refers to the information generated from trades executed within dark pools—private trading venues where large investors, such as institutions and hedge funds, can buy or sell significant amounts of assets without revealing their intentions to the broader market. Unlike public exchanges, dark pools do not display order books openly, making their activity less transparent but highly influential. The "print" in this context indicates the actual transaction data that appears post-trade, providing insights into large-volume trades that might otherwise remain hidden.
In cryptocurrency markets, dark pools have gained prominence as traders seek anonymity for sizable transactions. These platforms allow institutional players to execute large orders discreetly, minimizing market impact and avoiding price slippage. As a result, analyzing dark pool print data has become an essential part of technical analysis for traders aiming to understand underlying market sentiment and potential future movements.
The Significance of Dark Pool Data in Market Sentiment
One of the primary reasons traders focus on dark pool print data is its ability to reflect real-time market sentiment beyond what is visible on public exchanges. Large trades executed in these private venues often indicate significant buying or selling pressure from institutional investors who prefer discretion. When analysts observe a surge in buy-side prints within dark pools, it may signal accumulating bullish momentum ahead of a price rally.
Conversely, an increase in sell-side activity can suggest impending downward movement or profit-taking by major players. By monitoring these patterns over time—such as volume spikes or repeated large transactions—traders can gauge whether overall market sentiment leans bullish or bearish even before price action becomes apparent publicly.
Impact on Price Movements and Market Dynamics
Dark pool transactions can influence cryptocurrency prices subtly yet substantially. Since these trades are often substantial in size but not immediately visible on mainstream charts, they may cause hidden shifts that precede noticeable price changes on public exchanges.
For example:
- Large buy orders executed quietly could lead to upward price pressure once they leak into public markets.
- Conversely, significant sell-offs might be absorbed within dark pools temporarily suppressing volatility until the activity spills over publicly.
This dynamic creates a layer of complexity for technical analysts who aim to interpret true supply-demand conditions accurately. Recognizing patterns within dark pool prints helps traders anticipate potential breakouts or reversals before they manifest visibly on traditional charts.
Enhancing Risk Management Strategies
Incorporating dark pool print analysis into trading strategies enhances risk management by providing early signals about underlying market moves that are not yet reflected publicly. For instance:
- Detecting increased selling activity behind closed doors allows traders to tighten stop-loss levels.
- Spotting accumulation phases through persistent buying prints could encourage position building with controlled risk exposure.
By understanding these hidden activities alongside conventional technical indicators like moving averages and RSI (Relative Strength Index), traders develop more comprehensive views of potential trend shifts—reducing surprises caused by unanticipated large trades slipping under standard radar.
Advancements Facilitating Dark Pool Analysis
Recent technological developments have significantly improved access and interpretation of dark pool data:
- Transparency Initiatives: Some crypto exchanges now disclose more detailed information about their internal dark pools—a move driven partly by regulatory pressures aimed at increasing overall transparency.
- Analytics Tools: Sophisticated software leveraging machine learning algorithms enables analysts to sift through vast datasets efficiently—identifying meaningful patterns amid noise.
- Market Integration: As traditional financial practices merge with crypto markets, methodologies used for analyzing institutional activities are increasingly adapted for digital assets—including tracking anonymized trade flows across multiple platforms simultaneously.
These advancements empower both retail and professional traders with better tools for incorporating deep-layered insights into their decision-making processes.
Potential Risks and Ethical Considerations
While analyzing dark pool print data offers valuable advantages, it also presents certain risks:
- Market Manipulation: Large anonymous trades could be part of schemes designed intentionally to mislead other participants about true supply-demand dynamics.
- Regulatory Challenges: Increasing scrutiny from regulators aims at curbing unfair practices; stricter rules may limit access or impose restrictions on how this data is collected and used.
- Security Concerns: Sensitive trade information falling into malicious hands could facilitate insider trading or fraud if improperly secured.
Ethically speaking, using such confidential information responsibly is crucial; exploiting non-public trade details without disclosure raises questions about fairness and legality within financial markets.
Emerging Trends Shaping Future Use
The landscape surrounding dark pool print data continues evolving rapidly due to several key factors:
- Greater transparency initiatives led by regulators aim at reducing opacity while maintaining fair trading environments.
- The integration of advanced analytics tools makes it easier than ever for individual investors—and especially institutional ones—to interpret complex datasets effectively.
- Growing adoption across crypto exchanges signifies recognition that understanding behind-the-scenes activities enhances overall market integrity when managed properly.
How Traders Can Leverage Dark Pool Data Effectively
To maximize benefits from analyzing dark pool prints:
- Combine with Traditional Indicators – Use alongside volume analysis tools like OBV (On-Balance Volume) or MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence).
- Monitor Patterns Over Time – Look for consistent increases/decreases indicating sustained accumulation/distribution phases rather than one-off spikes.
- Stay Updated With Regulatory Changes – Be aware of legal frameworks affecting access rights which might impact your analytical capabilities.4.. Use Reliable Analytics Platforms – Invest in reputable software capable of processing vast datasets accurately while filtering out false signals.
Final Thoughts
Dark pool print data has become an integral component in modern technical analysis within cryptocurrency markets due to its ability to reveal hidden trader intentions behind major transactions. Its role extends beyond mere speculation; it provides critical insights into underlying sentiment shifts that precede visible price movements—a valuable advantage when navigating volatile digital asset landscapes.
