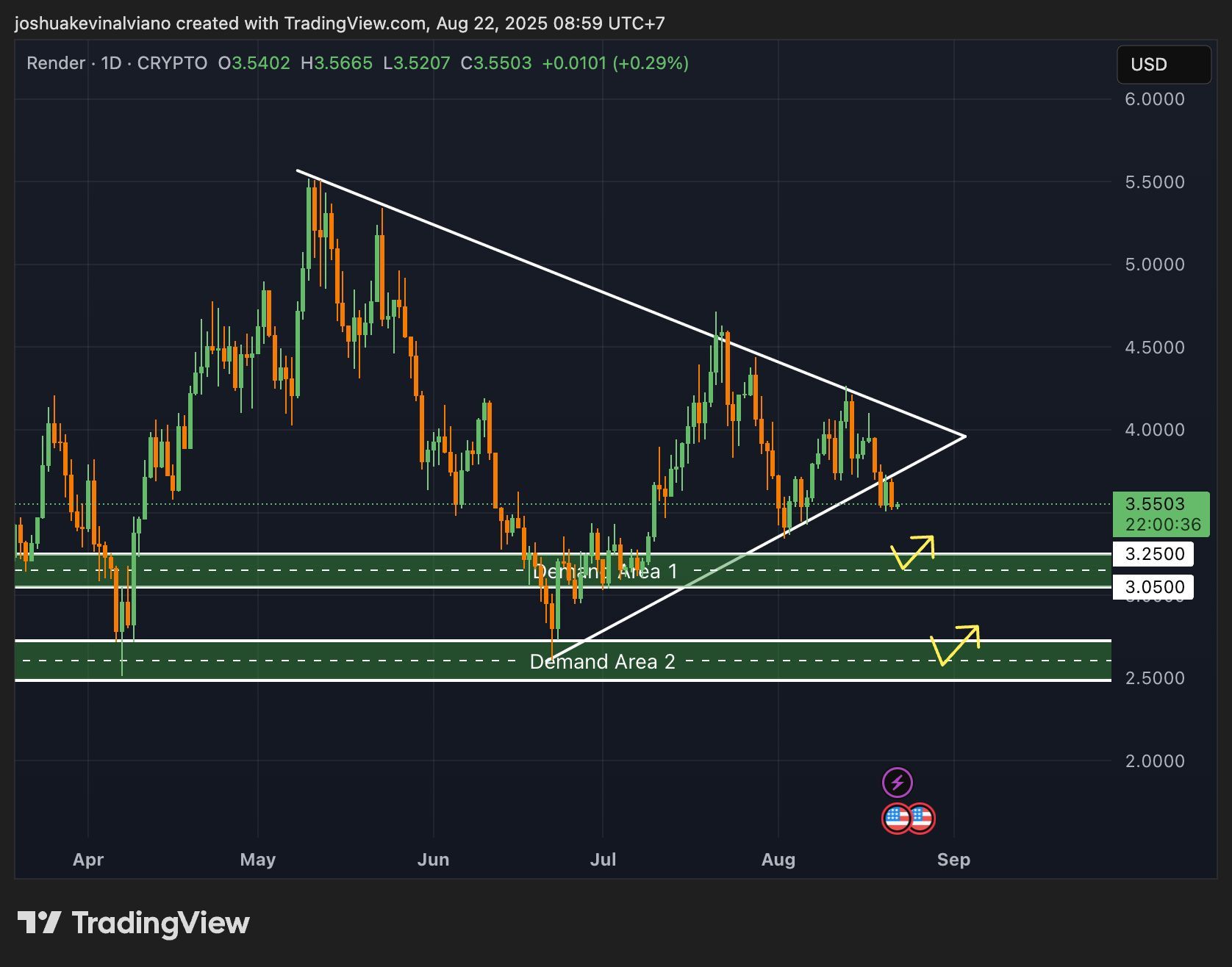
#Render glisse sous sa structure en triangle et approche la zone de demande $3.05–$3.25.
📊 Scénarios à surveiller : ✅ Si ça tient → possible rebond court terme vers $4.00+ 🚀 ❌ Si ça casse → chute probable vers la zone $2.50–$2.70 ⚠️
👉 Selon vous, $RNDR prépare un rebond solide ou une plongée plus profonde ?
#RNDR #AI #CryptoMarkets


Carmelita
2025-08-22 11:50
$RNDR en zone critique : rebond ou cassure ?
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are the Components of a Company’s Balance Sheet?
Understanding the components of a company's balance sheet is essential for investors, creditors, and financial analysts aiming to assess a firm's financial health. The balance sheet offers a snapshot of what the company owns and owes at a specific point in time, along with the residual interest belonging to shareholders. This article provides an in-depth look at each component, explaining their significance and recent developments that influence how these elements are viewed.
Assets: The Resources Owned by the Company
Assets form one of the core sections of a balance sheet and represent everything that a company owns or controls which has economic value. They are typically divided into current assets and non-current assets based on their liquidity.
Current Assets
Current assets are short-term resources expected to be converted into cash or used within one year. These include cash itself, accounts receivable (money owed by customers), inventory (goods ready for sale), and other liquid assets like marketable securities. Managing current assets effectively is crucial because they directly impact liquidity — the company's ability to meet its immediate obligations.
Non-Current Assets
Non-current assets, also known as long-term assets, include investments that are held over longer periods such as property, plant, equipment (PP&E), intangible assets like patents or trademarks, and long-term investments. These resources support ongoing operations and growth strategies but may not be easily converted into cash in the short term.
Recent developments show companies like State Street Corporation holding significant cash reserves—$20 billion as reported in May 2025—highlighting their focus on liquidity management amid evolving market conditions.
Liabilities: The Obligations Owed by the Company
Liabilities represent what a company owes to external parties such as lenders or suppliers. They are classified into current liabilities due within one year and non-current liabilities due after more than one year.
Current Liabilities
These include accounts payable (amounts owed to suppliers), short-term loans or credit lines, taxes payable, wages payable—and other debts that need settling soon. Effective management ensures that companies can meet these obligations without jeopardizing operational stability.
Non-Current Liabilities
Long-term debts such as bonds payable, mortgages on property holdings, pension obligations for employees—and other deferred payments—are categorized here. For example, Forestar Group Inc., strengthened its financial position through refinancing deals extending debt maturity profiles in early 2025—a strategic move aimed at reducing repayment pressures over time.
Equity: The Shareholders’ Ownership Stake
Equity reflects what remains after subtracting total liabilities from total assets; it essentially shows shareholders' ownership stake in the company. It comprises several key components:
- Common Stock: Represents capital raised through issuing shares publicly or privately.
- Retained Earnings: Profits reinvested back into business operations rather than distributed as dividends.
- Preferred Stock: A class of ownership with priority over common stock regarding dividends and asset claims during liquidation events; often used by firms seeking additional financing flexibility.
The level of equity indicates how much value shareholders have accumulated through retained earnings plus any additional paid-in capital from share issuance activities.
Recent Trends Impacting Balance Sheet Components
Recent corporate reports reveal shifts affecting balance sheets across industries:
State Street Corporation reported revenues exceeding $5 billion with net income around $500 million in May 2025 while maintaining substantial cash reserves ($20 billion). Such figures underscore strong liquidity positions vital during volatile markets.
Forestar Group Inc., focused on strengthening its financial foundation via debt refinancing strategies aimed at extending debt maturities—an approach designed to reduce near-term repayment risks while supporting future growth initiatives.
While some companies like XPEL Inc., have not disclosed detailed recent changes related specifically to their balance sheets publicly yet—but overall trends suggest an increased emphasis on liquidity management amidst economic uncertainties globally.
Why Understanding Balance Sheet Components Matters
A comprehensive grasp of each component helps stakeholders evaluate whether a firm has sufficient resources (assets) relative to its obligations (liabilities) while understanding shareholder value creation through equity accumulation. Changes within these components often signal underlying operational strengths or weaknesses—for instance:
Rising debt levels might indicate aggressive expansion but could also increase default risk if not managed properly.
Growing asset bases coupled with stable liabilities generally reflect healthy growth prospects.
In today’s dynamic economic environment—with fluctuating interest rates and evolving regulatory landscapes—it becomes even more critical for investors to analyze recent developments impacting these components carefully before making decisions.
How Changes Affect Financial Health
Alterations within any part of the balance sheet can significantly influence overall financial stability:
- Increased Debt Levels: While leveraging can boost growth potential temporarily; excessive borrowing raises default risks if revenue streams falter.
- Declining Cash Reserves: Insufficient liquidity hampers day-to-day operations leading potentially toward insolvency if not addressed promptly.
- Asset Quality Deterioration: Obsolete inventory or declining property values diminish earning capacity—a warning sign requiring deeper investigation.
By monitoring these indicators alongside industry trends—as seen with firms like State Street Corporation managing large cash reserves—it becomes possible for stakeholders to anticipate potential issues early enough for strategic adjustments.
Final Thoughts on Balance Sheet Components
A well-maintained balance sheet reflects sound financial management practices essential for sustainable business success. Recognizing how each component interacts provides valuable insights into operational efficiency—and understanding recent corporate actions reveals how firms adapt their strategies amidst changing economic conditions . Whether assessing short-term liquidity needs or long-term investment viability , analyzing these fundamental elements equips stakeholders with critical information necessary for informed decision-making.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 10:21
What are the components of a company’s balance sheet?
What Are the Components of a Company’s Balance Sheet?
Understanding the components of a company's balance sheet is essential for investors, creditors, and financial analysts aiming to assess a firm's financial health. The balance sheet offers a snapshot of what the company owns and owes at a specific point in time, along with the residual interest belonging to shareholders. This article provides an in-depth look at each component, explaining their significance and recent developments that influence how these elements are viewed.
Assets: The Resources Owned by the Company
Assets form one of the core sections of a balance sheet and represent everything that a company owns or controls which has economic value. They are typically divided into current assets and non-current assets based on their liquidity.
Current Assets
Current assets are short-term resources expected to be converted into cash or used within one year. These include cash itself, accounts receivable (money owed by customers), inventory (goods ready for sale), and other liquid assets like marketable securities. Managing current assets effectively is crucial because they directly impact liquidity — the company's ability to meet its immediate obligations.
Non-Current Assets
Non-current assets, also known as long-term assets, include investments that are held over longer periods such as property, plant, equipment (PP&E), intangible assets like patents or trademarks, and long-term investments. These resources support ongoing operations and growth strategies but may not be easily converted into cash in the short term.
Recent developments show companies like State Street Corporation holding significant cash reserves—$20 billion as reported in May 2025—highlighting their focus on liquidity management amid evolving market conditions.
Liabilities: The Obligations Owed by the Company
Liabilities represent what a company owes to external parties such as lenders or suppliers. They are classified into current liabilities due within one year and non-current liabilities due after more than one year.
Current Liabilities
These include accounts payable (amounts owed to suppliers), short-term loans or credit lines, taxes payable, wages payable—and other debts that need settling soon. Effective management ensures that companies can meet these obligations without jeopardizing operational stability.
Non-Current Liabilities
Long-term debts such as bonds payable, mortgages on property holdings, pension obligations for employees—and other deferred payments—are categorized here. For example, Forestar Group Inc., strengthened its financial position through refinancing deals extending debt maturity profiles in early 2025—a strategic move aimed at reducing repayment pressures over time.
Equity: The Shareholders’ Ownership Stake
Equity reflects what remains after subtracting total liabilities from total assets; it essentially shows shareholders' ownership stake in the company. It comprises several key components:
- Common Stock: Represents capital raised through issuing shares publicly or privately.
- Retained Earnings: Profits reinvested back into business operations rather than distributed as dividends.
- Preferred Stock: A class of ownership with priority over common stock regarding dividends and asset claims during liquidation events; often used by firms seeking additional financing flexibility.
The level of equity indicates how much value shareholders have accumulated through retained earnings plus any additional paid-in capital from share issuance activities.
Recent Trends Impacting Balance Sheet Components
Recent corporate reports reveal shifts affecting balance sheets across industries:
State Street Corporation reported revenues exceeding $5 billion with net income around $500 million in May 2025 while maintaining substantial cash reserves ($20 billion). Such figures underscore strong liquidity positions vital during volatile markets.
Forestar Group Inc., focused on strengthening its financial foundation via debt refinancing strategies aimed at extending debt maturities—an approach designed to reduce near-term repayment risks while supporting future growth initiatives.
While some companies like XPEL Inc., have not disclosed detailed recent changes related specifically to their balance sheets publicly yet—but overall trends suggest an increased emphasis on liquidity management amidst economic uncertainties globally.
Why Understanding Balance Sheet Components Matters
A comprehensive grasp of each component helps stakeholders evaluate whether a firm has sufficient resources (assets) relative to its obligations (liabilities) while understanding shareholder value creation through equity accumulation. Changes within these components often signal underlying operational strengths or weaknesses—for instance:
Rising debt levels might indicate aggressive expansion but could also increase default risk if not managed properly.
Growing asset bases coupled with stable liabilities generally reflect healthy growth prospects.
In today’s dynamic economic environment—with fluctuating interest rates and evolving regulatory landscapes—it becomes even more critical for investors to analyze recent developments impacting these components carefully before making decisions.
How Changes Affect Financial Health
Alterations within any part of the balance sheet can significantly influence overall financial stability:
- Increased Debt Levels: While leveraging can boost growth potential temporarily; excessive borrowing raises default risks if revenue streams falter.
- Declining Cash Reserves: Insufficient liquidity hampers day-to-day operations leading potentially toward insolvency if not addressed promptly.
- Asset Quality Deterioration: Obsolete inventory or declining property values diminish earning capacity—a warning sign requiring deeper investigation.
By monitoring these indicators alongside industry trends—as seen with firms like State Street Corporation managing large cash reserves—it becomes possible for stakeholders to anticipate potential issues early enough for strategic adjustments.
Final Thoughts on Balance Sheet Components
A well-maintained balance sheet reflects sound financial management practices essential for sustainable business success. Recognizing how each component interacts provides valuable insights into operational efficiency—and understanding recent corporate actions reveals how firms adapt their strategies amidst changing economic conditions . Whether assessing short-term liquidity needs or long-term investment viability , analyzing these fundamental elements equips stakeholders with critical information necessary for informed decision-making.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Options Greeks Chart: A Complete Guide for Traders and Investors
What Is an Options Greeks Chart?
An options Greeks chart is a vital analytical tool used by traders and investors to understand how various factors influence the price of options. It visually represents key metrics—Delta, Gamma, Theta, and Vega—that measure an option’s sensitivity to underlying asset movements, time decay, and volatility changes. These metrics help traders assess risk exposure, optimize trading strategies, and make informed decisions in both traditional markets like stocks or commodities and emerging sectors such as cryptocurrencies.
The chart consolidates complex mathematical data into an accessible format that allows users to quickly gauge how different market conditions might impact their options positions. By analyzing these sensitivities collectively on a single chart, traders can better anticipate potential profit or loss scenarios under varying circumstances.
The Four Main Components of Options Greeks
Understanding each component of the options Greeks is essential for effective trading:
Delta: This measures how much the price of an option will change with a $1 move in the underlying asset. For example, a Delta of 0.5 indicates that if the stock increases by $1, the option's price will increase by approximately $0.50. Delta also provides insight into whether an option behaves more like a stock (high Delta) or less (low Delta).
Gamma: Gamma indicates how much Delta will change when the underlying asset's price moves by one dollar. It reflects the curvature in the relationship between option prices and underlying prices—higher Gamma means greater sensitivity to small movements in asset prices.
Theta: Often called time decay, Theta quantifies how much value an option loses each day as expiration approaches if all other factors remain constant. For instance, a Theta of -0.05 suggests that daily time decay reduces the option’s value by five cents per day.
Vega: This measures sensitivity to volatility changes; specifically, it shows how much an option's premium will fluctuate with a 1% change in implied volatility of the underlying asset.
These components work together within an options Greeks chart to provide comprehensive insights into potential risks and rewards associated with specific trades.
Why Are Options Greeks Important for Traders?
Options trading involves managing multiple variables simultaneously; therefore understanding these sensitivities is crucial for risk management and strategic planning:
- They enable traders to predict how market movements affect their positions.
- Help determine optimal entry and exit points based on expected changes in volatility or time.
- Facilitate hedging strategies—adjusting portfolios against adverse market shifts.
For example, if you hold long calls with high Delta but low Gamma exposure during volatile periods (like earnings reports), you might want to adjust your position because sudden large moves could significantly impact your profits or losses.
Moreover, institutional investors rely heavily on these metrics for portfolio risk assessment while individual traders use them for tactical decision-making—especially when employing advanced strategies such as spreads or straddles.
Historical Development of Options Greeks
The concept originated during decades when financial mathematicians sought more precise models for pricing derivatives beyond simple formulas like Black-Scholes (1973). In particular:
During 1970s–1980s: Researchers developed sophisticated models incorporating multiple variables influencing options prices.
In 1990s: Emanuel Derman and Nassim Nicholas Taleb popularized terminology—the "Greeks"—to describe these sensitivities systematically.
This evolution allowed both institutional players and retail investors access to tools previously limited due to complexity but now integral across markets worldwide—including equities—and increasingly applied within cryptocurrency derivatives markets where high volatility amplifies importance.
Modern Applications & Recent Trends
In recent years:
Expansion into Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have introduced new opportunities—and challenges—for applying traditional options analysis due to their extreme volatility levels. Traders now utilize Greek-based models tailored specifically toward digital assets’ unique behavior patterns—a development driven partly by increasing institutional interest seeking hedging solutions against crypto exposure.
Advanced Trading Platforms
Modern software offers real-time analytics on Greek values enabling dynamic adjustments during trading sessions rather than static assessments at trade initiation—a significant advantage amid fast-moving markets like crypto exchanges or volatile equity sectors.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory bodies worldwide are scrutinizing derivatives activities more closely; transparency requirements are increasing which benefits informed trading based on solid Greek analysis while discouraging overly risky leverage practices that could lead to systemic issues if misused.
Risks Associated With Using Options Greeks
While powerful tools:
- Over-reliance can lead traders astray—particularly if they ignore broader market signals.
- High leverage combined with misjudged Greek values may amplify losses rapidly.
- Rapid shifts typical in cryptocurrency markets can cause sudden swings in Greek metrics making real-time monitoring essential but challenging.
Therefore understanding limitations alongside benefits ensures prudent application aligned with sound risk management principles.
Key Dates Shaping Understanding of Options Sensitivities
Tracking historical milestones helps contextualize current practices:
- 1970s–1980s: Development of foundational models like Black-Scholes laid groundwork for calculating initial "Greeks."
- 1990s: Formal naming ("Greeks") brought clarity; expanded understanding among practitioners globally.
- 2010s: Adoption within cryptocurrency derivatives increased awareness about adapting classical models beyond traditional assets.
- 2020s: Integration into advanced platforms enables seamless real-time analysis supporting complex multi-leg strategies across diverse markets.
This timeline underscores ongoing innovation driven by technological advances coupled with evolving financial landscapes.
How To Use An Options Greeks Chart Effectively
To maximize its utility:
- Regularly monitor all four components rather than focusing solely on one metric.
- Adjust positions dynamically based on changing Greek values during market fluctuations.
- Combine Greek analysis with fundamental research about underlying assets' prospects—for example, assessing macroeconomic trends affecting implied volatility (Vega).
By doing so — especially when managing large portfolios — traders can better control downside risks while capitalizing on favorable moves.
Final Thoughts
An options Greeks chart remains indispensable within modern financial analysis frameworks due its ability to distill complex derivative sensitivities into actionable insights. Whether applied traditionally across stocks or innovatively within cryptocurrencies' high-volatility environment—the core principles remain relevant today as they did decades ago—with continuous advancements enhancing accessibility through technology-driven solutions.
Understanding these metrics thoroughly empowers traders not only through improved decision-making but also fosters deeper trustworthiness grounded in quantitative rigor—a cornerstone principle aligning well with expert-level investment standards aimed at sustainable success over time.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-19 07:19
What is Options Greeks Chart?
Options Greeks Chart: A Complete Guide for Traders and Investors
What Is an Options Greeks Chart?
An options Greeks chart is a vital analytical tool used by traders and investors to understand how various factors influence the price of options. It visually represents key metrics—Delta, Gamma, Theta, and Vega—that measure an option’s sensitivity to underlying asset movements, time decay, and volatility changes. These metrics help traders assess risk exposure, optimize trading strategies, and make informed decisions in both traditional markets like stocks or commodities and emerging sectors such as cryptocurrencies.
The chart consolidates complex mathematical data into an accessible format that allows users to quickly gauge how different market conditions might impact their options positions. By analyzing these sensitivities collectively on a single chart, traders can better anticipate potential profit or loss scenarios under varying circumstances.
The Four Main Components of Options Greeks
Understanding each component of the options Greeks is essential for effective trading:
Delta: This measures how much the price of an option will change with a $1 move in the underlying asset. For example, a Delta of 0.5 indicates that if the stock increases by $1, the option's price will increase by approximately $0.50. Delta also provides insight into whether an option behaves more like a stock (high Delta) or less (low Delta).
Gamma: Gamma indicates how much Delta will change when the underlying asset's price moves by one dollar. It reflects the curvature in the relationship between option prices and underlying prices—higher Gamma means greater sensitivity to small movements in asset prices.
Theta: Often called time decay, Theta quantifies how much value an option loses each day as expiration approaches if all other factors remain constant. For instance, a Theta of -0.05 suggests that daily time decay reduces the option’s value by five cents per day.
Vega: This measures sensitivity to volatility changes; specifically, it shows how much an option's premium will fluctuate with a 1% change in implied volatility of the underlying asset.
These components work together within an options Greeks chart to provide comprehensive insights into potential risks and rewards associated with specific trades.
Why Are Options Greeks Important for Traders?
Options trading involves managing multiple variables simultaneously; therefore understanding these sensitivities is crucial for risk management and strategic planning:
- They enable traders to predict how market movements affect their positions.
- Help determine optimal entry and exit points based on expected changes in volatility or time.
- Facilitate hedging strategies—adjusting portfolios against adverse market shifts.
For example, if you hold long calls with high Delta but low Gamma exposure during volatile periods (like earnings reports), you might want to adjust your position because sudden large moves could significantly impact your profits or losses.
Moreover, institutional investors rely heavily on these metrics for portfolio risk assessment while individual traders use them for tactical decision-making—especially when employing advanced strategies such as spreads or straddles.
Historical Development of Options Greeks
The concept originated during decades when financial mathematicians sought more precise models for pricing derivatives beyond simple formulas like Black-Scholes (1973). In particular:
During 1970s–1980s: Researchers developed sophisticated models incorporating multiple variables influencing options prices.
In 1990s: Emanuel Derman and Nassim Nicholas Taleb popularized terminology—the "Greeks"—to describe these sensitivities systematically.
This evolution allowed both institutional players and retail investors access to tools previously limited due to complexity but now integral across markets worldwide—including equities—and increasingly applied within cryptocurrency derivatives markets where high volatility amplifies importance.
Modern Applications & Recent Trends
In recent years:
Expansion into Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have introduced new opportunities—and challenges—for applying traditional options analysis due to their extreme volatility levels. Traders now utilize Greek-based models tailored specifically toward digital assets’ unique behavior patterns—a development driven partly by increasing institutional interest seeking hedging solutions against crypto exposure.
Advanced Trading Platforms
Modern software offers real-time analytics on Greek values enabling dynamic adjustments during trading sessions rather than static assessments at trade initiation—a significant advantage amid fast-moving markets like crypto exchanges or volatile equity sectors.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory bodies worldwide are scrutinizing derivatives activities more closely; transparency requirements are increasing which benefits informed trading based on solid Greek analysis while discouraging overly risky leverage practices that could lead to systemic issues if misused.
Risks Associated With Using Options Greeks
While powerful tools:
- Over-reliance can lead traders astray—particularly if they ignore broader market signals.
- High leverage combined with misjudged Greek values may amplify losses rapidly.
- Rapid shifts typical in cryptocurrency markets can cause sudden swings in Greek metrics making real-time monitoring essential but challenging.
Therefore understanding limitations alongside benefits ensures prudent application aligned with sound risk management principles.
Key Dates Shaping Understanding of Options Sensitivities
Tracking historical milestones helps contextualize current practices:
- 1970s–1980s: Development of foundational models like Black-Scholes laid groundwork for calculating initial "Greeks."
- 1990s: Formal naming ("Greeks") brought clarity; expanded understanding among practitioners globally.
- 2010s: Adoption within cryptocurrency derivatives increased awareness about adapting classical models beyond traditional assets.
- 2020s: Integration into advanced platforms enables seamless real-time analysis supporting complex multi-leg strategies across diverse markets.
This timeline underscores ongoing innovation driven by technological advances coupled with evolving financial landscapes.
How To Use An Options Greeks Chart Effectively
To maximize its utility:
- Regularly monitor all four components rather than focusing solely on one metric.
- Adjust positions dynamically based on changing Greek values during market fluctuations.
- Combine Greek analysis with fundamental research about underlying assets' prospects—for example, assessing macroeconomic trends affecting implied volatility (Vega).
By doing so — especially when managing large portfolios — traders can better control downside risks while capitalizing on favorable moves.
Final Thoughts
An options Greeks chart remains indispensable within modern financial analysis frameworks due its ability to distill complex derivative sensitivities into actionable insights. Whether applied traditionally across stocks or innovatively within cryptocurrencies' high-volatility environment—the core principles remain relevant today as they did decades ago—with continuous advancements enhancing accessibility through technology-driven solutions.
Understanding these metrics thoroughly empowers traders not only through improved decision-making but also fosters deeper trustworthiness grounded in quantitative rigor—a cornerstone principle aligning well with expert-level investment standards aimed at sustainable success over time.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Can You Avoid Phishing Attacks?
Phishing remains one of the most prevalent cybersecurity threats today, targeting individuals and organizations alike. As cybercriminals develop more sophisticated methods, understanding how to protect yourself from falling victim is essential. This guide provides practical strategies rooted in recent developments and best practices to help you stay safe online.
Understanding Phishing and Its Risks
Phishing is a form of social engineering attack where scammers impersonate legitimate entities—such as banks, tech companies, or colleagues—to trick victims into revealing sensitive information. These attacks often occur via email, text messages (SMS), or even social media platforms. The goal may be to steal login credentials, financial data, or personal information that can be exploited for fraud or identity theft.
Recent trends show that phishing has become more targeted and convincing. Attackers now use personalized messages (spear phishing) aimed at specific individuals or organizations with valuable data. With the rise of digital services and remote work environments, the attack surface has expanded significantly.
Recognizing Common Signs of Phishing Attempts
Being able to identify suspicious communications is crucial in avoiding phishing scams. Typical indicators include:
- Unexpected requests for sensitive information
- Urgent language prompting immediate action
- Spelling mistakes or grammatical errors
- Unusual sender email addresses that mimic legitimate sources
- Links leading to unfamiliar websites
In recent developments like Google's AI-powered defenses (e.g., Gemini Nano), many sophisticated scams are detected before reaching users' inboxes. However, vigilance remains vital because attackers continually refine their tactics.
Practical Steps to Protect Yourself from Phishing
1. Be Cautious with Email Links and Attachments
Always hover over links before clicking them; this reveals the actual URL destination. If it looks suspicious or mismatched with the supposed sender's domain—such as a bank link pointing elsewhere—do not click it.
Similarly, avoid opening unexpected attachments unless you are certain about their legitimacy. Cybercriminals often embed malware within seemingly harmless files.
2. Use Strong Authentication Methods
Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords. Even if attackers obtain your login details through phishing, they will likely be blocked from accessing your accounts without the second verification step.
Recently adopted security measures like Microsoft's passkeys eliminate shared secrets between devices and servers altogether—making credential theft much harder for hackers.
3. Keep Software Up-to-Date
Regularly updating your operating system and applications patches known vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might exploit during phishing campaigns or other attacks. Many recent high-profile breaches have been facilitated by outdated software components lacking critical security fixes.
4. Educate Yourself About Phishing Tactics
Staying informed about current scam techniques enhances your ability to recognize potential threats early on:
- Be skeptical of unsolicited messages requesting personal info.
- Verify requests through official channels.
- Learn common signs of fake websites mimicking real brands.
Organizations should also invest in employee training programs emphasizing cybersecurity awareness—a proven method for reducing successful phishing attempts within workplaces.
5. Leverage Advanced Security Technologies
Modern defenses incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) tools capable of detecting complex scams before they reach users’ inboxes:
- Google’s Gemini Nano AI helps Chrome users identify malicious sites.
- On-device AI features in Android devices detect scam calls and texts proactively.
Employing such technologies significantly reduces risk exposure by catching threats early on rather than relying solely on user vigilance.
Best Practices for Organizations Against Phishing Threats
For businesses aiming to safeguard their assets:
1. Implement Multi-Layered Security Protocols: Combine technical controls like spam filters with user education programs.
2. Adopt Passwordless Authentication: Transition towards passkeys which eliminate shared secrets vulnerable during social engineering attacks.
3. Conduct Regular Security Training: Keep staff updated on evolving tactics used by cybercriminals; simulate phishing exercises periodically.
4. Monitor Network Traffic & User Behavior: Use advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying anomalies indicative of attempted breaches stemming from successful phishing campaigns.
Staying Ahead in an Evolving Threat Landscape
The landscape continues evolving rapidly; recent reports highlight a surge in credential theft surpassing traditional ransomware attacks globally[1]. Major corporations like Harrods faced significant cyberattacks recently[4], illustrating how even large organizations remain vulnerable despite advanced defenses such as AI-powered detection systems[2][3].
To effectively mitigate these risks requires ongoing vigilance combined with technological innovation—including adopting passkeys[5], leveraging AI-based tools—and fostering a culture aware of cybersecurity best practices across all levels within an organization.
Final Tips for Personal Cybersecurity Hygiene
While technology plays a vital role in defense strategies against phishing:
- Always verify identities before sharing sensitive data online.
- Use unique passwords across different accounts; consider password managers for convenience.
- Enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
By integrating these habits into daily routines alongside staying informed about emerging scams—and utilizing cutting-edge security solutions—you can substantially reduce your vulnerability to malicious schemes designed to deceive you into revealing confidential information.
References
1. Verizon's 2025 Report – Surge in Credential Theft Attacks
2. Google Rolls Out Gemini Nano AI Protection – Enhanced Browser Security
3. Android 16 Scam Detection Capabilities – On-device Artificial Intelligence
4. Harrods Cyberattack – Lessons from Recent Retail Breaches
5. Microsoft Passkey Adoption – Moving Towards Passwordless Authentication


Lo
2025-05-15 01:19
How can you avoid phishing attacks?
How Can You Avoid Phishing Attacks?
Phishing remains one of the most prevalent cybersecurity threats today, targeting individuals and organizations alike. As cybercriminals develop more sophisticated methods, understanding how to protect yourself from falling victim is essential. This guide provides practical strategies rooted in recent developments and best practices to help you stay safe online.
Understanding Phishing and Its Risks
Phishing is a form of social engineering attack where scammers impersonate legitimate entities—such as banks, tech companies, or colleagues—to trick victims into revealing sensitive information. These attacks often occur via email, text messages (SMS), or even social media platforms. The goal may be to steal login credentials, financial data, or personal information that can be exploited for fraud or identity theft.
Recent trends show that phishing has become more targeted and convincing. Attackers now use personalized messages (spear phishing) aimed at specific individuals or organizations with valuable data. With the rise of digital services and remote work environments, the attack surface has expanded significantly.
Recognizing Common Signs of Phishing Attempts
Being able to identify suspicious communications is crucial in avoiding phishing scams. Typical indicators include:
- Unexpected requests for sensitive information
- Urgent language prompting immediate action
- Spelling mistakes or grammatical errors
- Unusual sender email addresses that mimic legitimate sources
- Links leading to unfamiliar websites
In recent developments like Google's AI-powered defenses (e.g., Gemini Nano), many sophisticated scams are detected before reaching users' inboxes. However, vigilance remains vital because attackers continually refine their tactics.
Practical Steps to Protect Yourself from Phishing
1. Be Cautious with Email Links and Attachments
Always hover over links before clicking them; this reveals the actual URL destination. If it looks suspicious or mismatched with the supposed sender's domain—such as a bank link pointing elsewhere—do not click it.
Similarly, avoid opening unexpected attachments unless you are certain about their legitimacy. Cybercriminals often embed malware within seemingly harmless files.
2. Use Strong Authentication Methods
Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords. Even if attackers obtain your login details through phishing, they will likely be blocked from accessing your accounts without the second verification step.
Recently adopted security measures like Microsoft's passkeys eliminate shared secrets between devices and servers altogether—making credential theft much harder for hackers.
3. Keep Software Up-to-Date
Regularly updating your operating system and applications patches known vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might exploit during phishing campaigns or other attacks. Many recent high-profile breaches have been facilitated by outdated software components lacking critical security fixes.
4. Educate Yourself About Phishing Tactics
Staying informed about current scam techniques enhances your ability to recognize potential threats early on:
- Be skeptical of unsolicited messages requesting personal info.
- Verify requests through official channels.
- Learn common signs of fake websites mimicking real brands.
Organizations should also invest in employee training programs emphasizing cybersecurity awareness—a proven method for reducing successful phishing attempts within workplaces.
5. Leverage Advanced Security Technologies
Modern defenses incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) tools capable of detecting complex scams before they reach users’ inboxes:
- Google’s Gemini Nano AI helps Chrome users identify malicious sites.
- On-device AI features in Android devices detect scam calls and texts proactively.
Employing such technologies significantly reduces risk exposure by catching threats early on rather than relying solely on user vigilance.
Best Practices for Organizations Against Phishing Threats
For businesses aiming to safeguard their assets:
1. Implement Multi-Layered Security Protocols: Combine technical controls like spam filters with user education programs.
2. Adopt Passwordless Authentication: Transition towards passkeys which eliminate shared secrets vulnerable during social engineering attacks.
3. Conduct Regular Security Training: Keep staff updated on evolving tactics used by cybercriminals; simulate phishing exercises periodically.
4. Monitor Network Traffic & User Behavior: Use advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying anomalies indicative of attempted breaches stemming from successful phishing campaigns.
Staying Ahead in an Evolving Threat Landscape
The landscape continues evolving rapidly; recent reports highlight a surge in credential theft surpassing traditional ransomware attacks globally[1]. Major corporations like Harrods faced significant cyberattacks recently[4], illustrating how even large organizations remain vulnerable despite advanced defenses such as AI-powered detection systems[2][3].
To effectively mitigate these risks requires ongoing vigilance combined with technological innovation—including adopting passkeys[5], leveraging AI-based tools—and fostering a culture aware of cybersecurity best practices across all levels within an organization.
Final Tips for Personal Cybersecurity Hygiene
While technology plays a vital role in defense strategies against phishing:
- Always verify identities before sharing sensitive data online.
- Use unique passwords across different accounts; consider password managers for convenience.
- Enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
By integrating these habits into daily routines alongside staying informed about emerging scams—and utilizing cutting-edge security solutions—you can substantially reduce your vulnerability to malicious schemes designed to deceive you into revealing confidential information.
References
1. Verizon's 2025 Report – Surge in Credential Theft Attacks
2. Google Rolls Out Gemini Nano AI Protection – Enhanced Browser Security
3. Android 16 Scam Detection Capabilities – On-device Artificial Intelligence
4. Harrods Cyberattack – Lessons from Recent Retail Breaches
5. Microsoft Passkey Adoption – Moving Towards Passwordless Authentication
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding Gas Fee Dynamics on Ethereum After EIP-1559
Ethereum's network has long been a popular platform for decentralized applications, smart contracts, and digital assets. However, high and unpredictable gas fees have often hindered user experience and transaction efficiency. The introduction of EIP-1559 in August 2021 marked a pivotal shift in how transaction fees are calculated and prioritized on the Ethereum blockchain. To fully grasp how these changes influence transaction priority today, it’s essential to understand the mechanics behind gas fee dynamics post-EIP-1559.
What Are Gas Fees and Why Do They Matter?
Gas fees are the costs paid by users to process transactions or execute smart contracts on Ethereum. These fees compensate miners (or validators in proof-of-stake systems) for including transactions in blocks. Prior to EIP-1559, gas prices were determined through a first-price auction system where users bid against each other; higher bids meant faster processing but also led to volatile costs that could spike unpredictably during periods of network congestion.
High gas fees not only made small transactions less feasible but also created barriers for developers and users seeking cost-effective interactions with decentralized applications (dApps). This environment underscored the need for a more predictable fee structure—one that balances fairness with efficiency.
How EIP-1559 Changed Gas Fee Mechanics
EIP-1559 introduced several fundamental modifications aimed at stabilizing gas prices while improving transaction prioritization:
Base Fee and Priority Fee: The New Dual Components
The core innovation was splitting total transaction fees into two parts:
Base Fee: A mandatory fee paid to miners (or validators), dynamically adjusted based on network congestion.
Priority Fee (Tip): An optional incentive set by users to prioritize their transactions over others.
This separation allows the network to better manage fee volatility by setting a minimum base cost while giving users control over how quickly their transactions are processed through additional tips.
Dynamic Adjustment of Base Fees
Unlike previous fixed or auction-based models, the base fee is recalculated every 12 blocks depending on recent block utilization:
If blocks are consistently full, the base fee increases.
If there’s slack capacity, it decreases.
This mechanism helps maintain an optimal balance between throughput and cost stability by preventing sudden spikes or drops in gas prices.
Transaction Prioritization Based on User Set Tips
Prioritization now depends primarily on how much extra tip (priority fee) a user attaches rather than bidding against others’ bids. Transactions with higher tips get processed sooner because miners see them as more financially attractive—this encourages fairer competition based on willingness-to-pay rather than bidding wars that could inflate costs unnecessarily.