As technology advances and regulatory environments evolve towards greater transparency without compromising privacy rights, the utility derived from this type of data will likely grow further — empowering informed decision-making while emphasizing responsible use aligned with ethical standards.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Report Cryptocurrency Transactions for Tax Purposes
Understanding how to properly report cryptocurrency transactions is essential for maintaining compliance with tax laws and avoiding penalties. As cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others become more mainstream, tax authorities worldwide are increasing their focus on ensuring accurate reporting of digital asset activities. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key steps, requirements, and best practices for reporting crypto transactions on your taxes.
What Are Cryptocurrency Tax Obligations?
Cryptocurrency transactions are considered taxable events in many jurisdictions. The IRS in the United States, for example, treats cryptocurrencies as property rather than currency. This means that any gains or losses from buying, selling, trading, or using cryptocurrencies must be reported on your tax return.
Gains from cryptocurrency sales are typically subject to capital gains tax—whether short-term (held less than a year) or long-term (held over a year). Profits earned through mining activities or earning crypto as income also need to be reported as ordinary income or self-employment income depending on the nature of the activity.
Failing to report these transactions can lead to penalties and interest charges. Therefore, understanding what constitutes taxable events—such as exchanges between different cryptocurrencies or converting crypto into fiat—is crucial for accurate reporting.
Key Forms Used in Crypto Tax Reporting
Different countries have specific forms designed for reporting cryptocurrency activities. In the U.S., these include:
- Form 1040: The main individual income tax form where you declare overall income.
- Schedule D: Used specifically to report capital gains and losses from cryptocurrency sales.
- Form 8949: Details each individual transaction—buying, selling, exchanging—and calculates total gains/losses.
- Form W-9: If you receive payments via crypto from exchanges or clients that classify you as an independent contractor or trader; this form helps ensure proper reporting by third parties.
When filling out these forms:
- List each transaction separately if required.
- Calculate your gain/loss per transaction based on your cost basis (purchase price plus any associated fees).
- Aggregate totals accurately before submitting.
Proper documentation is vital because it supports your calculations during audits and ensures transparency with tax authorities.
How Do You Track Cryptocurrency Transactions?
Accurate recordkeeping is fundamental when preparing taxes involving cryptocurrencies. Every buy/sell/exchange/mining activity should be documented meticulously:
- Keep records of purchase dates and prices.
- Record sale dates and proceeds received.
- Note wallet addresses used during transactions.
- Save receipts from exchanges showing transaction details.
Many investors use specialized software tools that integrate with multiple wallets and exchange accounts to automate tracking efforts — such tools can generate reports compatible with tax filing requirements.
Additionally, some countries require virtual asset service providers (VASPs) like exchanges to maintain detailed records of all user transactions under regulations such as AMLD5 in Europe or FATF guidelines globally.
International Regulations Impacting Crypto Reporting
Tax rules regarding cryptocurrencies vary significantly across borders but share common themes around transparency and anti-money laundering measures:
In Europe’s EU member states under AMLD5 directive mandates VASPs report suspicious activity logs.
Countries like Australia Canada Japan have introduced specific guidance requiring taxpayers disclose holdings periodically if they exceed certain thresholds.
International cooperation efforts aim at combating illicit use while promoting compliance; organizations such as FATF recommend standardized procedures for cross-border information sharing about virtual assets’ movement — making it increasingly important for global investors to understand local regulations affecting their crypto holdings.
Recent Developments Shaping Crypto Tax Policies
Governments worldwide continue refining their approach toward regulating digital assets:
In March 2025—a notable development—the U.S. government issued an executive order establishing a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve composed partly of seized illicit assets highlighting growing recognition at high levels about integrating cryptos into national financial strategies[1].
Meanwhile regions like the Maldives plan massive blockchain hubs offering incentives such as tax holidays aimed at attracting blockchain companies[3]. These initiatives reflect broader trends toward embracing blockchain technology while simultaneously tightening regulatory oversight concerning taxation compliance.
Challenges & Risks in Crypto Tax Compliance
Despite increased regulation efforts globally,
tax evasion remains a concern due to the pseudonymous nature of many cryptocurrencies which complicates tracking activities effectively[1].
Complexity arises because users often hold multiple wallets across various platforms making comprehensive recordkeeping difficult without dedicated tools[1].
Failure-to-report consequences include hefty fines—sometimes amounting up into thousands of dollars—and potential legal action if authorities suspect deliberate evasion[1].
Staying informed about evolving rules through official guidance sources ensures better compliance management; consulting professionals experienced in crypto taxation can help navigate complex scenarios effectively.
Tips for Accurate Crypto Transaction Reporting
To streamline your process:
- Maintain detailed logs including date-stamped screenshots
- Use reputable portfolio management software
- Regularly reconcile wallet balances against exchange statements
- Consult updated IRS guidelines—or relevant local authority instructions—to stay compliant
By adopting disciplined recordkeeping habits early on—even before filing—you reduce risks associated with misreporting errors later down the line.
Staying Ahead With Evolving Regulations
As governments adapt their policies around digital currencies amid rising adoption rates,
it’s vital that investors remain proactive:
- Follow official updates from revenue agencies
- Engage with professional accountants familiar with crypto taxation
- Use compliant accounting methods tailored specifically toward digital assets
This proactive approach not only minimizes legal risks but also positions you advantageously within this rapidly changing landscape.