Impact of EIP-1559 on Transaction Priority
The new system significantly influences how quickly transactions are confirmed:
Increased Predictability & Stability
By fixing the minimum base fee per block interval, users can better anticipate their costs without worrying about sudden surges caused by competitive bidding wars. This predictability enhances planning capabilities for both individual users and businesses relying heavily on timely confirmations.
Fairness Through Tip-Based Prioritization
Rather than engaging in costly bidding wars during peak times—which often favored wealthier participants—the new model allows anyone willing to pay an appropriate tip to have their transaction prioritized efficiently. This approach promotes fairness across different user segments while maintaining overall network throughput.
Enhanced User Control & Experience
Users can now decide how urgent their transactions are by adjusting their priority tip accordingly. For example:
A user sending funds urgently might set a higher tip, whereas a routine transfer might opt for minimal additional payment. This flexibility improves transparency around costs compared with earlier models where bidders had little control over final outcomes beyond bid amounts alone.
Recent Developments Improving Gas Price Management
Since its deployment, ongoing refinements aim at optimizing this new dynamic:
Frequent Base Fee Adjustments: Every 12 blocks ensures real-time responsiveness aligned with current demand levels.
User Experimentation: Users have tested various priority tips under different conditions—helping developers understand optimal strategies for balancing cost versus speed.
Community Feedback Integration: Continuous feedback from stakeholders has led developers toward further improvements such as better algorithms for adjusting base fees or educating users about effective tip-setting practices.
Challenges & Limitations of Post-EIP-1559 Gas Dynamics
While EIP-1559 brought notable benefits, some issues remain:
Initial Adjustment Periods & Volatility
During early implementation phases, both miners/validators and users experienced transitional volatility as they adapted strategies within this new framework—a period marked by fluctuating gas prices until equilibrium was reached.
Scalability Concerns Persist
EIP-1559 does not directly address underlying scalability issues like limited block space or throughput constraints; thus high demand still results in elevated fees despite improved mechanisms—highlighting ongoing needs for layer 2 solutions such as rollups or sharding technologies.
Need For Better User Education
Effective use of priority tips requires understanding current network conditions; without proper guidance or tools—like real-time analytics—users may either overpay unnecessarily or face delays due to insufficient tipping strategies.
How Gas Price Dynamics Influence Transaction Efficiency Today
Post-EIP-1559 dynamics mean that:
- Users who set appropriate priority tips can expect faster confirmation times during congested periods.
- Network stability reduces unexpected spikes but still requires active management from end-users.
- Developers benefit from more predictable operational costs when designing dApps requiring frequent interactions.
Moreover, understanding these mechanics enables traders and businesses operating within DeFi ecosystems—or those conducting large-scale transfers—to optimize timing based on anticipated congestion patterns.
Future Outlook: Enhancing Ethereum’s Transaction Ecosystem
Looking ahead:
- Further protocol upgrades may improve scalability alongside existing fee mechanisms.
- Community-driven innovations aim at creating smarter tools that help estimate ideal tips based on real-time data.
- Educational initiatives will be vital so all participants—from casual traders to institutional actors—can navigate complex fee structures confidently.
By continuously refining these systems through community feedback—and integrating advanced Layer 2 solutions—the Ethereum ecosystem aims at delivering lower-cost transactions with reliable prioritization methods suited both casual use cases and enterprise-level demands.
Understanding how post-EIP-1558 gas price dynamics shape transaction priorities is crucial whether you're an everyday user aiming for affordable transfers or a developer optimizing dApp performance amid fluctuating demand levels. As Ethereum evolves—with ongoing improvements driven by community input—the goal remains clear: create an efficient, fairer system where transaction speed aligns transparently with user willingness-to-pay within sustainable economic parameters.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 19:34
How do gas fee dynamics post-EIP-1559 influence transaction priority on Ethereum (ETH)?
Understanding Gas Fee Dynamics on Ethereum After EIP-1559
Ethereum's network has long been a popular platform for decentralized applications, smart contracts, and digital assets. However, high and unpredictable gas fees have often hindered user experience and transaction efficiency. The introduction of EIP-1559 in August 2021 marked a pivotal shift in how transaction fees are calculated and prioritized on the Ethereum blockchain. To fully grasp how these changes influence transaction priority today, it’s essential to understand the mechanics behind gas fee dynamics post-EIP-1559.
What Are Gas Fees and Why Do They Matter?
Gas fees are the costs paid by users to process transactions or execute smart contracts on Ethereum. These fees compensate miners (or validators in proof-of-stake systems) for including transactions in blocks. Prior to EIP-1559, gas prices were determined through a first-price auction system where users bid against each other; higher bids meant faster processing but also led to volatile costs that could spike unpredictably during periods of network congestion.
High gas fees not only made small transactions less feasible but also created barriers for developers and users seeking cost-effective interactions with decentralized applications (dApps). This environment underscored the need for a more predictable fee structure—one that balances fairness with efficiency.
How EIP-1559 Changed Gas Fee Mechanics
EIP-1559 introduced several fundamental modifications aimed at stabilizing gas prices while improving transaction prioritization:
Base Fee and Priority Fee: The New Dual Components
The core innovation was splitting total transaction fees into two parts:
Base Fee: A mandatory fee paid to miners (or validators), dynamically adjusted based on network congestion.
Priority Fee (Tip): An optional incentive set by users to prioritize their transactions over others.
This separation allows the network to better manage fee volatility by setting a minimum base cost while giving users control over how quickly their transactions are processed through additional tips.
Dynamic Adjustment of Base Fees
Unlike previous fixed or auction-based models, the base fee is recalculated every 12 blocks depending on recent block utilization:
If blocks are consistently full, the base fee increases.
If there’s slack capacity, it decreases.
This mechanism helps maintain an optimal balance between throughput and cost stability by preventing sudden spikes or drops in gas prices.
Transaction Prioritization Based on User Set Tips
Prioritization now depends primarily on how much extra tip (priority fee) a user attaches rather than bidding against others’ bids. Transactions with higher tips get processed sooner because miners see them as more financially attractive—this encourages fairer competition based on willingness-to-pay rather than bidding wars that could inflate costs unnecessarily.
Impact of EIP-1559 on Transaction Priority
The new system significantly influences how quickly transactions are confirmed:
Increased Predictability & Stability
By fixing the minimum base fee per block interval, users can better anticipate their costs without worrying about sudden surges caused by competitive bidding wars. This predictability enhances planning capabilities for both individual users and businesses relying heavily on timely confirmations.
Fairness Through Tip-Based Prioritization
Rather than engaging in costly bidding wars during peak times—which often favored wealthier participants—the new model allows anyone willing to pay an appropriate tip to have their transaction prioritized efficiently. This approach promotes fairness across different user segments while maintaining overall network throughput.
Enhanced User Control & Experience
Users can now decide how urgent their transactions are by adjusting their priority tip accordingly. For example:
A user sending funds urgently might set a higher tip, whereas a routine transfer might opt for minimal additional payment. This flexibility improves transparency around costs compared with earlier models where bidders had little control over final outcomes beyond bid amounts alone.
Recent Developments Improving Gas Price Management
Since its deployment, ongoing refinements aim at optimizing this new dynamic:
Frequent Base Fee Adjustments: Every 12 blocks ensures real-time responsiveness aligned with current demand levels.
User Experimentation: Users have tested various priority tips under different conditions—helping developers understand optimal strategies for balancing cost versus speed.
Community Feedback Integration: Continuous feedback from stakeholders has led developers toward further improvements such as better algorithms for adjusting base fees or educating users about effective tip-setting practices.
Challenges & Limitations of Post-EIP-1559 Gas Dynamics
While EIP-1559 brought notable benefits, some issues remain:
Initial Adjustment Periods & Volatility
During early implementation phases, both miners/validators and users experienced transitional volatility as they adapted strategies within this new framework—a period marked by fluctuating gas prices until equilibrium was reached.
Scalability Concerns Persist
EIP-1559 does not directly address underlying scalability issues like limited block space or throughput constraints; thus high demand still results in elevated fees despite improved mechanisms—highlighting ongoing needs for layer 2 solutions such as rollups or sharding technologies.
Need For Better User Education
Effective use of priority tips requires understanding current network conditions; without proper guidance or tools—like real-time analytics—users may either overpay unnecessarily or face delays due to insufficient tipping strategies.
How Gas Price Dynamics Influence Transaction Efficiency Today
Post-EIP-1559 dynamics mean that:
- Users who set appropriate priority tips can expect faster confirmation times during congested periods.
- Network stability reduces unexpected spikes but still requires active management from end-users.
- Developers benefit from more predictable operational costs when designing dApps requiring frequent interactions.
Moreover, understanding these mechanics enables traders and businesses operating within DeFi ecosystems—or those conducting large-scale transfers—to optimize timing based on anticipated congestion patterns.
Future Outlook: Enhancing Ethereum’s Transaction Ecosystem
Looking ahead:
- Further protocol upgrades may improve scalability alongside existing fee mechanisms.
- Community-driven innovations aim at creating smarter tools that help estimate ideal tips based on real-time data.
- Educational initiatives will be vital so all participants—from casual traders to institutional actors—can navigate complex fee structures confidently.
By continuously refining these systems through community feedback—and integrating advanced Layer 2 solutions—the Ethereum ecosystem aims at delivering lower-cost transactions with reliable prioritization methods suited both casual use cases and enterprise-level demands.
Understanding how post-EIP-1558 gas price dynamics shape transaction priorities is crucial whether you're an everyday user aiming for affordable transfers or a developer optimizing dApp performance amid fluctuating demand levels. As Ethereum evolves—with ongoing improvements driven by community input—the goal remains clear: create an efficient, fairer system where transaction speed aligns transparently with user willingness-to-pay within sustainable economic parameters.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Use RSI with Bollinger Bands for Effective Trading
Understanding how to combine technical indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Bollinger Bands can significantly enhance your trading strategy, especially in volatile markets such as cryptocurrencies. Both tools provide unique insights—RSI measures momentum, while Bollinger Bands assess market volatility. When used together, they offer a comprehensive view of potential entry and exit points, helping traders make more informed decisions.
What Is RSI and How Does It Work?
The Relative Strength Index (RSI), developed by J. Welles Wilder, is a momentum oscillator that quantifies the speed and change of price movements over a specified period—commonly 14 days. The RSI ranges from 0 to 100; readings above 70 suggest an asset may be overbought, indicating a possible price correction or reversal downward. Conversely, readings below 30 imply oversold conditions that could precede an upward rebound.
Traders often use RSI to identify potential trend reversals or confirm existing trends. Its sensitivity can be adjusted by changing the period length: shorter periods (like 7 days) make it more reactive but prone to false signals; longer periods (such as 28 days) smooth out fluctuations but may lag behind current market conditions.
Understanding Bollinger Bands and Their Role in Volatility Analysis
Bollinger Bands consist of three components: a simple moving average (middle band) and two outer bands set at standard deviations away from this average—typically two standard deviations for each band. These bands expand during high volatility periods and contract when markets are calmer.
By observing where prices are relative to these bands, traders gain insights into market strength and potential breakout points:
- When prices approach or touch the upper band, it indicates strong upward momentum but also suggests overbought conditions.
- When prices near the lower band signal oversold levels with potential for upward movement.
- Narrowing bands often precede significant price moves due to low volatility phases setting up breakouts.
Combining RSI with Bollinger Bands: A Strategic Approach
Integrating RSI with Bollinger Bands allows traders to refine their signals by confirming momentum alongside volatility cues:
Identifying Overbought/Oversold Conditions
- An asset showing an RSI above 70 coupled with its price near or touching the upper Bollinger Band suggests strong buying pressure but also warns of possible exhaustion—a signal that a pullback might occur soon.
- Conversely, when RSI dips below 30 while prices hover near or at the lower band indicates overselling—potentially signaling an upcoming bounce or reversal.
Spotting Potential Entry Points
- A common tactic involves looking for instances where both indicators align: such as an oversold RSI (<30) combined with prices at the lower band could present a buy opportunity.
- Similarly, overbought signals (>70 on RSI) paired with upper-band proximity might indicate it's time to consider selling or taking profits.
Confirming Breakouts
- Breakouts beyond either bollinger band accompanied by extreme RSI levels can validate strong directional moves.
- For example, if price breaks above the upper band while RSI remains high (>70), it might signify continued bullishness rather than just temporary overextension—a cue for aggressive entries if confirmed further through volume analysis.
Practical Trading Strategies Using Both Indicators
Several strategies leverage this combination effectively:
RSI-Bollinger Band Crossover Strategy:
This involves entering trades when specific thresholds are crossed—for instance:- Buying when RSIs cross below 30 near the lower bollinger band
- Selling when RSIs cross above 70 near the upper bollinger band
Breakout Strategy:
Monitoring for breakouts beyond bands:- Enter long positions if price breaks out upwards past the upper bolliger band while RSIs stay elevated
- Enter short positions on downward breakouts past lower bands combined with low RSIs
These strategies benefit from confirming signals across both indicators before executing trades — reducing false positives common in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies.
Adjusting Indicator Settings for Better Results
Fine-tuning parameters enhances indicator responsiveness:
- For RSI, shorter periods increase sensitivity but risk more false signals; longer periods provide stability at expense of lagging behind rapid moves.
- For Bollinger Bands, increasing standard deviation widens bands during high-volatility phases; decreasing makes them tighter during calmer markets — aiding in detecting subtle shifts versus major breakouts.
Experimentation based on your trading timeframe and asset class is essential for optimal results without sacrificing reliability.
Risks & Limitations of Using Both Indicators Together
While combining RSI and Bollinger Bands offers valuable insights—and improves trade accuracy—it’s not foolproof:
- Both tools can generate false signals during highly volatile swings where rapid reversals occur unexpectedly.
- Overreliance on technical indicators without considering fundamental factors may lead you astray—especially in news-driven markets like cryptocurrencies.
- Market conditions influence effectiveness; trending markets tend to produce clearer signals than sideways consolidations where whipsaws are frequent.
To mitigate these risks, incorporate additional analysis methods such as volume confirmation or trend-following tools alongside your primary indicators.
Enhancing Your Trading Strategy With Technical Indicator Synergy
Using RSI in conjunction with Bollinger Bands provides traders a layered perspective—momentum coupled with volatility—that helps identify high-probability trade setups. By understanding how each indicator behaves individually—and how they interact—you can develop disciplined entry/exit rules aligned closely with current market dynamics.
In practice:
- Look for confluence between low/high RSIs and proximity to respective bolliger bands
- Confirm breakout validity through volume spikes
- Adjust indicator settings based on your preferred trading timeframe
Remember always to test strategies thoroughly before applying them live—and combine technical insights within broader risk management frameworks—to maximize success chances across different market environments.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-09 09:27
How can RSI be used in conjunction with Bollinger Bands?
How to Use RSI with Bollinger Bands for Effective Trading
Understanding how to combine technical indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Bollinger Bands can significantly enhance your trading strategy, especially in volatile markets such as cryptocurrencies. Both tools provide unique insights—RSI measures momentum, while Bollinger Bands assess market volatility. When used together, they offer a comprehensive view of potential entry and exit points, helping traders make more informed decisions.
What Is RSI and How Does It Work?
The Relative Strength Index (RSI), developed by J. Welles Wilder, is a momentum oscillator that quantifies the speed and change of price movements over a specified period—commonly 14 days. The RSI ranges from 0 to 100; readings above 70 suggest an asset may be overbought, indicating a possible price correction or reversal downward. Conversely, readings below 30 imply oversold conditions that could precede an upward rebound.
Traders often use RSI to identify potential trend reversals or confirm existing trends. Its sensitivity can be adjusted by changing the period length: shorter periods (like 7 days) make it more reactive but prone to false signals; longer periods (such as 28 days) smooth out fluctuations but may lag behind current market conditions.
Understanding Bollinger Bands and Their Role in Volatility Analysis
Bollinger Bands consist of three components: a simple moving average (middle band) and two outer bands set at standard deviations away from this average—typically two standard deviations for each band. These bands expand during high volatility periods and contract when markets are calmer.
By observing where prices are relative to these bands, traders gain insights into market strength and potential breakout points:
- When prices approach or touch the upper band, it indicates strong upward momentum but also suggests overbought conditions.
- When prices near the lower band signal oversold levels with potential for upward movement.
- Narrowing bands often precede significant price moves due to low volatility phases setting up breakouts.
Combining RSI with Bollinger Bands: A Strategic Approach
Integrating RSI with Bollinger Bands allows traders to refine their signals by confirming momentum alongside volatility cues:
Identifying Overbought/Oversold Conditions
- An asset showing an RSI above 70 coupled with its price near or touching the upper Bollinger Band suggests strong buying pressure but also warns of possible exhaustion—a signal that a pullback might occur soon.
- Conversely, when RSI dips below 30 while prices hover near or at the lower band indicates overselling—potentially signaling an upcoming bounce or reversal.
Spotting Potential Entry Points
- A common tactic involves looking for instances where both indicators align: such as an oversold RSI (<30) combined with prices at the lower band could present a buy opportunity.
- Similarly, overbought signals (>70 on RSI) paired with upper-band proximity might indicate it's time to consider selling or taking profits.
Confirming Breakouts
- Breakouts beyond either bollinger band accompanied by extreme RSI levels can validate strong directional moves.
- For example, if price breaks above the upper band while RSI remains high (>70), it might signify continued bullishness rather than just temporary overextension—a cue for aggressive entries if confirmed further through volume analysis.
Practical Trading Strategies Using Both Indicators
Several strategies leverage this combination effectively:
RSI-Bollinger Band Crossover Strategy:
This involves entering trades when specific thresholds are crossed—for instance:- Buying when RSIs cross below 30 near the lower bollinger band
- Selling when RSIs cross above 70 near the upper bollinger band
Breakout Strategy:
Monitoring for breakouts beyond bands:- Enter long positions if price breaks out upwards past the upper bolliger band while RSIs stay elevated
- Enter short positions on downward breakouts past lower bands combined with low RSIs
These strategies benefit from confirming signals across both indicators before executing trades — reducing false positives common in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies.
Adjusting Indicator Settings for Better Results
Fine-tuning parameters enhances indicator responsiveness:
- For RSI, shorter periods increase sensitivity but risk more false signals; longer periods provide stability at expense of lagging behind rapid moves.
- For Bollinger Bands, increasing standard deviation widens bands during high-volatility phases; decreasing makes them tighter during calmer markets — aiding in detecting subtle shifts versus major breakouts.
Experimentation based on your trading timeframe and asset class is essential for optimal results without sacrificing reliability.
Risks & Limitations of Using Both Indicators Together
While combining RSI and Bollinger Bands offers valuable insights—and improves trade accuracy—it’s not foolproof:
- Both tools can generate false signals during highly volatile swings where rapid reversals occur unexpectedly.
- Overreliance on technical indicators without considering fundamental factors may lead you astray—especially in news-driven markets like cryptocurrencies.
- Market conditions influence effectiveness; trending markets tend to produce clearer signals than sideways consolidations where whipsaws are frequent.
To mitigate these risks, incorporate additional analysis methods such as volume confirmation or trend-following tools alongside your primary indicators.
Enhancing Your Trading Strategy With Technical Indicator Synergy
Using RSI in conjunction with Bollinger Bands provides traders a layered perspective—momentum coupled with volatility—that helps identify high-probability trade setups. By understanding how each indicator behaves individually—and how they interact—you can develop disciplined entry/exit rules aligned closely with current market dynamics.
In practice:
- Look for confluence between low/high RSIs and proximity to respective bolliger bands
- Confirm breakout validity through volume spikes
- Adjust indicator settings based on your preferred trading timeframe
Remember always to test strategies thoroughly before applying them live—and combine technical insights within broader risk management frameworks—to maximize success chances across different market environments.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does the Fractal Adaptive Moving Average Incorporate Oscillators?
The Fractal Adaptive Moving Average (FAMA) has gained significant attention among traders, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. Its ability to adapt dynamically to changing market conditions makes it a powerful tool for technical analysis. When combined with oscillators, FAMA offers a comprehensive approach that enhances trend detection and momentum assessment. This article explores how FAMA incorporates oscillators into its framework, providing traders with deeper insights into market behavior.
Understanding FAMA: A Brief Overview
FAMA is a type of moving average designed to adjust its length based on market volatility and fractal patterns in price movements. Unlike traditional fixed-period moving averages, FAMA uses fractal theory—analyzing patterns that repeat at different scales—to identify trends more accurately. Its adaptive nature allows it to respond swiftly during high-volatility periods while smoothing out noise during calmer phases.
This flexibility makes FAMA particularly suitable for markets characterized by rapid shifts, such as cryptocurrencies. Traders rely on it not only for trend identification but also as part of broader strategies involving other technical indicators.
The Role of Oscillators in Technical Analysis
Oscillators are tools used to measure the momentum or strength of price movements within a specific range or over time. They help traders identify potential reversal points by signaling overbought or oversold conditions—critical signals for timing entries and exits.
Some common oscillators include:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures recent price changes to determine if an asset is overbought (>70) or oversold (<30).
- Stochastic Oscillator: Compares closing prices relative to their recent trading range, highlighting potential reversals.
- Bollinger Bands: Volatility bands placed above and below a moving average; while not strictly an oscillator, they indicate periods of high or low volatility.
When integrated with FAMA, these oscillators provide complementary information—trend direction from the adaptive moving average combined with momentum signals from the oscillators enhances decision-making accuracy.
How Does FAMA Incorporate Oscillators?
FAMA's integration with oscillators involves using these tools alongside its dynamic trend signals to confirm or question potential trade setups. Here’s how this synergy typically works:
Trend Identification via FAMA:
First, traders observe the direction indicated by the FAMA line—whether it's trending upward (bullish) or downward (bearish). Because FAMA adjusts its sensitivity based on market fractals and volatility levels, it provides reliable trend cues even in choppy markets like crypto assets.Momentum Confirmation through Oscillators:
Once a trend is identified by FAMA, traders look at relevant oscillators such as RSI or Stochastic Oscillator:- If the trend is bullish per FAMA but RSI indicates overbought conditions (>70), this may signal caution before entering new long positions.
- Conversely, if both suggest bullishness—with rising RSI below 70—the probability of continuation increases.
Detecting Reversals:
When divergence occurs—for example:- Price makes new highs while RSI fails to do so,
- Or when stochastic shows oversold levels during an uptrend,
these can serve as early warning signs that a reversal might be imminent despite what the trend indicator suggests.
Volatility Insights via Bollinger Bands:
Although not strictly an oscillator, Bollinger Bands help gauge current volatility levels around the adaptive MA line:- Narrow bands suggest low volatility; wide bands indicate high activity.
- Breakouts beyond bands often coincide with strong moves confirmed by both FAMAs' trend signals and oscillator readings.
This layered approach ensures that traders aren’t relying solely on one indicator but are instead confirming signals across multiple tools—a practice rooted in sound trading principles aimed at reducing false positives and improving success rates.
Practical Applications in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets exemplify environments where combining adaptive indicators like FAMAs with oscillators proves especially beneficial due to their inherent unpredictability and rapid swings. Traders often use this combination for:
- Spotting early signs of breakout opportunities
- Confirming reversals amidst volatile price action
- Managing risk through multi-layered confirmation before executing trades
For instance, during Bitcoin’s sharp rallies or sudden dips seen frequently in crypto markets, an adaptive MA like Fama can quickly adjust its sensitivity while momentum indicators highlight whether those moves are sustainable—or just temporary corrections.
Limitations & Best Practices
While integrating oscillators with FAMAs enhances analytical depth — offering clearer insights into trends versus momentum — there are limitations worth noting:
- Overreliance can lead to false signals if used without context
- Market manipulation tactics prevalent in crypto spaces may distort indicator readings
- No single setup guarantees success; always consider broader factors including volume analysis and fundamental news
Best practices involve combining these technical tools within comprehensive trading plans that incorporate risk management strategies such as stop-loss orders and position sizing aligned with overall market conditions.
By understanding how Fractal Adaptive Moving Averages incorporate various oscillatory tools into their framework—and recognizing their strengths alongside limitations—traders can develop more nuanced strategies suited for modern financial landscapes like cryptocurrency trading environments where adaptability is key.


kai
2025-05-09 09:22
How does the Fractal Adaptive Moving Average incorporate oscillators?
How Does the Fractal Adaptive Moving Average Incorporate Oscillators?
The Fractal Adaptive Moving Average (FAMA) has gained significant attention among traders, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. Its ability to adapt dynamically to changing market conditions makes it a powerful tool for technical analysis. When combined with oscillators, FAMA offers a comprehensive approach that enhances trend detection and momentum assessment. This article explores how FAMA incorporates oscillators into its framework, providing traders with deeper insights into market behavior.
Understanding FAMA: A Brief Overview
FAMA is a type of moving average designed to adjust its length based on market volatility and fractal patterns in price movements. Unlike traditional fixed-period moving averages, FAMA uses fractal theory—analyzing patterns that repeat at different scales—to identify trends more accurately. Its adaptive nature allows it to respond swiftly during high-volatility periods while smoothing out noise during calmer phases.
This flexibility makes FAMA particularly suitable for markets characterized by rapid shifts, such as cryptocurrencies. Traders rely on it not only for trend identification but also as part of broader strategies involving other technical indicators.
The Role of Oscillators in Technical Analysis
Oscillators are tools used to measure the momentum or strength of price movements within a specific range or over time. They help traders identify potential reversal points by signaling overbought or oversold conditions—critical signals for timing entries and exits.
Some common oscillators include:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures recent price changes to determine if an asset is overbought (>70) or oversold (<30).
- Stochastic Oscillator: Compares closing prices relative to their recent trading range, highlighting potential reversals.
- Bollinger Bands: Volatility bands placed above and below a moving average; while not strictly an oscillator, they indicate periods of high or low volatility.
When integrated with FAMA, these oscillators provide complementary information—trend direction from the adaptive moving average combined with momentum signals from the oscillators enhances decision-making accuracy.
How Does FAMA Incorporate Oscillators?
FAMA's integration with oscillators involves using these tools alongside its dynamic trend signals to confirm or question potential trade setups. Here’s how this synergy typically works:
Trend Identification via FAMA:
First, traders observe the direction indicated by the FAMA line—whether it's trending upward (bullish) or downward (bearish). Because FAMA adjusts its sensitivity based on market fractals and volatility levels, it provides reliable trend cues even in choppy markets like crypto assets.Momentum Confirmation through Oscillators:
Once a trend is identified by FAMA, traders look at relevant oscillators such as RSI or Stochastic Oscillator:- If the trend is bullish per FAMA but RSI indicates overbought conditions (>70), this may signal caution before entering new long positions.
- Conversely, if both suggest bullishness—with rising RSI below 70—the probability of continuation increases.
Detecting Reversals:
When divergence occurs—for example:- Price makes new highs while RSI fails to do so,
- Or when stochastic shows oversold levels during an uptrend,
these can serve as early warning signs that a reversal might be imminent despite what the trend indicator suggests.
Volatility Insights via Bollinger Bands:
Although not strictly an oscillator, Bollinger Bands help gauge current volatility levels around the adaptive MA line:- Narrow bands suggest low volatility; wide bands indicate high activity.
- Breakouts beyond bands often coincide with strong moves confirmed by both FAMAs' trend signals and oscillator readings.
This layered approach ensures that traders aren’t relying solely on one indicator but are instead confirming signals across multiple tools—a practice rooted in sound trading principles aimed at reducing false positives and improving success rates.
Practical Applications in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets exemplify environments where combining adaptive indicators like FAMAs with oscillators proves especially beneficial due to their inherent unpredictability and rapid swings. Traders often use this combination for:
- Spotting early signs of breakout opportunities
- Confirming reversals amidst volatile price action
- Managing risk through multi-layered confirmation before executing trades
For instance, during Bitcoin’s sharp rallies or sudden dips seen frequently in crypto markets, an adaptive MA like Fama can quickly adjust its sensitivity while momentum indicators highlight whether those moves are sustainable—or just temporary corrections.
Limitations & Best Practices
While integrating oscillators with FAMAs enhances analytical depth — offering clearer insights into trends versus momentum — there are limitations worth noting:
- Overreliance can lead to false signals if used without context
- Market manipulation tactics prevalent in crypto spaces may distort indicator readings
- No single setup guarantees success; always consider broader factors including volume analysis and fundamental news
Best practices involve combining these technical tools within comprehensive trading plans that incorporate risk management strategies such as stop-loss orders and position sizing aligned with overall market conditions.
By understanding how Fractal Adaptive Moving Averages incorporate various oscillatory tools into their framework—and recognizing their strengths alongside limitations—traders can develop more nuanced strategies suited for modern financial landscapes like cryptocurrency trading environments where adaptability is key.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Redundancy Exists for Exchange APIs?
In the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrency and financial markets, ensuring data reliability and system uptime is critical. Exchange APIs serve as the backbone for real-time trading, portfolio management, and market analysis. As such, redundancy in these APIs is essential to prevent data outages, maintain regulatory compliance, and support scalable operations. This article explores the various forms of redundancy implemented in exchange APIs, recent technological advancements supporting these efforts, and potential risks associated with redundant systems.
Types of Exchange APIs Supporting Redundancy
Exchange platforms typically utilize multiple API types to facilitate different aspects of data exchange and trading operations. The most common include RESTful APIs, WebSocket APIs, and GraphQL interfaces.
RESTful APIs are widely used due to their simplicity; they allow clients to request specific data at any given moment through standard HTTP methods. While reliable for static or less time-sensitive information like account details or historical data, they may not be optimal for real-time updates.
WebSocket APIs provide persistent connections that enable continuous streaming of market prices or trade events in real time. This makes them indispensable for traders who rely on instant updates to execute timely decisions.
GraphQL offers a flexible query language that allows clients to specify exactly what data they need from an API endpoint. This reduces unnecessary data transfer—an advantage when bandwidth or latency is a concern—and supports efficient redundant querying strategies.
Combining these API types enhances overall system resilience by providing multiple pathways for accessing critical market information.
Strategies Employed in Redundant API Systems
To ensure high availability and fault tolerance within exchange infrastructures, several redundancy strategies are commonly employed:
Load Balancing: Distributing incoming requests across multiple servers prevents any single point from becoming overwhelmed or failing under high traffic volumes. Load balancers can reroute traffic seamlessly if one server goes offline.
Caching: Frequently accessed data—such as current prices or order book snapshots—is stored temporarily in cache layers closer to users or applications. Caching reduces load on primary systems while delivering faster response times.
Backup Systems: Maintaining duplicate infrastructure components ensures continuity during outages. These backups can be activated automatically if primary systems encounter failures—often managed through automated failover protocols.
By integrating these strategies into their architecture design, exchanges improve both resilience against technical failures and capacity handling during peak periods.
Recent Technological Developments Enhancing Redundancy
The landscape of exchange API redundancy has been significantly influenced by emerging technologies:
Blockchain Integration: Many exchanges incorporate blockchain technology directly into their infrastructure to provide immutable transaction records that serve as an additional layer of verification beyond traditional databases.
Cloud Computing Platforms: Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure offer scalable solutions capable of deploying geographically distributed redundant systems quickly—facilitating disaster recovery plans with minimal downtime.
Open-source Messaging Solutions: Tools such as Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ enable robust messaging architectures supporting event-driven communication between services with built-in fault tolerance features.
These innovations have lowered barriers for implementing comprehensive redundancy measures while improving overall system robustness against failures or cyber threats.
Risks Associated With Implementing Redundant Systems
While redundancy enhances reliability, it also introduces certain challenges:
Security Vulnerabilities: Expanding attack surfaces become a concern when multiple systems are interconnected; each additional component could potentially be exploited by malicious actors if not properly secured.
Higher Operational Costs: Maintaining duplicate hardware resources—including servers, storage solutions—and managing complex configurations require significant investment both financially and administratively.
Increased Complexity: Orchestrating synchronized operations across diverse systems demands sophisticated monitoring tools; failure to manage this complexity can lead to configuration errors that undermine reliability rather than enhance it.
Exchanges must carefully balance the benefits of redundancy against these potential drawbacks through rigorous security practices and efficient resource management strategies.
Examples From Leading Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Several prominent exchanges exemplify effective implementation of redundant API architectures:
Binance employs a combination of RESTful endpoints alongside WebSocket streams tailored specifically for high-frequency trading environments—a setup designed for maximum uptime even during extreme market volatility.
Coinbase has integrated blockchain technology into its infrastructure not only for transparency but also as part of its broader strategy toward immutable record keeping which supports auditability amidst operational redundancies.
Kraken uses advanced load balancing techniques across geographically dispersed servers ensuring uninterrupted service even under heavy user loads or regional disruptions.
These examples highlight how industry leaders prioritize system resilience through layered redundancies aligned with their operational needs.
Maintaining reliable exchange APIs requires ongoing attention toward implementing diverse forms of redundancy supported by modern technological advances while managing inherent risks effectively. As markets grow more competitive—and regulatory scrutiny intensifies—the importance placed on resilient infrastructure will continue rising among crypto platforms worldwide._


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-26 17:32
What redundancy exists for exchange APIs?
What Redundancy Exists for Exchange APIs?
In the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrency and financial markets, ensuring data reliability and system uptime is critical. Exchange APIs serve as the backbone for real-time trading, portfolio management, and market analysis. As such, redundancy in these APIs is essential to prevent data outages, maintain regulatory compliance, and support scalable operations. This article explores the various forms of redundancy implemented in exchange APIs, recent technological advancements supporting these efforts, and potential risks associated with redundant systems.
Types of Exchange APIs Supporting Redundancy
Exchange platforms typically utilize multiple API types to facilitate different aspects of data exchange and trading operations. The most common include RESTful APIs, WebSocket APIs, and GraphQL interfaces.
RESTful APIs are widely used due to their simplicity; they allow clients to request specific data at any given moment through standard HTTP methods. While reliable for static or less time-sensitive information like account details or historical data, they may not be optimal for real-time updates.
WebSocket APIs provide persistent connections that enable continuous streaming of market prices or trade events in real time. This makes them indispensable for traders who rely on instant updates to execute timely decisions.
GraphQL offers a flexible query language that allows clients to specify exactly what data they need from an API endpoint. This reduces unnecessary data transfer—an advantage when bandwidth or latency is a concern—and supports efficient redundant querying strategies.
Combining these API types enhances overall system resilience by providing multiple pathways for accessing critical market information.
Strategies Employed in Redundant API Systems
To ensure high availability and fault tolerance within exchange infrastructures, several redundancy strategies are commonly employed:
Load Balancing: Distributing incoming requests across multiple servers prevents any single point from becoming overwhelmed or failing under high traffic volumes. Load balancers can reroute traffic seamlessly if one server goes offline.
Caching: Frequently accessed data—such as current prices or order book snapshots—is stored temporarily in cache layers closer to users or applications. Caching reduces load on primary systems while delivering faster response times.
Backup Systems: Maintaining duplicate infrastructure components ensures continuity during outages. These backups can be activated automatically if primary systems encounter failures—often managed through automated failover protocols.
By integrating these strategies into their architecture design, exchanges improve both resilience against technical failures and capacity handling during peak periods.
Recent Technological Developments Enhancing Redundancy
The landscape of exchange API redundancy has been significantly influenced by emerging technologies:
Blockchain Integration: Many exchanges incorporate blockchain technology directly into their infrastructure to provide immutable transaction records that serve as an additional layer of verification beyond traditional databases.
Cloud Computing Platforms: Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure offer scalable solutions capable of deploying geographically distributed redundant systems quickly—facilitating disaster recovery plans with minimal downtime.
Open-source Messaging Solutions: Tools such as Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ enable robust messaging architectures supporting event-driven communication between services with built-in fault tolerance features.
These innovations have lowered barriers for implementing comprehensive redundancy measures while improving overall system robustness against failures or cyber threats.
Risks Associated With Implementing Redundant Systems
While redundancy enhances reliability, it also introduces certain challenges:
Security Vulnerabilities: Expanding attack surfaces become a concern when multiple systems are interconnected; each additional component could potentially be exploited by malicious actors if not properly secured.
Higher Operational Costs: Maintaining duplicate hardware resources—including servers, storage solutions—and managing complex configurations require significant investment both financially and administratively.
Increased Complexity: Orchestrating synchronized operations across diverse systems demands sophisticated monitoring tools; failure to manage this complexity can lead to configuration errors that undermine reliability rather than enhance it.
Exchanges must carefully balance the benefits of redundancy against these potential drawbacks through rigorous security practices and efficient resource management strategies.
Examples From Leading Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Several prominent exchanges exemplify effective implementation of redundant API architectures:
Binance employs a combination of RESTful endpoints alongside WebSocket streams tailored specifically for high-frequency trading environments—a setup designed for maximum uptime even during extreme market volatility.
Coinbase has integrated blockchain technology into its infrastructure not only for transparency but also as part of its broader strategy toward immutable record keeping which supports auditability amidst operational redundancies.
Kraken uses advanced load balancing techniques across geographically dispersed servers ensuring uninterrupted service even under heavy user loads or regional disruptions.
These examples highlight how industry leaders prioritize system resilience through layered redundancies aligned with their operational needs.
Maintaining reliable exchange APIs requires ongoing attention toward implementing diverse forms of redundancy supported by modern technological advances while managing inherent risks effectively. As markets grow more competitive—and regulatory scrutiny intensifies—the importance placed on resilient infrastructure will continue rising among crypto platforms worldwide._
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Coinbase Pro’s AML Policy?
Understanding Coinbase Pro’s Approach to Anti-Money Laundering Regulations
Coinbase Pro, one of the most prominent cryptocurrency exchanges globally, has established comprehensive Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies to ensure compliance with financial regulations and safeguard its users. These policies are vital in maintaining the integrity of the platform and fostering trust among users and regulators alike. This article explores what Coinbase Pro’s AML policy entails, why it is essential, and how it aligns with industry standards.