By understanding how cryptocurrency transactions are taxed—and implementing proper tracking methods—you ensure full compliance while avoiding costly penalties. Staying informed about international standards further enhances your ability to navigate this complex yet rewarding space responsibly.
References
[1] Trump Considers Using Tariffs To Create Strategic Bitcoin Reserve – Perplexity AI (2025)
[2] Blockchain Moon Acquisition Corp Stock Price – Perplexity AI (2025)
[3] Maldives To Build $8.8B Blockchain Hub In Bid To Ease Debt – Perplexity AI (2025)


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-14 08:07
How do you report crypto transactions for tax purposes?
How to Report Cryptocurrency Transactions for Tax Purposes
Understanding how to properly report cryptocurrency transactions is essential for maintaining compliance with tax laws and avoiding penalties. As cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others become more mainstream, tax authorities worldwide are increasing their focus on ensuring accurate reporting of digital asset activities. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key steps, requirements, and best practices for reporting crypto transactions on your taxes.
What Are Cryptocurrency Tax Obligations?
Cryptocurrency transactions are considered taxable events in many jurisdictions. The IRS in the United States, for example, treats cryptocurrencies as property rather than currency. This means that any gains or losses from buying, selling, trading, or using cryptocurrencies must be reported on your tax return.
Gains from cryptocurrency sales are typically subject to capital gains tax—whether short-term (held less than a year) or long-term (held over a year). Profits earned through mining activities or earning crypto as income also need to be reported as ordinary income or self-employment income depending on the nature of the activity.
Failing to report these transactions can lead to penalties and interest charges. Therefore, understanding what constitutes taxable events—such as exchanges between different cryptocurrencies or converting crypto into fiat—is crucial for accurate reporting.
Key Forms Used in Crypto Tax Reporting
Different countries have specific forms designed for reporting cryptocurrency activities. In the U.S., these include:
- Form 1040: The main individual income tax form where you declare overall income.
- Schedule D: Used specifically to report capital gains and losses from cryptocurrency sales.
- Form 8949: Details each individual transaction—buying, selling, exchanging—and calculates total gains/losses.
- Form W-9: If you receive payments via crypto from exchanges or clients that classify you as an independent contractor or trader; this form helps ensure proper reporting by third parties.
When filling out these forms:
- List each transaction separately if required.
- Calculate your gain/loss per transaction based on your cost basis (purchase price plus any associated fees).
- Aggregate totals accurately before submitting.
Proper documentation is vital because it supports your calculations during audits and ensures transparency with tax authorities.
How Do You Track Cryptocurrency Transactions?
Accurate recordkeeping is fundamental when preparing taxes involving cryptocurrencies. Every buy/sell/exchange/mining activity should be documented meticulously:
- Keep records of purchase dates and prices.
- Record sale dates and proceeds received.
- Note wallet addresses used during transactions.
- Save receipts from exchanges showing transaction details.
Many investors use specialized software tools that integrate with multiple wallets and exchange accounts to automate tracking efforts — such tools can generate reports compatible with tax filing requirements.
Additionally, some countries require virtual asset service providers (VASPs) like exchanges to maintain detailed records of all user transactions under regulations such as AMLD5 in Europe or FATF guidelines globally.
International Regulations Impacting Crypto Reporting
Tax rules regarding cryptocurrencies vary significantly across borders but share common themes around transparency and anti-money laundering measures:
In Europe’s EU member states under AMLD5 directive mandates VASPs report suspicious activity logs.
Countries like Australia Canada Japan have introduced specific guidance requiring taxpayers disclose holdings periodically if they exceed certain thresholds.
International cooperation efforts aim at combating illicit use while promoting compliance; organizations such as FATF recommend standardized procedures for cross-border information sharing about virtual assets’ movement — making it increasingly important for global investors to understand local regulations affecting their crypto holdings.
Recent Developments Shaping Crypto Tax Policies
Governments worldwide continue refining their approach toward regulating digital assets:
In March 2025—a notable development—the U.S. government issued an executive order establishing a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve composed partly of seized illicit assets highlighting growing recognition at high levels about integrating cryptos into national financial strategies[1].
Meanwhile regions like the Maldives plan massive blockchain hubs offering incentives such as tax holidays aimed at attracting blockchain companies[3]. These initiatives reflect broader trends toward embracing blockchain technology while simultaneously tightening regulatory oversight concerning taxation compliance.
Challenges & Risks in Crypto Tax Compliance
Despite increased regulation efforts globally,
tax evasion remains a concern due to the pseudonymous nature of many cryptocurrencies which complicates tracking activities effectively[1].
Complexity arises because users often hold multiple wallets across various platforms making comprehensive recordkeeping difficult without dedicated tools[1].
Failure-to-report consequences include hefty fines—sometimes amounting up into thousands of dollars—and potential legal action if authorities suspect deliberate evasion[1].
Staying informed about evolving rules through official guidance sources ensures better compliance management; consulting professionals experienced in crypto taxation can help navigate complex scenarios effectively.
Tips for Accurate Crypto Transaction Reporting
To streamline your process:
- Maintain detailed logs including date-stamped screenshots
- Use reputable portfolio management software
- Regularly reconcile wallet balances against exchange statements
- Consult updated IRS guidelines—or relevant local authority instructions—to stay compliant
By adopting disciplined recordkeeping habits early on—even before filing—you reduce risks associated with misreporting errors later down the line.