The Role of AML Policies in Cryptocurrency Exchanges
AML policies are designed to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, fraud, and other financial crimes. In traditional finance, these measures have long been standard; however, in the rapidly evolving world of digital assets like cryptocurrencies, they have become even more critical. Cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase Pro operate as gateways for users to buy, sell, and transfer digital currencies—making them attractive targets for illicit actors seeking to launder money or fund illegal operations.
Given this context, regulatory bodies worldwide—including the U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)—require cryptocurrency platforms to implement robust AML procedures. These include customer verification processes (KYC), transaction monitoring systems that flag suspicious activity, reporting mechanisms for authorities when necessary—and ongoing staff training on compliance protocols.
Key Components of Coinbase Pro's AML Policy
- Customer Verification (KYC)
Coinbase Pro mandates thorough Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures before allowing users access to its services fully. Users must submit personal identification documents such as passports or driver’s licenses during account registration or verification stages. This process helps establish user identities accurately—reducing anonymity that could facilitate illicit activities—and ensures compliance with legal requirements.
- Transaction Monitoring Systems
To detect potential money laundering schemes or suspicious transactions proactively—Coinbase Pro employs advanced transaction monitoring tools powered by machine learning algorithms and behavioral analysis techniques. These systems analyze transaction patterns over time—looking for red flags like unusual volume spikes or rapid transfers between accounts—to identify potentially illicit activity early on.
- Reporting Suspicious Activities
When a transaction raises suspicion based on predefined criteria or system alerts—Coinbase Pro is obligated under law to report these instances promptly to relevant authorities such as FinCEN through Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). Such transparency not only fulfills legal obligations but also demonstrates a commitment toward responsible operation within the crypto industry.
- Regular Audits & Risk Assessments
Ongoing audits help ensure that AML measures remain effective amid changing regulatory landscapes and technological advancements. Coinbase Pro conducts periodic reviews of its compliance programs—including risk assessments—to adapt swiftly when new threats emerge or regulations evolve.
- Staff Training & Education
An often-overlooked aspect is continuous staff training regarding AML policies and procedures—a crucial element in maintaining high standards across all operational levels within an exchange platform like Coinbase Pro.
Recent Developments Enhancing Compliance Standards
Over recent years—and especially following guidance issued by regulators—the landscape around AML regulation for virtual asset service providers (VASPs) has intensified significantly:
Regulatory Updates: The U.S Treasury Department's FinCEN issued clarifications in 2020 emphasizing VASPs' obligations under existing laws such as the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA). These updates reinforce mandatory KYC/AML practices across platforms.
Industry Guidelines: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an international body setting global standards against money laundering—has issued guidelines urging VASPs worldwide—including exchanges like Coinbase—to adopt comprehensive KYC/AML frameworks.
Technological Innovations: To stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated criminal tactics—which include layering transactions across multiple accounts—the exchange leverages cutting-edge technology including machine learning models capable of analyzing vast amounts of data efficiently.
Industry Collaboration & Transparency: By collaborating with other market players—as well as engaging openly with regulators—Coinbase Pro demonstrates leadership within the crypto community committed to ethical standards.
Risks Associated With Non-Compliance
Failing to adhere strictly to AML regulations can lead not only to hefty fines but also severe reputational damage:
Legal Penalties: Non-compliance may result in substantial fines from regulatory agencies; repeated violations could even lead license revocations.
Damage To Reputation: Public scrutiny over perceived lapses can erode user trust—a critical factor given how heavily consumers rely on security assurances when choosing a crypto platform.
Operational Challenges: Smaller exchanges might struggle more due to limited resources; however larger entities like Coinbase have dedicated teams investing heavily into advanced compliance infrastructure.
Evolving Regulations: As governments tighten rules around cryptocurrencies—for example through stricter reporting requirements—they must continuously update their policies accordingly.
Why Robust AML Policies Matter For Crypto Users And Investors
For individuals using platforms like Coinbase Pro—or considering doing so—it’s reassuring knowing that strict anti-money laundering measures are actively enforced behind-the-scenes:
• Enhanced Security – Rigorous KYC reduces identity theft risks while deterring malicious actors from exploiting user accounts
• Greater Trustworthiness – Transparent reporting practices foster confidence among investors who want assurance their funds aren’t being used illegally
• Regulatory Compliance – Ensures your assets are protected under legal frameworks which support long-term growth
• Industry Leadership – Platforms committed fully comply set higher standards that benefit all participants
Maintaining Effective Compliance Amid Rapid Change
As cryptocurrency markets continue expanding—with new tokens emerging regularly—and regulatory environments becoming more complex—it remains imperative for exchanges like Coinbase Pro continually refine their AML strategies:
Stay updated on global guidelines from FATF and local regulators
Invest in technological upgrades including AI-driven monitoring tools
Conduct regular staff training sessions
Engage proactively with industry peers and policymakers
Adapt swiftly whenever new legislation comes into effect
By doing so—with a focus on transparency and responsibility—they can uphold high standards while supporting innovation within a secure framework.
How Does CoinBase Protect Its Users Through Its AML Policy?
Through rigorous customer verification processes combined with sophisticated transaction monitoring systems—Coinbase ensures that only legitimate users access its services while minimizing risks associated with illicit activities . Additionally,
– Continuous staff education keeps employees aware of emerging threats
– Prompt reporting mechanisms enable swift action against suspicious behavior
– Regular audits verify ongoing effectiveness
This multi-layered approach underscores their commitment not just legally but ethically—to create a safer environment for everyone involved.
The Future Outlook For Cryptocurrency Exchanges And Their Compliance Strategies
Looking ahead—in light of increasing regulation globally—the importance of strong anti-money laundering frameworks will only grow stronger . As authorities introduce stricter rules aimed at curbing illegal use cases involving cryptocurrencies,
exchanges will need innovative solutions—from blockchain analytics tools to decentralized identity verification methods—to stay compliant without stifling innovation .
Platforms adopting proactive strategies today will be better positioned tomorrow—not just legally but also competitively—in building trust among users worldwide.
Summary
In essence — understanding what constitutes Coinbase pro’s AML policy reveals how seriously they take their role in preventing financial crimes within the crypto space . From rigorous customer checks through advanced transaction analysis—all designed according to evolving regulations—they exemplify best practices needed today by any compliant digital asset platform aiming at sustainability , security ,and reputation management.
Keywords: coinbase pro aml policy | cryptocurrency exchange aml | virtual asset service provider aml | KYC procedures coinbase pro | anti-money laundering crypto | fintech compliance best practices


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-26 15:28
What is Coinbase Pro’s AML policy?
What Is Coinbase Pro’s AML Policy?
Understanding Coinbase Pro’s Approach to Anti-Money Laundering Regulations
Coinbase Pro, one of the most prominent cryptocurrency exchanges globally, has established comprehensive Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies to ensure compliance with financial regulations and safeguard its users. These policies are vital in maintaining the integrity of the platform and fostering trust among users and regulators alike. This article explores what Coinbase Pro’s AML policy entails, why it is essential, and how it aligns with industry standards.
The Role of AML Policies in Cryptocurrency Exchanges
AML policies are designed to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, fraud, and other financial crimes. In traditional finance, these measures have long been standard; however, in the rapidly evolving world of digital assets like cryptocurrencies, they have become even more critical. Cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase Pro operate as gateways for users to buy, sell, and transfer digital currencies—making them attractive targets for illicit actors seeking to launder money or fund illegal operations.
Given this context, regulatory bodies worldwide—including the U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)—require cryptocurrency platforms to implement robust AML procedures. These include customer verification processes (KYC), transaction monitoring systems that flag suspicious activity, reporting mechanisms for authorities when necessary—and ongoing staff training on compliance protocols.
Key Components of Coinbase Pro's AML Policy
- Customer Verification (KYC)
Coinbase Pro mandates thorough Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures before allowing users access to its services fully. Users must submit personal identification documents such as passports or driver’s licenses during account registration or verification stages. This process helps establish user identities accurately—reducing anonymity that could facilitate illicit activities—and ensures compliance with legal requirements.
- Transaction Monitoring Systems
To detect potential money laundering schemes or suspicious transactions proactively—Coinbase Pro employs advanced transaction monitoring tools powered by machine learning algorithms and behavioral analysis techniques. These systems analyze transaction patterns over time—looking for red flags like unusual volume spikes or rapid transfers between accounts—to identify potentially illicit activity early on.
- Reporting Suspicious Activities
When a transaction raises suspicion based on predefined criteria or system alerts—Coinbase Pro is obligated under law to report these instances promptly to relevant authorities such as FinCEN through Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). Such transparency not only fulfills legal obligations but also demonstrates a commitment toward responsible operation within the crypto industry.
- Regular Audits & Risk Assessments
Ongoing audits help ensure that AML measures remain effective amid changing regulatory landscapes and technological advancements. Coinbase Pro conducts periodic reviews of its compliance programs—including risk assessments—to adapt swiftly when new threats emerge or regulations evolve.
- Staff Training & Education
An often-overlooked aspect is continuous staff training regarding AML policies and procedures—a crucial element in maintaining high standards across all operational levels within an exchange platform like Coinbase Pro.
Recent Developments Enhancing Compliance Standards
Over recent years—and especially following guidance issued by regulators—the landscape around AML regulation for virtual asset service providers (VASPs) has intensified significantly:
Regulatory Updates: The U.S Treasury Department's FinCEN issued clarifications in 2020 emphasizing VASPs' obligations under existing laws such as the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA). These updates reinforce mandatory KYC/AML practices across platforms.
Industry Guidelines: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an international body setting global standards against money laundering—has issued guidelines urging VASPs worldwide—including exchanges like Coinbase—to adopt comprehensive KYC/AML frameworks.
Technological Innovations: To stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated criminal tactics—which include layering transactions across multiple accounts—the exchange leverages cutting-edge technology including machine learning models capable of analyzing vast amounts of data efficiently.
Industry Collaboration & Transparency: By collaborating with other market players—as well as engaging openly with regulators—Coinbase Pro demonstrates leadership within the crypto community committed to ethical standards.
Risks Associated With Non-Compliance
Failing to adhere strictly to AML regulations can lead not only to hefty fines but also severe reputational damage:
Legal Penalties: Non-compliance may result in substantial fines from regulatory agencies; repeated violations could even lead license revocations.
Damage To Reputation: Public scrutiny over perceived lapses can erode user trust—a critical factor given how heavily consumers rely on security assurances when choosing a crypto platform.
Operational Challenges: Smaller exchanges might struggle more due to limited resources; however larger entities like Coinbase have dedicated teams investing heavily into advanced compliance infrastructure.
Evolving Regulations: As governments tighten rules around cryptocurrencies—for example through stricter reporting requirements—they must continuously update their policies accordingly.
Why Robust AML Policies Matter For Crypto Users And Investors
For individuals using platforms like Coinbase Pro—or considering doing so—it’s reassuring knowing that strict anti-money laundering measures are actively enforced behind-the-scenes:
• Enhanced Security – Rigorous KYC reduces identity theft risks while deterring malicious actors from exploiting user accounts
• Greater Trustworthiness – Transparent reporting practices foster confidence among investors who want assurance their funds aren’t being used illegally
• Regulatory Compliance – Ensures your assets are protected under legal frameworks which support long-term growth
• Industry Leadership – Platforms committed fully comply set higher standards that benefit all participants
Maintaining Effective Compliance Amid Rapid Change
As cryptocurrency markets continue expanding—with new tokens emerging regularly—and regulatory environments becoming more complex—it remains imperative for exchanges like Coinbase Pro continually refine their AML strategies:
Stay updated on global guidelines from FATF and local regulators
Invest in technological upgrades including AI-driven monitoring tools
Conduct regular staff training sessions
Engage proactively with industry peers and policymakers
Adapt swiftly whenever new legislation comes into effect
By doing so—with a focus on transparency and responsibility—they can uphold high standards while supporting innovation within a secure framework.
How Does CoinBase Protect Its Users Through Its AML Policy?
Through rigorous customer verification processes combined with sophisticated transaction monitoring systems—Coinbase ensures that only legitimate users access its services while minimizing risks associated with illicit activities . Additionally,
– Continuous staff education keeps employees aware of emerging threats
– Prompt reporting mechanisms enable swift action against suspicious behavior
– Regular audits verify ongoing effectiveness
This multi-layered approach underscores their commitment not just legally but ethically—to create a safer environment for everyone involved.
The Future Outlook For Cryptocurrency Exchanges And Their Compliance Strategies
Looking ahead—in light of increasing regulation globally—the importance of strong anti-money laundering frameworks will only grow stronger . As authorities introduce stricter rules aimed at curbing illegal use cases involving cryptocurrencies,
exchanges will need innovative solutions—from blockchain analytics tools to decentralized identity verification methods—to stay compliant without stifling innovation .
Platforms adopting proactive strategies today will be better positioned tomorrow—not just legally but also competitively—in building trust among users worldwide.
Summary
In essence — understanding what constitutes Coinbase pro’s AML policy reveals how seriously they take their role in preventing financial crimes within the crypto space . From rigorous customer checks through advanced transaction analysis—all designed according to evolving regulations—they exemplify best practices needed today by any compliant digital asset platform aiming at sustainability , security ,and reputation management.
Keywords: coinbase pro aml policy | cryptocurrency exchange aml | virtual asset service provider aml | KYC procedures coinbase pro | anti-money laundering crypto | fintech compliance best practices
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Avoid Confirmation Bias in Financial Decision-Making
Confirmation bias is a common cognitive pitfall that can significantly impair investment judgment. Recognizing and mitigating this bias is essential for making informed, rational financial decisions. This guide explores practical strategies to help investors and financial professionals avoid confirmation bias, thereby enhancing decision quality and reducing exposure to market volatility.
Understanding Confirmation Bias in Finance
Confirmation bias occurs when individuals favor information that supports their preexisting beliefs while disregarding evidence that contradicts them. In finance, this tendency can lead investors to interpret data selectively, reinforcing their existing opinions about particular stocks, sectors, or market trends. For example, an investor convinced of a stock’s potential might ignore warning signs like declining earnings or industry downturns, leading to overconfidence and potentially costly mistakes.
This bias is especially prevalent during volatile markets or speculative environments such as cryptocurrencies or trending stocks on social media platforms. The ease of access to information—both accurate and misleading—can further entrench confirmation biases if not critically evaluated.
Why Avoiding Confirmation Bias Matters
Failing to recognize confirmation bias can result in poor investment outcomes. Investors may hold onto losing positions longer than advisable or miss opportunities by dismissing emerging evidence contrary to their views. Overconfidence fueled by biased information processing also increases the risk of significant financial losses during market downturns.
Moreover, regulatory bodies increasingly emphasize transparency and due diligence as part of investor protection initiatives. Cultivating awareness about cognitive biases like confirmation bias aligns with best practices for responsible investing.
Practical Strategies for Mitigating Confirmation Bias
Implementing specific tactics can help investors develop a more balanced approach:
1. Diversify Your Information Sources
Relying on a single news outlet or social media echo chamber amplifies confirmation bias risks. Seek out multiple perspectives from reputable sources—including financial news outlets, analyst reports, economic research papers, and independent expert opinions—to gain a comprehensive view of the market landscape.
2. Regularly Review Your Investment Assumptions
Set periodic reviews of your investment thesis based on new data rather than sticking rigidly to initial beliefs. Ask yourself whether recent developments support your original assumptions or suggest reconsideration.
3. Engage in Critical Thinking
Challenge your own viewpoints actively by asking questions such as:
- What evidence contradicts my current belief?
- Are there alternative explanations for recent market movements?
- What are the risks I might be overlooking?
Encouraging critical analysis helps prevent tunnel vision driven by biases.
4. Use Decision-Making Frameworks
Structured tools like decision trees or scenario planning enable systematic evaluation of different outcomes under various conditions:
- Decision Trees: Map out possible choices along with potential consequences.
- Scenario Planning: Consider best-case, worst-case, and most-likely scenarios before acting.These methods promote objective analysis over emotional reactions rooted in biases.
5. Seek Objective Professional Advice
Consult with qualified financial advisors who are trained to provide unbiased guidance based on data-driven insights rather than personal beliefs or herd mentality tendencies.
Incorporating Cognitive Awareness into Investment Practices
Beyond tactical measures—such as diversifying sources and structured decision-making—investors should cultivate an ongoing awareness of cognitive biases through education:
- Attend workshops focused on behavioral finance.
- Read literature highlighting common pitfalls like loss aversion (fear of losing money) and the endowment effect (overvaluing owned assets).This knowledge fosters mindfulness about one’s thought processes during critical decision points.
Leveraging Technology Responsibly
The rise of algorithmic trading tools offers both opportunities and challenges regarding confirmation bias:
- Properly designed algorithms can reduce human emotional influence but may reinforce existing biases if built without safeguards.
- Regular audits and validation checks ensure these tools operate objectively.Investors should understand how AI-driven insights are generated rather than blindly trusting automated outputs alone.
Promoting Transparency & Education
Financial literacy initiatives increasingly emphasize understanding psychological factors affecting investing behavior:
- Educational programs now include modules on cognitive biases.
- Regulatory agencies advocate for transparent disclosure practices that encourage diversified viewpoints among investors.By fostering an environment where questioning assumptions is normalized—and supported through accessible resources—markets become more resilient against collective herding behaviors driven by confirmation bias.
Final Thoughts: Building Better Investment Habits
Avoiding confirmation bias requires conscious effort but yields substantial benefits: improved decision-making accuracy, reduced susceptibility to market swings caused by herd mentality—or overconfidence—and ultimately better long-term investment performance. Developing habits such as seeking diverse perspectives regularly reviewing one's assumptions ensures you remain adaptable amid changing economic conditions.
Investors who prioritize continuous learning about behavioral finance principles position themselves advantageously against common psychological pitfalls like confirmation bias—a crucial step toward achieving sustainable wealth growth while maintaining rationality amidst volatile markets.
Keywords: Confirmation Bias Prevention | Financial Decision-Making Strategies | Avoid Investing Mistakes | Behavioral Finance Tips | Market Volatility Management


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-19 23:44
How to avoid confirmation bias?
How to Avoid Confirmation Bias in Financial Decision-Making
Confirmation bias is a common cognitive pitfall that can significantly impair investment judgment. Recognizing and mitigating this bias is essential for making informed, rational financial decisions. This guide explores practical strategies to help investors and financial professionals avoid confirmation bias, thereby enhancing decision quality and reducing exposure to market volatility.
Understanding Confirmation Bias in Finance
Confirmation bias occurs when individuals favor information that supports their preexisting beliefs while disregarding evidence that contradicts them. In finance, this tendency can lead investors to interpret data selectively, reinforcing their existing opinions about particular stocks, sectors, or market trends. For example, an investor convinced of a stock’s potential might ignore warning signs like declining earnings or industry downturns, leading to overconfidence and potentially costly mistakes.