Staying Ahead With Evolving Regulations
As governments adapt their policies around digital currencies amid rising adoption rates,
it’s vital that investors remain proactive:
- Follow official updates from revenue agencies
- Engage with professional accountants familiar with crypto taxation
- Use compliant accounting methods tailored specifically toward digital assets
This proactive approach not only minimizes legal risks but also positions you advantageously within this rapidly changing landscape.
By understanding how cryptocurrency transactions are taxed—and implementing proper tracking methods—you ensure full compliance while avoiding costly penalties. Staying informed about international standards further enhances your ability to navigate this complex yet rewarding space responsibly.
References
[1] Trump Considers Using Tariffs To Create Strategic Bitcoin Reserve – Perplexity AI (2025)
[2] Blockchain Moon Acquisition Corp Stock Price – Perplexity AI (2025)
[3] Maldives To Build $8.8B Blockchain Hub In Bid To Ease Debt – Perplexity AI (2025)
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Where Can You Buy or Sell the Trump-Linked USD1 Stablecoin?
Understanding where and how to buy or sell the Trump-linked USD1 stablecoin requires a clear grasp of its current market presence, trading platforms, and regulatory environment. As a relatively new digital currency associated with high-profile political figures, this stablecoin has garnered attention but remains limited in mainstream exchange listings. This article explores the key avenues for acquiring or liquidating USD1, along with considerations for investors.
The Nature of the Trump-Linked USD1 Stablecoin
The USD1 stablecoin is designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the US dollar, offering stability amid volatile crypto markets. Its association with the Trump family adds a layer of political significance that influences its acceptance and perception among traders and investors. Currently, it is primarily positioned as a settlement tool for large-scale transactions—most notably being chosen to settle MGX’s $2 billion debt—rather than as an everyday trading asset.
Availability on Cryptocurrency Exchanges
One of the primary factors determining where you can buy or sell any cryptocurrency is its listing status on exchanges. For newly launched or politically linked tokens like USD1:
Limited Exchange Listings: As of now, USD1 may not be widely available on major global exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, or Bitstamp due to regulatory concerns and limited adoption.
Specialized Platforms: Some niche or regional exchanges focusing on stablecoins or politically affiliated cryptocurrencies might list USD1 temporarily. These platforms often cater to institutional clients or specific investor groups interested in unique assets.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): If an ERC-20 token version exists (common for many stablecoins), it could potentially be traded on decentralized platforms like Uniswap or SushiSwap. However, this depends heavily on whether developers have made such versions available publicly.
How to Find Trading Opportunities
Given its niche status:
Research Official Announcements: Keep track of official statements from entities involved in issuing USD1—such as any affiliated companies—or from credible crypto news sources reporting listings.
Use Cryptocurrency Data Aggregators: Platforms like CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko provide information about token availability across various exchanges if listed publicly.
Join Community Forums & Social Media Groups: Crypto communities often share updates about new listings and trading opportunities related to emerging tokens like USD1.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading Options
For high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors seeking large volumes:
OTC Desks: Many specialized OTC desks facilitate private trades involving unique tokens that are not yet broadly listed on public exchanges.
Direct Negotiations: Sometimes direct negotiations with holders or issuers are necessary if liquidity pools are thin; this approach requires careful due diligence regarding counterparty credibility.
Regulatory Considerations When Buying & Selling
Since stablecoins linked directly to political figures can attract regulatory scrutiny:
Ensure compliance with local laws governing cryptocurrency transactions.
Verify whether your jurisdiction permits trading in politically associated digital assets without restrictions.
Be aware that some platforms may restrict access based on regional regulations concerning certain types of cryptocurrencies.
Risks Associated With Limited Liquidity & Market Access
Limited availability means higher spreads between bid and ask prices when buying/selling via less liquid channels. This can lead to increased transaction costs compared to more established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or USDT (Tether). Additionally:
Liquidity constraints could result in slippage during large trades—a critical factor for institutional players considering significant transactions involving USD1.
Summary: Best Practices for Trading the Trump-Liked Stablecoin
To effectively buy or sell the USD1 stablecoin:
For Retail Investors:
- Monitor reputable data aggregators for potential exchange listings.
- Engage through trusted OTC brokers if dealing with substantial amounts.
- Stay informed via official channels regarding platform support and legal considerations.
For Institutional Traders:
- Establish relationships with OTC desks experienced in niche tokens.
- Conduct thorough due diligence before executing large trades privately.
- Keep abreast of regulatory developments affecting politically linked cryptocurrencies.
Final Thoughts
While currently limited in mainstream accessibility, opportunities exist through specialized platforms such as OTC services and select regional exchanges catering specifically to unique digital assets likeUSD₁ . As awareness grows around this coin's role within geopolitical financial strategies—and given ongoing developments such as blockchain projects in Maldives—the liquidity landscape may evolve further. Staying informed through credible sources ensures you’re prepared when more trading venues open up for this distinctive stablecoin.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-11 10:10
Where can you buy or sell this coin easily?
Where Can You Buy or Sell the Trump-Linked USD1 Stablecoin?