This bias is especially prevalent during volatile markets or speculative environments such as cryptocurrencies or trending stocks on social media platforms. The ease of access to information—both accurate and misleading—can further entrench confirmation biases if not critically evaluated.
Why Avoiding Confirmation Bias Matters
Failing to recognize confirmation bias can result in poor investment outcomes. Investors may hold onto losing positions longer than advisable or miss opportunities by dismissing emerging evidence contrary to their views. Overconfidence fueled by biased information processing also increases the risk of significant financial losses during market downturns.
Moreover, regulatory bodies increasingly emphasize transparency and due diligence as part of investor protection initiatives. Cultivating awareness about cognitive biases like confirmation bias aligns with best practices for responsible investing.
Practical Strategies for Mitigating Confirmation Bias
Implementing specific tactics can help investors develop a more balanced approach:
1. Diversify Your Information Sources
Relying on a single news outlet or social media echo chamber amplifies confirmation bias risks. Seek out multiple perspectives from reputable sources—including financial news outlets, analyst reports, economic research papers, and independent expert opinions—to gain a comprehensive view of the market landscape.
2. Regularly Review Your Investment Assumptions
Set periodic reviews of your investment thesis based on new data rather than sticking rigidly to initial beliefs. Ask yourself whether recent developments support your original assumptions or suggest reconsideration.
3. Engage in Critical Thinking
Challenge your own viewpoints actively by asking questions such as:
- What evidence contradicts my current belief?
- Are there alternative explanations for recent market movements?
- What are the risks I might be overlooking?
Encouraging critical analysis helps prevent tunnel vision driven by biases.
4. Use Decision-Making Frameworks
Structured tools like decision trees or scenario planning enable systematic evaluation of different outcomes under various conditions:
- Decision Trees: Map out possible choices along with potential consequences.
- Scenario Planning: Consider best-case, worst-case, and most-likely scenarios before acting.These methods promote objective analysis over emotional reactions rooted in biases.
5. Seek Objective Professional Advice
Consult with qualified financial advisors who are trained to provide unbiased guidance based on data-driven insights rather than personal beliefs or herd mentality tendencies.
Incorporating Cognitive Awareness into Investment Practices
Beyond tactical measures—such as diversifying sources and structured decision-making—investors should cultivate an ongoing awareness of cognitive biases through education:
- Attend workshops focused on behavioral finance.
- Read literature highlighting common pitfalls like loss aversion (fear of losing money) and the endowment effect (overvaluing owned assets).This knowledge fosters mindfulness about one’s thought processes during critical decision points.
Leveraging Technology Responsibly
The rise of algorithmic trading tools offers both opportunities and challenges regarding confirmation bias:
- Properly designed algorithms can reduce human emotional influence but may reinforce existing biases if built without safeguards.
- Regular audits and validation checks ensure these tools operate objectively.Investors should understand how AI-driven insights are generated rather than blindly trusting automated outputs alone.
Promoting Transparency & Education
Financial literacy initiatives increasingly emphasize understanding psychological factors affecting investing behavior:
- Educational programs now include modules on cognitive biases.
- Regulatory agencies advocate for transparent disclosure practices that encourage diversified viewpoints among investors.By fostering an environment where questioning assumptions is normalized—and supported through accessible resources—markets become more resilient against collective herding behaviors driven by confirmation bias.
Final Thoughts: Building Better Investment Habits
Avoiding confirmation bias requires conscious effort but yields substantial benefits: improved decision-making accuracy, reduced susceptibility to market swings caused by herd mentality—or overconfidence—and ultimately better long-term investment performance. Developing habits such as seeking diverse perspectives regularly reviewing one's assumptions ensures you remain adaptable amid changing economic conditions.
Investors who prioritize continuous learning about behavioral finance principles position themselves advantageously against common psychological pitfalls like confirmation bias—a crucial step toward achieving sustainable wealth growth while maintaining rationality amidst volatile markets.
Keywords: Confirmation Bias Prevention | Financial Decision-Making Strategies | Avoid Investing Mistakes | Behavioral Finance Tips | Market Volatility Management
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Should You Verify Before Sending a Cryptocurrency Transaction?
When engaging in cryptocurrency transactions, ensuring the accuracy and legitimacy of each transfer is vital to protect your assets and maintain financial safety. Unlike traditional banking, crypto transactions are irreversible once confirmed, making thorough verification essential. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of what you need to verify before sending a transaction, emphasizing best practices rooted in blockchain security principles.
Confirm the Recipient’s Wallet Address
One of the most critical steps before initiating any crypto transfer is verifying the recipient's wallet address. Blockchain addresses are long strings of alphanumeric characters that uniquely identify digital wallets. Due to their complexity, even minor errors can lead to lost funds or sending assets to unintended recipients.
Always double-check the address by copying and pasting it directly from trusted sources or scanning QR codes when available. Avoid manual entry unless necessary, as typos are common causes of transaction failures or asset loss. Some users employ checksum mechanisms embedded within certain address formats (like Bech32 for Bitcoin) that help detect invalid addresses automatically.
Validate Transaction Details: Amount and Currency
Before confirming a transaction, ensure that the amount you intend to send matches your intention precisely. Mistakes in specifying amounts can lead to significant financial discrepancies—sending too much or too little can be costly.
Additionally, verify that you're selecting the correct cryptocurrency token if dealing with multiple assets on one platform (e.g., ETH vs. ERC-20 tokens). Confirming these details prevents accidental transfers across different tokens or networks where they might not be compatible.
Check Network Compatibility and Fees
Different cryptocurrencies operate on distinct blockchains with unique protocols; therefore, verifying network compatibility is crucial—sending Bitcoin on an Ethereum network would result in failure or loss of funds. Ensure you're using the correct network for your transaction type.
Transaction fees vary depending on network congestion; higher fees typically mean faster confirmation times but also increased costs. Use reputable blockchain explorers or fee estimation tools (like those integrated into wallets) to determine appropriate fee levels based on current conditions—this helps avoid delays caused by underfunded transactions.
Verify Digital Signatures and Authentication
Cryptocurrency transactions rely heavily on cryptographic signatures for validation purposes. When you initiate a transfer from your wallet, it must be signed with your private key—a process ensuring authenticity and authorization.
Ensure that your wallet software correctly signs transactions without errors before submission. If using third-party services or exchanges, confirm they employ secure signing processes compliant with industry standards like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and hardware security modules (HSMs).
Conduct Due Diligence Against Scams
Crypto scams such as phishing attacks often target users during transaction processes by impersonating legitimate entities through fake websites or malicious links. Always verify you're interacting with official platforms—check URLs carefully for typos or suspicious domains—and avoid sharing sensitive information like private keys.
Research recipient addresses when possible—especially if receiving funds from unknown parties—to confirm their legitimacy through blockchain explorers which display associated activity history if publicly available.
Use Secure Wallets and Storage Practices
Your wallet’s security directly impacts transaction safety; weak passwords, unsecured devices, or compromised private keys increase vulnerability risks during transfers. Employ strong passwords combined with two-factor authentication (2FA), hardware wallets for large sums, and keep backup seed phrases stored securely offline away from potential threats like malware infections.
Regularly update wallet software to patch vulnerabilities identified through security audits; this proactive approach minimizes exposure during critical operations such as sending transactions.
Leverage Blockchain Explorers for Transparency
Blockchain explorers serve as invaluable tools allowing users to track their pending and confirmed transactions transparently in real-time—for example: Etherscan for Ethereum-based tokens or Blockchain.com for Bitcoin networks.By entering your transaction ID (hash), you can verify whether it has been included in a block yet—and monitor confirmation counts which influence settlement finality.This transparency helps build confidence that you've sent funds correctly while providing proof-of-transaction should disputes arise later.
Final Tips: Best Practices Before Sending Crypto Transactions
- Double-check all details — recipient address, amount, currency.
- Use reputable wallets equipped with robust security features.
- Verify network conditions — fees & congestion levels.
- Confirm signatures have been properly applied via secure signing methods.
- Stay vigilant against scams — always authenticate sources before proceeding.
- Monitor via blockchain explorers until confirmation completes.
By adhering to these verification steps rooted in blockchain technology's core principles of cryptography & decentralization—and staying vigilant against common pitfalls—you significantly reduce risks associated with crypto transfers while safeguarding your digital assets effectively.
References
- "Blockchain Security: A Comprehensive Guide" by Blockchain Council
2."Smart Contracts: The Future of Blockchain" by CoinDesk
3."How Blockchain Transactions Are Verified" by Investopedia
4."Blockchain Explorer: A Tool for Transparency" by CryptoSlate
5."Due Diligence in Crypto Transactions" by Coindoo
6."Wallet Security Best Practices" by Binance Academy
7."Layer 2 Solutions: Enhancing Blockchain Scalability" by The Block
8."Regulatory Clarity in Crypto: A Global Perspective" by Forbes
9."Crypto Scams: How to Avoid Them" by Cointelegraph
10.“Smart Contract Security Risks” by Medium


kai
2025-05-15 00:48
What should you verify before sending a transaction?
What Should You Verify Before Sending a Cryptocurrency Transaction?
When engaging in cryptocurrency transactions, ensuring the accuracy and legitimacy of each transfer is vital to protect your assets and maintain financial safety. Unlike traditional banking, crypto transactions are irreversible once confirmed, making thorough verification essential. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of what you need to verify before sending a transaction, emphasizing best practices rooted in blockchain security principles.
Confirm the Recipient’s Wallet Address
One of the most critical steps before initiating any crypto transfer is verifying the recipient's wallet address. Blockchain addresses are long strings of alphanumeric characters that uniquely identify digital wallets. Due to their complexity, even minor errors can lead to lost funds or sending assets to unintended recipients.
Always double-check the address by copying and pasting it directly from trusted sources or scanning QR codes when available. Avoid manual entry unless necessary, as typos are common causes of transaction failures or asset loss. Some users employ checksum mechanisms embedded within certain address formats (like Bech32 for Bitcoin) that help detect invalid addresses automatically.
Validate Transaction Details: Amount and Currency
Before confirming a transaction, ensure that the amount you intend to send matches your intention precisely. Mistakes in specifying amounts can lead to significant financial discrepancies—sending too much or too little can be costly.
Additionally, verify that you're selecting the correct cryptocurrency token if dealing with multiple assets on one platform (e.g., ETH vs. ERC-20 tokens). Confirming these details prevents accidental transfers across different tokens or networks where they might not be compatible.
Check Network Compatibility and Fees
Different cryptocurrencies operate on distinct blockchains with unique protocols; therefore, verifying network compatibility is crucial—sending Bitcoin on an Ethereum network would result in failure or loss of funds. Ensure you're using the correct network for your transaction type.
Transaction fees vary depending on network congestion; higher fees typically mean faster confirmation times but also increased costs. Use reputable blockchain explorers or fee estimation tools (like those integrated into wallets) to determine appropriate fee levels based on current conditions—this helps avoid delays caused by underfunded transactions.
Verify Digital Signatures and Authentication
Cryptocurrency transactions rely heavily on cryptographic signatures for validation purposes. When you initiate a transfer from your wallet, it must be signed with your private key—a process ensuring authenticity and authorization.
Ensure that your wallet software correctly signs transactions without errors before submission. If using third-party services or exchanges, confirm they employ secure signing processes compliant with industry standards like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and hardware security modules (HSMs).
Conduct Due Diligence Against Scams
Crypto scams such as phishing attacks often target users during transaction processes by impersonating legitimate entities through fake websites or malicious links. Always verify you're interacting with official platforms—check URLs carefully for typos or suspicious domains—and avoid sharing sensitive information like private keys.
Research recipient addresses when possible—especially if receiving funds from unknown parties—to confirm their legitimacy through blockchain explorers which display associated activity history if publicly available.
Use Secure Wallets and Storage Practices
Your wallet’s security directly impacts transaction safety; weak passwords, unsecured devices, or compromised private keys increase vulnerability risks during transfers. Employ strong passwords combined with two-factor authentication (2FA), hardware wallets for large sums, and keep backup seed phrases stored securely offline away from potential threats like malware infections.
Regularly update wallet software to patch vulnerabilities identified through security audits; this proactive approach minimizes exposure during critical operations such as sending transactions.
Leverage Blockchain Explorers for Transparency
Blockchain explorers serve as invaluable tools allowing users to track their pending and confirmed transactions transparently in real-time—for example: Etherscan for Ethereum-based tokens or Blockchain.com for Bitcoin networks.By entering your transaction ID (hash), you can verify whether it has been included in a block yet—and monitor confirmation counts which influence settlement finality.This transparency helps build confidence that you've sent funds correctly while providing proof-of-transaction should disputes arise later.
Final Tips: Best Practices Before Sending Crypto Transactions
- Double-check all details — recipient address, amount, currency.
- Use reputable wallets equipped with robust security features.
- Verify network conditions — fees & congestion levels.
- Confirm signatures have been properly applied via secure signing methods.
- Stay vigilant against scams — always authenticate sources before proceeding.
- Monitor via blockchain explorers until confirmation completes.
By adhering to these verification steps rooted in blockchain technology's core principles of cryptography & decentralization—and staying vigilant against common pitfalls—you significantly reduce risks associated with crypto transfers while safeguarding your digital assets effectively.
References
- "Blockchain Security: A Comprehensive Guide" by Blockchain Council
2."Smart Contracts: The Future of Blockchain" by CoinDesk
3."How Blockchain Transactions Are Verified" by Investopedia
4."Blockchain Explorer: A Tool for Transparency" by CryptoSlate
5."Due Diligence in Crypto Transactions" by Coindoo
6."Wallet Security Best Practices" by Binance Academy
7."Layer 2 Solutions: Enhancing Blockchain Scalability" by The Block
8."Regulatory Clarity in Crypto: A Global Perspective" by Forbes
9."Crypto Scams: How to Avoid Them" by Cointelegraph
10.“Smart Contract Security Risks” by Medium
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Fundamental Analysis of a Crypto Asset?
Understanding the true value of a cryptocurrency is essential for making informed investment decisions. Fundamental analysis (FA) offers a comprehensive approach to evaluating crypto assets by examining their intrinsic qualities, rather than relying solely on price movements or technical charts. This method helps investors identify potential long-term growth opportunities and assess risks associated with digital assets.
What Does Fundamental Analysis Involve in Cryptocurrency?
Fundamental analysis in the crypto space involves scrutinizing various factors that influence an asset’s value. Unlike traditional stocks, cryptocurrencies are unique due to their decentralized nature, technological features, and evolving regulatory landscape. Therefore, FA for crypto combines financial metrics with project-specific details and external environment factors.
Key areas include:
- Economic Indicators: Metrics such as market capitalization, trading volume, and liquidity provide insights into the overall size and activity level of a cryptocurrency.
- Project Fundamentals: The core team behind the project, its development roadmap, partnerships, and use cases shape its potential for future success.
- Regulatory Environment: Legal frameworks can significantly impact adoption rates and market stability.
- Adoption & Use Cases: Widespread acceptance by users or businesses enhances utility and long-term viability.
- Security & Scalability: Robust blockchain technology capable of handling growth ensures sustainability.
By analyzing these components collectively, investors can gauge whether a crypto asset is undervalued or overhyped based on its underlying strengths.
Why Is Fundamental Analysis Important for Crypto Investors?
Crypto markets are known for their volatility—prices can swing dramatically within short periods due to news events or speculative trading. While technical analysis helps predict short-term price movements based on historical data, fundamental analysis provides insight into an asset’s inherent worth. This perspective enables investors to differentiate between hype-driven tokens and those with solid fundamentals that could appreciate over time.
Moreover, as institutional interest in cryptocurrencies increases—alongside regulatory clarity—the importance of FA grows. It allows investors to evaluate whether an asset aligns with broader economic trends or technological advancements that could influence its long-term success.
Key Factors Assessed During Crypto Fundamental Analysis
Market Capitalization
Market cap reflects the total value of all circulating coins or tokens; it indicates how established an asset is within the ecosystem. Larger market caps often correlate with greater stability but may also suggest slower growth compared to smaller-cap projects which might have higher risk but more significant upside potential.
Trading Volume & Liquidity
High trading volumes imply active markets where buying or selling large amounts won’t drastically affect prices—a crucial aspect for traders seeking flexibility without risking substantial slippage.
Project Team & Development Roadmap
The experience level of developers influences confidence in project delivery. A transparent roadmap outlining upcoming milestones reassures investors about future progress while partnerships with reputable organizations can add credibility.
Regulatory Environment
Legal clarity reduces uncertainty around compliance costs or restrictions that could hinder adoption efforts—especially important given varying regulations across jurisdictions worldwide.
Adoption & Use Cases
A cryptocurrency’s real-world utility depends heavily on user engagement and business integration; widespread adoption often translates into increased demand which supports valuation growth over time.
Security & Scalability Features
Blockchain security mechanisms like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) ensure network integrity against malicious attacks. Additionally, scalability solutions address transaction speed limitations critical during mass adoption phases.
Recent Trends Enhancing Crypto Fundamental Analysis
Recent developments have made fundamental analysis more relevant than ever:
- Institutional Investment Growth: Large financial institutions entering crypto markets bring rigorous evaluation standards similar to traditional finance.
- Regulatory Clarity: Governments providing clearer guidelines help reduce uncertainties around legal compliance.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements such as layer 2 scaling solutions increase transaction speeds while maintaining security.
- Growing Adoption: More companies accepting cryptocurrencies as payment options expand real-world use cases.
- Market Volatility Awareness: Recognizing external factors influencing prices aids in better risk management strategies.
Risks That Can Affect Cryptocurrency Valuations
While fundamental analysis aims at identifying promising assets based on intrinsic qualities, several risks remain:
Regulatory Risks: Sudden policy changes may restrict usage rights or impose compliance costs leading to declines in valuation.
Security Vulnerabilities: Flaws within blockchain protocols could be exploited by hackers causing losses or eroding trust among users.
Market Manipulation: Lack of centralized oversight makes some tokens susceptible to pump-and-dump schemes affecting price stability temporarily.
Technological Challenges: Issues like limited scalability might prevent widespread adoption despite strong fundamentals.
How Investors Can Use Fundamental Analysis Effectively
To leverage FA effectively when investing in cryptocurrencies:
- Conduct thorough research into project whitepapers detailing technology goals and use cases.
- Evaluate team backgrounds through professional profiles like LinkedIn; experienced teams tend to execute better plans.
- Monitor regulatory updates across key markets impacting your chosen assets’ legality status.
- Observe community engagement levels—active developer communities often indicate ongoing innovation efforts.5.Gauge partnership announcements from reputable firms signaling strategic growth opportunities.
By combining these insights with ongoing market observations—and balancing them against technical signals—investors can develop well-rounded perspectives suited for both short-term trades and long-term holdings.
In essence, understanding what constitutes fundamental analysis within cryptocurrency investments equips you with tools necessary for making smarter decisions amid volatile markets—and positions you better prepared for emerging opportunities driven by technological progress and evolving regulations alike.