Understanding where and how to buy or sell the Trump-linked USD1 stablecoin requires a clear grasp of its current market presence, trading platforms, and regulatory environment. As a relatively new digital currency associated with high-profile political figures, this stablecoin has garnered attention but remains limited in mainstream exchange listings. This article explores the key avenues for acquiring or liquidating USD1, along with considerations for investors.
The Nature of the Trump-Linked USD1 Stablecoin
The USD1 stablecoin is designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the US dollar, offering stability amid volatile crypto markets. Its association with the Trump family adds a layer of political significance that influences its acceptance and perception among traders and investors. Currently, it is primarily positioned as a settlement tool for large-scale transactions—most notably being chosen to settle MGX’s $2 billion debt—rather than as an everyday trading asset.
Availability on Cryptocurrency Exchanges
One of the primary factors determining where you can buy or sell any cryptocurrency is its listing status on exchanges. For newly launched or politically linked tokens like USD1:
Limited Exchange Listings: As of now, USD1 may not be widely available on major global exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, or Bitstamp due to regulatory concerns and limited adoption.
Specialized Platforms: Some niche or regional exchanges focusing on stablecoins or politically affiliated cryptocurrencies might list USD1 temporarily. These platforms often cater to institutional clients or specific investor groups interested in unique assets.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): If an ERC-20 token version exists (common for many stablecoins), it could potentially be traded on decentralized platforms like Uniswap or SushiSwap. However, this depends heavily on whether developers have made such versions available publicly.
How to Find Trading Opportunities
Given its niche status:
Research Official Announcements: Keep track of official statements from entities involved in issuing USD1—such as any affiliated companies—or from credible crypto news sources reporting listings.
Use Cryptocurrency Data Aggregators: Platforms like CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko provide information about token availability across various exchanges if listed publicly.
Join Community Forums & Social Media Groups: Crypto communities often share updates about new listings and trading opportunities related to emerging tokens like USD1.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading Options
For high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors seeking large volumes:
OTC Desks: Many specialized OTC desks facilitate private trades involving unique tokens that are not yet broadly listed on public exchanges.
Direct Negotiations: Sometimes direct negotiations with holders or issuers are necessary if liquidity pools are thin; this approach requires careful due diligence regarding counterparty credibility.
Regulatory Considerations When Buying & Selling
Since stablecoins linked directly to political figures can attract regulatory scrutiny:
Ensure compliance with local laws governing cryptocurrency transactions.
Verify whether your jurisdiction permits trading in politically associated digital assets without restrictions.
Be aware that some platforms may restrict access based on regional regulations concerning certain types of cryptocurrencies.
Risks Associated With Limited Liquidity & Market Access
Limited availability means higher spreads between bid and ask prices when buying/selling via less liquid channels. This can lead to increased transaction costs compared to more established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or USDT (Tether). Additionally:
Liquidity constraints could result in slippage during large trades—a critical factor for institutional players considering significant transactions involving USD1.
Summary: Best Practices for Trading the Trump-Liked Stablecoin
To effectively buy or sell the USD1 stablecoin:
For Retail Investors:
- Monitor reputable data aggregators for potential exchange listings.
- Engage through trusted OTC brokers if dealing with substantial amounts.
- Stay informed via official channels regarding platform support and legal considerations.
For Institutional Traders:
- Establish relationships with OTC desks experienced in niche tokens.
- Conduct thorough due diligence before executing large trades privately.
- Keep abreast of regulatory developments affecting politically linked cryptocurrencies.
Final Thoughts
While currently limited in mainstream accessibility, opportunities exist through specialized platforms such as OTC services and select regional exchanges catering specifically to unique digital assets likeUSD₁ . As awareness grows around this coin's role within geopolitical financial strategies—and given ongoing developments such as blockchain projects in Maldives—the liquidity landscape may evolve further. Staying informed through credible sources ensures you’re prepared when more trading venues open up for this distinctive stablecoin.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Blockchain Oracle Network and How Is Decentralization Ensured?
Understanding Blockchain Oracle Networks
A blockchain oracle network is a vital infrastructure component that connects smart contracts with external data sources. In the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automatically trigger actions based on predefined conditions. However, these contracts cannot inherently access real-world information such as weather data, stock prices, or sports results. This is where blockchain oracle networks come into play—they serve as bridges that securely fetch and deliver external data to smart contracts.
The core function of an oracle network is to provide accurate, reliable, and tamper-proof data inputs for blockchain applications. Without oracles, the potential of smart contracts would be limited to on-chain information only—rendering many DeFi applications impractical or impossible. For example, decentralized insurance platforms rely heavily on real-world event verification; without trustworthy oracles delivering this data, claims processing could become unreliable.
How Do Blockchain Oracles Work?
The operation of a blockchain oracle network involves several key steps:
- Data Collection: External sources such as APIs from financial markets, sensors in IoT devices, or public databases gather relevant information.
- Relay Nodes: These nodes act as intermediaries that transmit collected data into the oracle network.
- Verification Process: Multiple nodes verify the accuracy and integrity of incoming data through consensus mechanisms.
- Feeding Data into Smart Contracts: Once verified, the trusted data is fed into specific smart contracts on the blockchain platform for execution.
This process ensures that only validated information influences contract outcomes—an essential feature for maintaining trustworthiness in decentralized systems.
Ensuring Decentralization in Oracle Networks
Decentralization remains at the heart of blockchain technology’s appeal because it reduces reliance on single points of failure and mitigates risks associated with centralized control. Achieving decentralization within oracle networks involves several strategies:
Distributed Architecture: Instead of relying on a single node or entity to provide external data, multiple independent nodes participate in collecting and verifying information. This distribution prevents any one party from manipulating outcomes.
Consensus Mechanisms: Protocols like proof-of-stake (PoS) or proof-of-work (PoW) are employed among relay nodes to agree upon which data should be accepted by smart contracts. These mechanisms ensure collective validation rather than trusting individual sources blindly.
Multi-Signature Security: Some networks implement multi-signature wallets requiring multiple signatures before feeding data into a contract—adding an extra layer of security against malicious actors.
Open-Source Development: Many oracle solutions operate under open-source licenses allowing community audits and contributions—further enhancing transparency and decentralization by enabling continuous security improvements.
Recent Innovations in Blockchain Oracles
Over recent years, notable developments have advanced how decentralized oracles operate across different blockchains:
In 2020, Chainlink emerged as one of the most prominent players by introducing its hybrid model combining both off-chain (external API calls) and on-chain components to improve reliability while maintaining decentralization standards.
The following year saw Polkadot launching its own dedicated oracle solution designed for interoperability between various blockchains—a crucial step toward seamless cross-chain communication essential for complex DeFi ecosystems.
Cosmos joined this movement in 2022 by developing its own robust decentralized oracle service utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithms aimed at fostering secure inter-blockchain communication within its ecosystem.
Despite these advancements’ benefits—such as increased accuracy and interoperability—the space has also faced challenges related to security vulnerabilities exposed through attacks targeting certain protocols’ codebases.
Security Concerns & Risks
While blockchain oracles enable powerful functionalities within DeFi platforms—and beyond—they introduce unique security considerations:
External Data Manipulation: Malicious actors may attempt to feed false information if not properly verified.
Hacking Attacks: Vulnerabilities within relay nodes’ code can be exploited leading to compromised datasets; recent incidents have resulted in significant financial losses during 2023 due to such breaches.
These risks underscore why continuous security audits are critical alongside implementing multi-layered verification processes—a necessity reinforced by ongoing research into resilient consensus algorithms tailored specifically for decentralized oracles.
Potential Challenges Facing Oracle Networks
As demand grows for real-time accurate external data across diverse applications—from gaming platforms to supply chain management—the scalability limitations become apparent:
- Increased latency can delay transaction execution
- Higher throughput requirements strain existing infrastructure
- Maintaining trustworthiness amid rapid updates demands sophisticated validation techniques
Addressing these issues requires ongoing innovation around protocol design—including off-chain computation solutions—and collaborative efforts among developers worldwide aiming at creating more resilient architectures capable of handling future growth efficiently.
The Role Of Blockchain Oracles In Decentralized Ecosystems
Blockchain oracle networks underpin many innovative use cases beyond simple financial transactions—they enable complex interactions involving real-world events seamlessly integrated with digital assets:
Decentralized Insurance: Claims processing based on verified weather reportsPrediction Markets: Accurate event outcome reportingSupply Chain Management: Authenticity verification via sensor-based tracking
By providing trustworthy external inputs while preserving decentralization principles through distributed architecture models—which prevent single points of failure—these networks foster greater trustworthiness across entire ecosystems.
Future Outlook And Industry Trends
Looking ahead from 2024 onward,the importance of secure , scalable ,and interoperableoracle solutions will intensify given their central role in expanding DeFi capabilities globally . Emerging trends include:
- Adoption of cross-chain compatible protocols facilitating broader interoperability
- Enhanced focus on cybersecurity measures including formal verification methods
- Integration with AI-driven analytics for smarter decision-making
Moreover,the evolution toward fully autonomous “oracle-as-a-service” models promises simplified deployment coupled with improved resilience against attacks—all contributing towards more robust decentralized applications.
Building Trust Through Transparency And Security Standards
Maintaining user confidence hinges upon rigorous transparency practices:
- Open-source codebases allow community review
- Regular third-party audits identify vulnerabilities proactively
- Clear governance frameworks define responsibility sharing
Such measures align with industry best practices aimed at reinforcing trustworthiness—a critical factor given increasing regulatory scrutiny over DeFi operations.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain oracle networks stand at a pivotal intersection where technological innovation meets fundamental principles like decentralization and security . As they continue evolving amidst emerging threats—and opportunities—they will remain indispensable tools powering next-generation decentralized applications across finance,supply chains,and beyond . Ensuring their robustness through transparent development practices will be key drivers shaping their future trajectory.
Keywords: Blockchain Oracle Network | Decentralized Data Feeds | Smart Contract Integration | Cross-chain Compatibility | Security Audits | Open-source Protocols


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 18:08
What is a blockchain oracle network and how is decentralization ensured?
What Is a Blockchain Oracle Network and How Is Decentralization Ensured?
Understanding Blockchain Oracle Networks
A blockchain oracle network is a vital infrastructure component that connects smart contracts with external data sources. In the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automatically trigger actions based on predefined conditions. However, these contracts cannot inherently access real-world information such as weather data, stock prices, or sports results. This is where blockchain oracle networks come into play—they serve as bridges that securely fetch and deliver external data to smart contracts.