Note: Always remember that no single metric guarantees investment success; instead focus on holistic evaluation aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals.*


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-11 13:41
What is fundamental analysis of a crypto asset?
What Is Fundamental Analysis of a Crypto Asset?
Understanding the true value of a cryptocurrency is essential for making informed investment decisions. Fundamental analysis (FA) offers a comprehensive approach to evaluating crypto assets by examining their intrinsic qualities, rather than relying solely on price movements or technical charts. This method helps investors identify potential long-term growth opportunities and assess risks associated with digital assets.
What Does Fundamental Analysis Involve in Cryptocurrency?
Fundamental analysis in the crypto space involves scrutinizing various factors that influence an asset’s value. Unlike traditional stocks, cryptocurrencies are unique due to their decentralized nature, technological features, and evolving regulatory landscape. Therefore, FA for crypto combines financial metrics with project-specific details and external environment factors.
Key areas include:
- Economic Indicators: Metrics such as market capitalization, trading volume, and liquidity provide insights into the overall size and activity level of a cryptocurrency.
- Project Fundamentals: The core team behind the project, its development roadmap, partnerships, and use cases shape its potential for future success.
- Regulatory Environment: Legal frameworks can significantly impact adoption rates and market stability.
- Adoption & Use Cases: Widespread acceptance by users or businesses enhances utility and long-term viability.
- Security & Scalability: Robust blockchain technology capable of handling growth ensures sustainability.
By analyzing these components collectively, investors can gauge whether a crypto asset is undervalued or overhyped based on its underlying strengths.
Why Is Fundamental Analysis Important for Crypto Investors?
Crypto markets are known for their volatility—prices can swing dramatically within short periods due to news events or speculative trading. While technical analysis helps predict short-term price movements based on historical data, fundamental analysis provides insight into an asset’s inherent worth. This perspective enables investors to differentiate between hype-driven tokens and those with solid fundamentals that could appreciate over time.
Moreover, as institutional interest in cryptocurrencies increases—alongside regulatory clarity—the importance of FA grows. It allows investors to evaluate whether an asset aligns with broader economic trends or technological advancements that could influence its long-term success.
Key Factors Assessed During Crypto Fundamental Analysis
Market Capitalization
Market cap reflects the total value of all circulating coins or tokens; it indicates how established an asset is within the ecosystem. Larger market caps often correlate with greater stability but may also suggest slower growth compared to smaller-cap projects which might have higher risk but more significant upside potential.
Trading Volume & Liquidity
High trading volumes imply active markets where buying or selling large amounts won’t drastically affect prices—a crucial aspect for traders seeking flexibility without risking substantial slippage.
Project Team & Development Roadmap
The experience level of developers influences confidence in project delivery. A transparent roadmap outlining upcoming milestones reassures investors about future progress while partnerships with reputable organizations can add credibility.
Regulatory Environment
Legal clarity reduces uncertainty around compliance costs or restrictions that could hinder adoption efforts—especially important given varying regulations across jurisdictions worldwide.
Adoption & Use Cases
A cryptocurrency’s real-world utility depends heavily on user engagement and business integration; widespread adoption often translates into increased demand which supports valuation growth over time.
Security & Scalability Features
Blockchain security mechanisms like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) ensure network integrity against malicious attacks. Additionally, scalability solutions address transaction speed limitations critical during mass adoption phases.
Recent Trends Enhancing Crypto Fundamental Analysis
Recent developments have made fundamental analysis more relevant than ever:
- Institutional Investment Growth: Large financial institutions entering crypto markets bring rigorous evaluation standards similar to traditional finance.
- Regulatory Clarity: Governments providing clearer guidelines help reduce uncertainties around legal compliance.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements such as layer 2 scaling solutions increase transaction speeds while maintaining security.
- Growing Adoption: More companies accepting cryptocurrencies as payment options expand real-world use cases.
- Market Volatility Awareness: Recognizing external factors influencing prices aids in better risk management strategies.
Risks That Can Affect Cryptocurrency Valuations
While fundamental analysis aims at identifying promising assets based on intrinsic qualities, several risks remain:
Regulatory Risks: Sudden policy changes may restrict usage rights or impose compliance costs leading to declines in valuation.
Security Vulnerabilities: Flaws within blockchain protocols could be exploited by hackers causing losses or eroding trust among users.
Market Manipulation: Lack of centralized oversight makes some tokens susceptible to pump-and-dump schemes affecting price stability temporarily.
Technological Challenges: Issues like limited scalability might prevent widespread adoption despite strong fundamentals.
How Investors Can Use Fundamental Analysis Effectively
To leverage FA effectively when investing in cryptocurrencies:
- Conduct thorough research into project whitepapers detailing technology goals and use cases.
- Evaluate team backgrounds through professional profiles like LinkedIn; experienced teams tend to execute better plans.
- Monitor regulatory updates across key markets impacting your chosen assets’ legality status.
- Observe community engagement levels—active developer communities often indicate ongoing innovation efforts.5.Gauge partnership announcements from reputable firms signaling strategic growth opportunities.
By combining these insights with ongoing market observations—and balancing them against technical signals—investors can develop well-rounded perspectives suited for both short-term trades and long-term holdings.
In essence, understanding what constitutes fundamental analysis within cryptocurrency investments equips you with tools necessary for making smarter decisions amid volatile markets—and positions you better prepared for emerging opportunities driven by technological progress and evolving regulations alike.
Note: Always remember that no single metric guarantees investment success; instead focus on holistic evaluation aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Stateless Client Design and Why Is It Important?
Understanding the concept of stateless client design is essential for anyone involved in modern software development, especially in web applications, distributed systems, and blockchain technology. This architecture approach fundamentally influences how applications handle user interactions, scalability, security, and maintenance. In this article, we will explore what stateless client design entails, why it has become a cornerstone of contemporary software architecture, and its implications across various domains.
Defining Stateless Client Design
At its core, stateless client design refers to a system where each request from the client to the server contains all necessary information to process that request independently. Unlike stateful systems—which remember previous interactions through stored session data—stateless systems do not retain any memory of past requests once they are completed.
This means that every interaction is treated as an isolated transaction. For example, when you log into a website using a stateless API-based system like REST (Representational State Transfer), your login credentials or session details are sent with each request rather than being stored on the server side between requests. As a result, servers do not need to keep track of user sessions or maintain context across multiple interactions.
Why Statelessness Matters in Modern Software Development
The shift towards stateless architectures stems from several critical needs within today's digital landscape:
Scalability: As user bases grow rapidly online, systems must efficiently handle increased load without becoming bottlenecked by session management complexities. Stateless designs facilitate horizontal scaling because new servers can be added seamlessly without sharing session data.
Security: Since no sensitive session information resides on the server after processing each request (or is minimized), risks related to data breaches or unauthorized access are reduced. This aligns with best practices for protecting user privacy and sensitive data.
Maintainability: Debugging becomes more straightforward because each request operates independently; developers can isolate issues more easily without tracking complex state dependencies.
Deployment Flexibility: Stateless systems simplify deployment strategies such as cloud migration or updates since there’s no need for synchronized session storage across different environments.
These advantages make statelessness particularly appealing for large-scale web services and distributed architectures where efficiency and security are paramount.
Examples of Stateless Client Design in Practice
Several prominent technologies exemplify the principles of stateless client design:
RESTful APIs
RESTful APIs have popularized this approach by defining standards where each API call contains all necessary information—such as authentication tokens—to complete an operation. Because REST emphasizes resource-based interactions without maintaining server-side sessions between calls, it inherently supports scalability and ease of maintenance.
Microservices Architecture
In microservices setups—where applications are broken down into smaller independent services—each service often adopts a stateless model. This allows individual components to scale independently based on demand while reducing inter-service dependencies that could complicate deployment or troubleshooting processes.
Blockchain-Based Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Blockchain platforms like Ethereum enable decentralized apps that operate without centralized control over user data. These dApps leverage smart contracts—self-executing code embedded directly into blockchain transactions—that rely on immutable states rather than storing extensive user-specific information centrally. This enhances transparency while reducing vulnerabilities associated with centralized storage.
Challenges Associated With Stateless Systems
While there are many benefits to adopting a stateless approach, it also introduces certain challenges:
User Experience Concerns
- Without persistent sessions managed by servers (like cookies or server-side sessions), users may experience repeated login prompts unless token-based authentication mechanisms such as JWTs (JSON Web Tokens) are employed effectively.
- Multi-step workflows require careful handling so users don’t lose context during navigation.
Implementation Complexity
- Designing truly stateless APIs demands meticulous planning; developers must ensure all necessary state-related info is included within each request.
- Handling complex workflows might involve additional logic at the client side or sophisticated token management strategies which can increase development effort.
Despite these hurdles, many organizations find that their gains in scalability and security outweigh potential drawbacks when implementing proper solutions like token-based authentication schemes.
The Evolution of Statelss Architectures Over Time
The adoption of stateless designs has evolved significantly over recent decades:
The concept gained prominence around 2000 following Roy Fielding’s dissertation introducing REST—a style emphasizing resource-oriented operations with no reliance on server-side sessions.
Blockchain technology introduced decentralized applications around 2017 that inherently follow principles similar to those found in traditional web APIs but applied within distributed ledger contexts.
Microservices architecture emerged prominently during the early 2010s but gained widespread acceptance after influential publications like Sam Newman’s "Building Microservices" around 2015 emphasized designing services as independent units capable of scaling horizontally without shared state dependencies.
This historical progression underscores how architectural paradigms favoring simplicity—and supporting rapid growth—have become central themes in modern software engineering practices.
How To Implement Effective Stateless Systems
Implementing successful static architectures requires strategic planning:
Use token-based authentication methods such as JWTs instead of traditional sessions.
Ensure all required context is included within requests—for example:
- User identity
- Permissions
- Transaction details
Minimize reliance on local storage unless necessary; prefer secure tokens stored securely on clients’ devices.
Design APIs carefully so they support idempotent operations—that is actions producing consistent results regardless if repeated multiple times—which simplifies error handling.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Statelessness for Future-Proof Applications
Stateless client design remains fundamental for building scalable , secure ,and maintainable modern applications . Its principles underpin many successful technologies—from RESTful web services powering global internet infrastructure to blockchain networks ensuring transparency without central authority control .
While challenges exist—in particular regarding preserving seamless user experiences—the benefits strongly advocate adopting this paradigm whenever feasible . As digital ecosystems continue evolving toward decentralization and cloud-native deployments , understanding how to leverage true statelss architecture will be vital for developers aiming at resilient future-proof solutions.
By grasping what makes system components truly 'statless', organizations can better align their development efforts with industry best practices aimed at delivering robust digital experiences today—and tomorrow.*


Lo
2025-05-09 19:16
What is stateless client design and why is it significant?
What Is Stateless Client Design and Why Is It Important?
Understanding the concept of stateless client design is essential for anyone involved in modern software development, especially in web applications, distributed systems, and blockchain technology. This architecture approach fundamentally influences how applications handle user interactions, scalability, security, and maintenance. In this article, we will explore what stateless client design entails, why it has become a cornerstone of contemporary software architecture, and its implications across various domains.
Defining Stateless Client Design
At its core, stateless client design refers to a system where each request from the client to the server contains all necessary information to process that request independently. Unlike stateful systems—which remember previous interactions through stored session data—stateless systems do not retain any memory of past requests once they are completed.
This means that every interaction is treated as an isolated transaction. For example, when you log into a website using a stateless API-based system like REST (Representational State Transfer), your login credentials or session details are sent with each request rather than being stored on the server side between requests. As a result, servers do not need to keep track of user sessions or maintain context across multiple interactions.
Why Statelessness Matters in Modern Software Development
The shift towards stateless architectures stems from several critical needs within today's digital landscape:
Scalability: As user bases grow rapidly online, systems must efficiently handle increased load without becoming bottlenecked by session management complexities. Stateless designs facilitate horizontal scaling because new servers can be added seamlessly without sharing session data.
Security: Since no sensitive session information resides on the server after processing each request (or is minimized), risks related to data breaches or unauthorized access are reduced. This aligns with best practices for protecting user privacy and sensitive data.
Maintainability: Debugging becomes more straightforward because each request operates independently; developers can isolate issues more easily without tracking complex state dependencies.
Deployment Flexibility: Stateless systems simplify deployment strategies such as cloud migration or updates since there’s no need for synchronized session storage across different environments.
These advantages make statelessness particularly appealing for large-scale web services and distributed architectures where efficiency and security are paramount.
Examples of Stateless Client Design in Practice
Several prominent technologies exemplify the principles of stateless client design:
RESTful APIs
RESTful APIs have popularized this approach by defining standards where each API call contains all necessary information—such as authentication tokens—to complete an operation. Because REST emphasizes resource-based interactions without maintaining server-side sessions between calls, it inherently supports scalability and ease of maintenance.
Microservices Architecture
In microservices setups—where applications are broken down into smaller independent services—each service often adopts a stateless model. This allows individual components to scale independently based on demand while reducing inter-service dependencies that could complicate deployment or troubleshooting processes.
Blockchain-Based Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Blockchain platforms like Ethereum enable decentralized apps that operate without centralized control over user data. These dApps leverage smart contracts—self-executing code embedded directly into blockchain transactions—that rely on immutable states rather than storing extensive user-specific information centrally. This enhances transparency while reducing vulnerabilities associated with centralized storage.
Challenges Associated With Stateless Systems
While there are many benefits to adopting a stateless approach, it also introduces certain challenges:
User Experience Concerns
- Without persistent sessions managed by servers (like cookies or server-side sessions), users may experience repeated login prompts unless token-based authentication mechanisms such as JWTs (JSON Web Tokens) are employed effectively.
- Multi-step workflows require careful handling so users don’t lose context during navigation.
Implementation Complexity
- Designing truly stateless APIs demands meticulous planning; developers must ensure all necessary state-related info is included within each request.
- Handling complex workflows might involve additional logic at the client side or sophisticated token management strategies which can increase development effort.
Despite these hurdles, many organizations find that their gains in scalability and security outweigh potential drawbacks when implementing proper solutions like token-based authentication schemes.
The Evolution of Statelss Architectures Over Time
The adoption of stateless designs has evolved significantly over recent decades:
The concept gained prominence around 2000 following Roy Fielding’s dissertation introducing REST—a style emphasizing resource-oriented operations with no reliance on server-side sessions.
Blockchain technology introduced decentralized applications around 2017 that inherently follow principles similar to those found in traditional web APIs but applied within distributed ledger contexts.
Microservices architecture emerged prominently during the early 2010s but gained widespread acceptance after influential publications like Sam Newman’s "Building Microservices" around 2015 emphasized designing services as independent units capable of scaling horizontally without shared state dependencies.
This historical progression underscores how architectural paradigms favoring simplicity—and supporting rapid growth—have become central themes in modern software engineering practices.
How To Implement Effective Stateless Systems
Implementing successful static architectures requires strategic planning:
Use token-based authentication methods such as JWTs instead of traditional sessions.
Ensure all required context is included within requests—for example:
- User identity
- Permissions
- Transaction details
Minimize reliance on local storage unless necessary; prefer secure tokens stored securely on clients’ devices.
Design APIs carefully so they support idempotent operations—that is actions producing consistent results regardless if repeated multiple times—which simplifies error handling.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Statelessness for Future-Proof Applications
Stateless client design remains fundamental for building scalable , secure ,and maintainable modern applications . Its principles underpin many successful technologies—from RESTful web services powering global internet infrastructure to blockchain networks ensuring transparency without central authority control .
While challenges exist—in particular regarding preserving seamless user experiences—the benefits strongly advocate adopting this paradigm whenever feasible . As digital ecosystems continue evolving toward decentralization and cloud-native deployments , understanding how to leverage true statelss architecture will be vital for developers aiming at resilient future-proof solutions.
By grasping what makes system components truly 'statless', organizations can better align their development efforts with industry best practices aimed at delivering robust digital experiences today—and tomorrow.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Effect of Smoothing Periods on Moving Average Responsiveness?
Understanding how moving averages respond to market changes is essential for traders and investors, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. One of the key factors influencing this responsiveness is the smoothing period — a parameter that determines how sensitive the moving average is to recent price fluctuations. In this article, we will explore what smoothing periods are, how they affect moving average responsiveness, and why choosing the right period matters for effective technical analysis.
What Are Moving Averages and How Do They Work?
Moving averages (MAs) are popular technical indicators used to smooth out price data over a specified time frame. They help traders identify trends by filtering out short-term volatility and highlighting longer-term movements. The most common types include Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
The calculation involves averaging closing prices over a set number of periods — for example, 20 days or 50 days — which results in a line that moves along with price action but with varying degrees of smoothness depending on the period selected.
The Role of Smoothing Periods in Moving Averages
The smoothing period refers to the number of data points used when calculating the moving average. It directly influences how quickly or slowly this indicator reacts to recent market changes:
Shorter Smoothing Periods (e.g., 5-day or 10-day MA): These produce more responsive lines that closely follow current prices. They react swiftly to sudden shifts but can also generate false signals due to noise.
Longer Smoothing Periods (e.g., 100-day or 200-day MA): These create smoother lines that lag behind rapid market movements but provide clearer signals about long-term trends.
Choosing an appropriate smoothing period depends on your trading style—whether you prefer quick signals suitable for short-term trading or more stable indicators aligned with long-term investing.
How Does Smoothing Period Affect Market Responsiveness?
Responsiveness refers to how quickly a moving average adjusts when prices change. Shorter periods make MAs highly sensitive; they will shift direction rapidly as new data comes in, making them useful for catching early trend reversals or entry points in fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies.
Conversely, longer periods tend to filter out minor fluctuations—often considered noise—and focus on overarching trends. While this reduces false alarms caused by random price swings, it also means delayed responses which could cause missed opportunities during rapid market shifts.
For example:
- A 20-day EMA might signal an upward trend sooner than a 200-day SMA, but it may also be prone to whipsaws during volatile phases.
- Traders seeking quick entries might favor shorter SMAs/EMAs despite increased risk of false signals.
- Investors aiming for stability often rely on longer-period MAs as confirmation tools rather than primary triggers.
Impact on Trading Strategies
The choice of smoothing period influences various aspects of trading strategies:
Support and Resistance Levels
Moving averages often act as dynamic support/resistance zones; their responsiveness determines how well these levels hold during volatile conditions.
Trend Reversal Signals
Shorter MAs can indicate potential reversals earlier but at risk of false positives; longer MAs provide confirmation at expense of speed.
Combining Multiple Moving Averages
Many traders use multiple MAs with different periods—such as crossovers between short-term and long-term averages—to generate buy/sell signals based on their interactions:
- When short-term MA crosses above long-term MA: bullish signal.
- When it crosses below: bearish signal.
This approach leverages different sensitivities created by varying smoothing periods for more robust decision-making.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrency Markets & Algorithmic Trading
In recent years, cryptocurrency markets have experienced heightened volatility due to factors like regulatory news, technological developments, and macroeconomic shifts. As such:
Traders increasingly prefer shorter-moving averages (like 20-day or even weekly) because they offer quicker insights into rapid price movements.