The core function of an oracle network is to provide accurate, reliable, and tamper-proof data inputs for blockchain applications. Without oracles, the potential of smart contracts would be limited to on-chain information only—rendering many DeFi applications impractical or impossible. For example, decentralized insurance platforms rely heavily on real-world event verification; without trustworthy oracles delivering this data, claims processing could become unreliable.
How Do Blockchain Oracles Work?
The operation of a blockchain oracle network involves several key steps:
- Data Collection: External sources such as APIs from financial markets, sensors in IoT devices, or public databases gather relevant information.
- Relay Nodes: These nodes act as intermediaries that transmit collected data into the oracle network.
- Verification Process: Multiple nodes verify the accuracy and integrity of incoming data through consensus mechanisms.
- Feeding Data into Smart Contracts: Once verified, the trusted data is fed into specific smart contracts on the blockchain platform for execution.
This process ensures that only validated information influences contract outcomes—an essential feature for maintaining trustworthiness in decentralized systems.
Ensuring Decentralization in Oracle Networks
Decentralization remains at the heart of blockchain technology’s appeal because it reduces reliance on single points of failure and mitigates risks associated with centralized control. Achieving decentralization within oracle networks involves several strategies:
Distributed Architecture: Instead of relying on a single node or entity to provide external data, multiple independent nodes participate in collecting and verifying information. This distribution prevents any one party from manipulating outcomes.
Consensus Mechanisms: Protocols like proof-of-stake (PoS) or proof-of-work (PoW) are employed among relay nodes to agree upon which data should be accepted by smart contracts. These mechanisms ensure collective validation rather than trusting individual sources blindly.
Multi-Signature Security: Some networks implement multi-signature wallets requiring multiple signatures before feeding data into a contract—adding an extra layer of security against malicious actors.
Open-Source Development: Many oracle solutions operate under open-source licenses allowing community audits and contributions—further enhancing transparency and decentralization by enabling continuous security improvements.
Recent Innovations in Blockchain Oracles
Over recent years, notable developments have advanced how decentralized oracles operate across different blockchains:
In 2020, Chainlink emerged as one of the most prominent players by introducing its hybrid model combining both off-chain (external API calls) and on-chain components to improve reliability while maintaining decentralization standards.
The following year saw Polkadot launching its own dedicated oracle solution designed for interoperability between various blockchains—a crucial step toward seamless cross-chain communication essential for complex DeFi ecosystems.
Cosmos joined this movement in 2022 by developing its own robust decentralized oracle service utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithms aimed at fostering secure inter-blockchain communication within its ecosystem.
Despite these advancements’ benefits—such as increased accuracy and interoperability—the space has also faced challenges related to security vulnerabilities exposed through attacks targeting certain protocols’ codebases.
Security Concerns & Risks
While blockchain oracles enable powerful functionalities within DeFi platforms—and beyond—they introduce unique security considerations:
External Data Manipulation: Malicious actors may attempt to feed false information if not properly verified.
Hacking Attacks: Vulnerabilities within relay nodes’ code can be exploited leading to compromised datasets; recent incidents have resulted in significant financial losses during 2023 due to such breaches.
These risks underscore why continuous security audits are critical alongside implementing multi-layered verification processes—a necessity reinforced by ongoing research into resilient consensus algorithms tailored specifically for decentralized oracles.
Potential Challenges Facing Oracle Networks
As demand grows for real-time accurate external data across diverse applications—from gaming platforms to supply chain management—the scalability limitations become apparent:
- Increased latency can delay transaction execution
- Higher throughput requirements strain existing infrastructure
- Maintaining trustworthiness amid rapid updates demands sophisticated validation techniques
Addressing these issues requires ongoing innovation around protocol design—including off-chain computation solutions—and collaborative efforts among developers worldwide aiming at creating more resilient architectures capable of handling future growth efficiently.
The Role Of Blockchain Oracles In Decentralized Ecosystems
Blockchain oracle networks underpin many innovative use cases beyond simple financial transactions—they enable complex interactions involving real-world events seamlessly integrated with digital assets:
Decentralized Insurance: Claims processing based on verified weather reportsPrediction Markets: Accurate event outcome reportingSupply Chain Management: Authenticity verification via sensor-based tracking
By providing trustworthy external inputs while preserving decentralization principles through distributed architecture models—which prevent single points of failure—these networks foster greater trustworthiness across entire ecosystems.
Future Outlook And Industry Trends
Looking ahead from 2024 onward,the importance of secure , scalable ,and interoperableoracle solutions will intensify given their central role in expanding DeFi capabilities globally . Emerging trends include:
- Adoption of cross-chain compatible protocols facilitating broader interoperability
- Enhanced focus on cybersecurity measures including formal verification methods
- Integration with AI-driven analytics for smarter decision-making
Moreover,the evolution toward fully autonomous “oracle-as-a-service” models promises simplified deployment coupled with improved resilience against attacks—all contributing towards more robust decentralized applications.
Building Trust Through Transparency And Security Standards
Maintaining user confidence hinges upon rigorous transparency practices:
- Open-source codebases allow community review
- Regular third-party audits identify vulnerabilities proactively
- Clear governance frameworks define responsibility sharing
Such measures align with industry best practices aimed at reinforcing trustworthiness—a critical factor given increasing regulatory scrutiny over DeFi operations.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain oracle networks stand at a pivotal intersection where technological innovation meets fundamental principles like decentralization and security . As they continue evolving amidst emerging threats—and opportunities—they will remain indispensable tools powering next-generation decentralized applications across finance,supply chains,and beyond . Ensuring their robustness through transparent development practices will be key drivers shaping their future trajectory.
Keywords: Blockchain Oracle Network | Decentralized Data Feeds | Smart Contract Integration | Cross-chain Compatibility | Security Audits | Open-source Protocols
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📅 August 6 2025
🎉 Stay updated with the latest crypto market trends!
👉 Trade on:https://bit.ly/3DFYq30
👉 X:https://twitter.com/Jucoinex
👉 APP download: https://www.jucoin.com/en/community-downloads
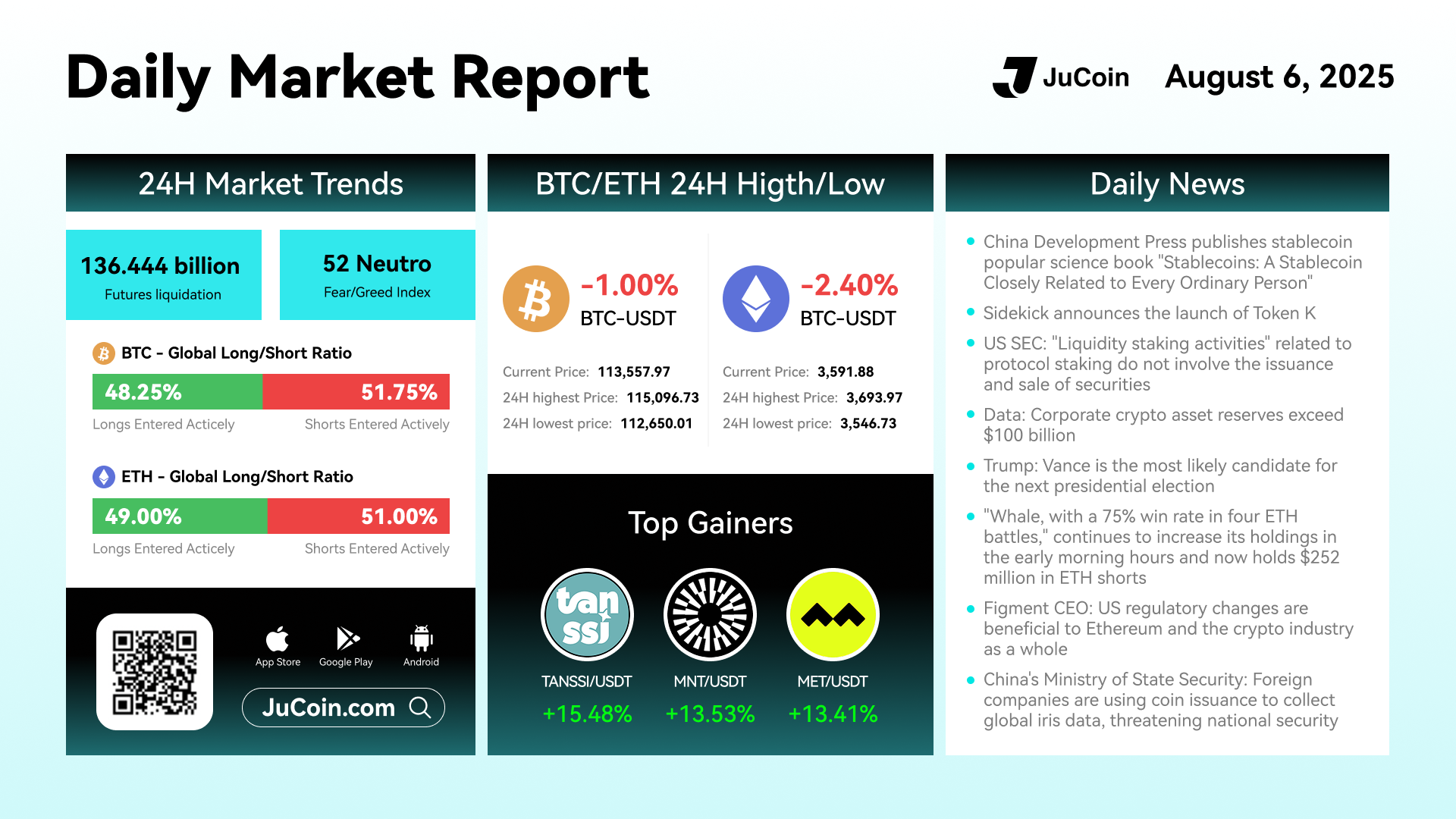


JuCoin Community
2025-08-06 04:51
#JuCoin Daily Market Report
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
👌JuCoin will list the CMEW/USDT trading pair on August 7, 2025
🔹 Deposit: August 6, 2025 at 04:00 (UTC)
🔹 Trading: August 7, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
🔹 Withdrawal: August 8, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
🪧More:https://bit.ly/458FkfG



JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 07:45
📢 New Listing|CMEW (CelestialMew) 🔥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Bitcoin Investment — every time she walks by, even the ETH crowd turns their heads 🫣 Main character energy in the crypto streets 🧿 She’s the MVP of the blockchain
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BitcoinInvestment #MainCharacterVibes #CryptoAttraction


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:21
How a Bitcoin Investment Steals the Show Every Time ✨
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