Algorithmic trading systems incorporate multiple smoothing periods simultaneously—sometimes blending several MAs—to adapt dynamically across different time frames while minimizing lag effects.
Furthermore, sentiment analysis techniques now compare short vs long-period MAs—for instance, using crossover strategies—to gauge overall market mood effectively amid unpredictable swings.
Risks Associated With Different Smoothing Periods
While selecting an appropriate window size is crucial, both extremes carry risks:
Overfitting With Very Short Periods
Using very short durations can lead your moving average too closely following random noise rather than meaningful trends—a phenomenon known as overfitting—which results in frequent false signals leading traders astray.
Missing Opportunities With Long Durations
On the other hand, overly long periods may delay recognition of genuine trend changes because these smooth out significant moves until they're well established—potentially causing missed profit windows especially during fast-paced markets like crypto assets.
| Key Consideration | Short-Term Focus | Long-Term Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Responsiveness | High | Low |
| Noise Sensitivity | High | Low |
| Signal Reliability | Lower | Higher |
Balancing these factors requires understanding your specific trading goals and risk tolerance.
Selecting The Right Smoothing Period For Your Strategy
To optimize your use of moving averages:
- Define your investment horizon – day trading versus position holding.
- Test different window sizes through backtesting historical data relevant to your asset class.
- Combine multiple SMAs/EMAs with varying lengths—for example: using both 50-day and 200-day MA—to confirm trend directions before acting.
- Be aware that no single setting fits all scenarios; adapt based on current market volatility levels.
Why Understanding Moving Average Responsiveness Matters
Grasping how smoothing periods influence responsiveness helps improve decision-making accuracy across diverse markets—from stocks and forex to cryptocurrencies—and enhances risk management practices by reducing reliance on noisy signals while capturing genuine trend shifts effectively.
By tailoring your technical analysis tools—including selecting appropriate moving average lengths—you gain better insight into ongoing market dynamics without falling prey either to premature entries triggered by fleeting fluctuations or delayed reactions missing profitable opportunities.
In summary, adjusting the smoothing period alters a moving average’s sensitivity: shorter ones respond faster but are noisier; longer ones are smoother yet slower at signaling changes. Recognizing this trade-off enables traders not only refine their strategies but also better interpret chart patterns within volatile environments such as crypto markets where timely reactions can make all difference.*


Lo
2025-05-09 08:14
What is the effect of smoothing periods on moving average responsiveness?
What Is the Effect of Smoothing Periods on Moving Average Responsiveness?
Understanding how moving averages respond to market changes is essential for traders and investors, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. One of the key factors influencing this responsiveness is the smoothing period — a parameter that determines how sensitive the moving average is to recent price fluctuations. In this article, we will explore what smoothing periods are, how they affect moving average responsiveness, and why choosing the right period matters for effective technical analysis.
What Are Moving Averages and How Do They Work?
Moving averages (MAs) are popular technical indicators used to smooth out price data over a specified time frame. They help traders identify trends by filtering out short-term volatility and highlighting longer-term movements. The most common types include Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
The calculation involves averaging closing prices over a set number of periods — for example, 20 days or 50 days — which results in a line that moves along with price action but with varying degrees of smoothness depending on the period selected.
The Role of Smoothing Periods in Moving Averages
The smoothing period refers to the number of data points used when calculating the moving average. It directly influences how quickly or slowly this indicator reacts to recent market changes:
Shorter Smoothing Periods (e.g., 5-day or 10-day MA): These produce more responsive lines that closely follow current prices. They react swiftly to sudden shifts but can also generate false signals due to noise.
Longer Smoothing Periods (e.g., 100-day or 200-day MA): These create smoother lines that lag behind rapid market movements but provide clearer signals about long-term trends.
Choosing an appropriate smoothing period depends on your trading style—whether you prefer quick signals suitable for short-term trading or more stable indicators aligned with long-term investing.
How Does Smoothing Period Affect Market Responsiveness?
Responsiveness refers to how quickly a moving average adjusts when prices change. Shorter periods make MAs highly sensitive; they will shift direction rapidly as new data comes in, making them useful for catching early trend reversals or entry points in fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies.
Conversely, longer periods tend to filter out minor fluctuations—often considered noise—and focus on overarching trends. While this reduces false alarms caused by random price swings, it also means delayed responses which could cause missed opportunities during rapid market shifts.
For example:
- A 20-day EMA might signal an upward trend sooner than a 200-day SMA, but it may also be prone to whipsaws during volatile phases.
- Traders seeking quick entries might favor shorter SMAs/EMAs despite increased risk of false signals.
- Investors aiming for stability often rely on longer-period MAs as confirmation tools rather than primary triggers.
Impact on Trading Strategies
The choice of smoothing period influences various aspects of trading strategies:
Support and Resistance Levels
Moving averages often act as dynamic support/resistance zones; their responsiveness determines how well these levels hold during volatile conditions.
Trend Reversal Signals
Shorter MAs can indicate potential reversals earlier but at risk of false positives; longer MAs provide confirmation at expense of speed.
Combining Multiple Moving Averages
Many traders use multiple MAs with different periods—such as crossovers between short-term and long-term averages—to generate buy/sell signals based on their interactions:
- When short-term MA crosses above long-term MA: bullish signal.
- When it crosses below: bearish signal.
This approach leverages different sensitivities created by varying smoothing periods for more robust decision-making.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrency Markets & Algorithmic Trading
In recent years, cryptocurrency markets have experienced heightened volatility due to factors like regulatory news, technological developments, and macroeconomic shifts. As such:
Traders increasingly prefer shorter-moving averages (like 20-day or even weekly) because they offer quicker insights into rapid price movements.
Algorithmic trading systems incorporate multiple smoothing periods simultaneously—sometimes blending several MAs—to adapt dynamically across different time frames while minimizing lag effects.
Furthermore, sentiment analysis techniques now compare short vs long-period MAs—for instance, using crossover strategies—to gauge overall market mood effectively amid unpredictable swings.
Risks Associated With Different Smoothing Periods
While selecting an appropriate window size is crucial, both extremes carry risks:
Overfitting With Very Short Periods
Using very short durations can lead your moving average too closely following random noise rather than meaningful trends—a phenomenon known as overfitting—which results in frequent false signals leading traders astray.
Missing Opportunities With Long Durations
On the other hand, overly long periods may delay recognition of genuine trend changes because these smooth out significant moves until they're well established—potentially causing missed profit windows especially during fast-paced markets like crypto assets.
| Key Consideration | Short-Term Focus | Long-Term Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Responsiveness | High | Low |
| Noise Sensitivity | High | Low |
| Signal Reliability | Lower | Higher |
Balancing these factors requires understanding your specific trading goals and risk tolerance.
Selecting The Right Smoothing Period For Your Strategy
To optimize your use of moving averages:
- Define your investment horizon – day trading versus position holding.
- Test different window sizes through backtesting historical data relevant to your asset class.
- Combine multiple SMAs/EMAs with varying lengths—for example: using both 50-day and 200-day MA—to confirm trend directions before acting.
- Be aware that no single setting fits all scenarios; adapt based on current market volatility levels.
Why Understanding Moving Average Responsiveness Matters
Grasping how smoothing periods influence responsiveness helps improve decision-making accuracy across diverse markets—from stocks and forex to cryptocurrencies—and enhances risk management practices by reducing reliance on noisy signals while capturing genuine trend shifts effectively.
By tailoring your technical analysis tools—including selecting appropriate moving average lengths—you gain better insight into ongoing market dynamics without falling prey either to premature entries triggered by fleeting fluctuations or delayed reactions missing profitable opportunities.
In summary, adjusting the smoothing period alters a moving average’s sensitivity: shorter ones respond faster but are noisier; longer ones are smoother yet slower at signaling changes. Recognizing this trade-off enables traders not only refine their strategies but also better interpret chart patterns within volatile environments such as crypto markets where timely reactions can make all difference.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does a Market Order Affect Stock Prices?
Understanding the Impact of Market Orders on Financial Markets
Market orders are among the most common types of transactions used by investors and traders across various financial markets, including traditional stock exchanges and cryptocurrency platforms. They are straightforward: an order to buy or sell a security immediately at the best available current price. While this simplicity makes market orders appealing for quick execution, their influence on stock prices can be complex and sometimes unpredictable.
What Is a Market Order?
A market order is designed for immediate execution. When an investor places a buy market order, it instructs the broker to purchase shares at the lowest available price in the current order book. Conversely, a sell market order directs selling shares at the highest bid price currently available. Because these orders prioritize speed over price control, they often fill almost instantly—especially in highly liquid markets like major stocks or cryptocurrencies.
However, this immediacy means that investors may not know exactly what price they will pay or receive until after execution occurs. In fast-moving markets with high volatility or low liquidity, prices can shift rapidly between placing an order and its completion.
The Effect of Market Orders on Stock Prices
Market orders influence stock prices primarily through their interaction with existing supply and demand dynamics. When large volumes of buy or sell orders are executed quickly via market orders, they can cause noticeable shifts in stock prices—sometimes even triggering broader market movements.
For example:
- Price Impact from Large Buy Orders: A substantial buy market order can deplete existing sell limit orders at current levels, pushing up the prevailing ask price as new sellers enter higher bids to match increased demand.
- Price Drop from Large Sell Orders: Conversely, executing large sell market orders may absorb much of the buying interest at current bid levels, leading to downward pressure on share prices as buyers withdraw or wait for lower prices.
In highly liquid markets such as major U.S. stocks (e.g., Apple or Microsoft), these effects tend to be minimal unless dealing with exceptionally large volumes relative to average trading activity. However, in less liquid stocks or emerging markets where trading volume is lower, even modest-sized market orders can significantly impact prices.
Liquidity’s Role in Price Movements
Liquidity—the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without affecting their price—is crucial when considering how market orders affect stock values. In highly liquid environments like NASDAQ-listed companies or popular cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum:
- The bid-ask spread (difference between highest bid and lowest ask) tends to be narrow.
- Large trades are absorbed more smoothly without causing drastic swings.
In contrast, illiquid securities have wider spreads; thus,
- A single large-market buy could push up prices sharply,
- A big sale might cause rapid declines,
potentially leading to increased volatility during periods of stress.
Risks Associated With Market Orders
While immediate execution offers convenience and speed—particularly important during volatile trading sessions—it also introduces specific risks:
- Price Slippage: The actual transaction may occur at a worse-than-expected price due to rapid changes in supply/demand conditions.
- Market Manipulation Risks: Unscrupulous traders might exploit fast executions for manipulative practices like "spoofing"—placing fake bids/offers intended only temporarily—to influence perceived supply/demand.
- Liquidity Shortfalls: During sudden liquidity crises (e.g., flash crashes), executing large-market orders could exacerbate downward spirals by triggering further panic selling.
Recent Developments Amplifying These Effects
The past few years have highlighted how volatile markets amplify these risks:
During 2020’s COVID-induced chaos, rapid fluctuations made it difficult for traders using solely market orders to predict final transaction prices accurately.
The collapse of cryptocurrency exchanges such as FTX in 2022 underscored vulnerabilities associated with high-frequency trading algorithms that execute numerous rapid-fire transactions—including many via aggressive use of market-orders—which contributed both directly and indirectly to systemic instability.
Furthermore,
Regulatory Changes: Authorities worldwide have introduced measures aimed at increasing transparency around high-frequency trading activities while imposing restrictions designed to curb manipulative practices involving aggressive use of instant-market executions.
Technological Advancements & Their Influence
Advances like algorithmic trading platforms enable traders—and institutional investors—to place complex strategies involving multiple types of orders simultaneously—including sophisticated uses of limit versus market commands—to manage risk better while attempting optimal entry/exit points.
However,
These same technologies introduce new risks, such as errors caused by faulty algorithms ("flash crashes") that execute massive quantities of trades within seconds—all often relying heavily on instantaneousmarket-order executions—highlighting why understanding their impact remains vital for all participants involved.
Implications for Investors & Traders
Investors should recognize that while marketplace efficiency benefits from quick trade executions enabled by modern technology—and especially so during periods when liquidity is abundant—they must also remain cautious about potential adverse effects when placing large-volume trades via market orders:
• Use limit rather than purely_market_orders_ where possible• Be aware that sudden volatility can lead your trade being executed far from expected pricing• Educate yourself about how different securities react under varying liquidity conditions
This awareness helps mitigate unintended consequences such as significant losses due solely to unforeseen short-term price swings triggered by your own trades.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Risks & Opportunities
Market orders serve as powerful tools within financial markets but come bundled with inherent risks tied closely both to overall liquidity conditions and prevailing volatility levels—a fact underscored repeatedly through recent events across traditional equities and digital assets alike.
By understanding how these simple yet impactful instructions interact with existing supply-demand dynamics—and staying informed about technological developments—you position yourself better equipped either capitalize on opportunities efficiently—or avoid pitfalls associated with poorly managed instant executions.
Keywords: Market Order Impact; Stock Price Movement; Liquidity Effect; Trading Volatility; Price Slippage; Cryptocurrency Markets; High-Frequency Trading Risks


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-29 08:35
How does a market order affect stock prices?
How Does a Market Order Affect Stock Prices?
Understanding the Impact of Market Orders on Financial Markets
Market orders are among the most common types of transactions used by investors and traders across various financial markets, including traditional stock exchanges and cryptocurrency platforms. They are straightforward: an order to buy or sell a security immediately at the best available current price. While this simplicity makes market orders appealing for quick execution, their influence on stock prices can be complex and sometimes unpredictable.
What Is a Market Order?
A market order is designed for immediate execution. When an investor places a buy market order, it instructs the broker to purchase shares at the lowest available price in the current order book. Conversely, a sell market order directs selling shares at the highest bid price currently available. Because these orders prioritize speed over price control, they often fill almost instantly—especially in highly liquid markets like major stocks or cryptocurrencies.
However, this immediacy means that investors may not know exactly what price they will pay or receive until after execution occurs. In fast-moving markets with high volatility or low liquidity, prices can shift rapidly between placing an order and its completion.
The Effect of Market Orders on Stock Prices
Market orders influence stock prices primarily through their interaction with existing supply and demand dynamics. When large volumes of buy or sell orders are executed quickly via market orders, they can cause noticeable shifts in stock prices—sometimes even triggering broader market movements.
For example:
- Price Impact from Large Buy Orders: A substantial buy market order can deplete existing sell limit orders at current levels, pushing up the prevailing ask price as new sellers enter higher bids to match increased demand.
- Price Drop from Large Sell Orders: Conversely, executing large sell market orders may absorb much of the buying interest at current bid levels, leading to downward pressure on share prices as buyers withdraw or wait for lower prices.
In highly liquid markets such as major U.S. stocks (e.g., Apple or Microsoft), these effects tend to be minimal unless dealing with exceptionally large volumes relative to average trading activity. However, in less liquid stocks or emerging markets where trading volume is lower, even modest-sized market orders can significantly impact prices.
Liquidity’s Role in Price Movements
Liquidity—the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without affecting their price—is crucial when considering how market orders affect stock values. In highly liquid environments like NASDAQ-listed companies or popular cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum:
- The bid-ask spread (difference between highest bid and lowest ask) tends to be narrow.
- Large trades are absorbed more smoothly without causing drastic swings.
In contrast, illiquid securities have wider spreads; thus,
- A single large-market buy could push up prices sharply,
- A big sale might cause rapid declines,
potentially leading to increased volatility during periods of stress.
Risks Associated With Market Orders
While immediate execution offers convenience and speed—particularly important during volatile trading sessions—it also introduces specific risks:
- Price Slippage: The actual transaction may occur at a worse-than-expected price due to rapid changes in supply/demand conditions.
- Market Manipulation Risks: Unscrupulous traders might exploit fast executions for manipulative practices like "spoofing"—placing fake bids/offers intended only temporarily—to influence perceived supply/demand.
- Liquidity Shortfalls: During sudden liquidity crises (e.g., flash crashes), executing large-market orders could exacerbate downward spirals by triggering further panic selling.
Recent Developments Amplifying These Effects
The past few years have highlighted how volatile markets amplify these risks:
During 2020’s COVID-induced chaos, rapid fluctuations made it difficult for traders using solely market orders to predict final transaction prices accurately.
The collapse of cryptocurrency exchanges such as FTX in 2022 underscored vulnerabilities associated with high-frequency trading algorithms that execute numerous rapid-fire transactions—including many via aggressive use of market-orders—which contributed both directly and indirectly to systemic instability.
Furthermore,
Regulatory Changes: Authorities worldwide have introduced measures aimed at increasing transparency around high-frequency trading activities while imposing restrictions designed to curb manipulative practices involving aggressive use of instant-market executions.
Technological Advancements & Their Influence
Advances like algorithmic trading platforms enable traders—and institutional investors—to place complex strategies involving multiple types of orders simultaneously—including sophisticated uses of limit versus market commands—to manage risk better while attempting optimal entry/exit points.
However,
These same technologies introduce new risks, such as errors caused by faulty algorithms ("flash crashes") that execute massive quantities of trades within seconds—all often relying heavily on instantaneousmarket-order executions—highlighting why understanding their impact remains vital for all participants involved.
Implications for Investors & Traders
Investors should recognize that while marketplace efficiency benefits from quick trade executions enabled by modern technology—and especially so during periods when liquidity is abundant—they must also remain cautious about potential adverse effects when placing large-volume trades via market orders:
• Use limit rather than purely_market_orders_ where possible• Be aware that sudden volatility can lead your trade being executed far from expected pricing• Educate yourself about how different securities react under varying liquidity conditions
This awareness helps mitigate unintended consequences such as significant losses due solely to unforeseen short-term price swings triggered by your own trades.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Risks & Opportunities
Market orders serve as powerful tools within financial markets but come bundled with inherent risks tied closely both to overall liquidity conditions and prevailing volatility levels—a fact underscored repeatedly through recent events across traditional equities and digital assets alike.
By understanding how these simple yet impactful instructions interact with existing supply-demand dynamics—and staying informed about technological developments—you position yourself better equipped either capitalize on opportunities efficiently—or avoid pitfalls associated with poorly managed instant executions.
Keywords: Market Order Impact; Stock Price Movement; Liquidity Effect; Trading Volatility; Price Slippage; Cryptocurrency Markets; High-Frequency Trading Risks
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Regulations Affecting ICOs: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the regulatory landscape surrounding Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) is essential for investors, entrepreneurs, and regulators alike. As a pioneering method of fundraising in the cryptocurrency space, ICOs have experienced rapid growth and significant scrutiny. This article provides an in-depth look at how regulations influence ICOs, recent developments shaping the industry, and potential implications for stakeholders.
What Are ICOs and How Do They Work?
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are a form of crowdfunding that allows blockchain projects to raise capital by issuing new digital tokens. Unlike traditional funding methods such as IPOs or bond sales, ICO tokens are typically created on existing blockchain platforms like Ethereum. These tokens can represent various assets—such as utility rights within a platform, ownership stakes, or other utilities—depending on the project's design.
The process involves a project team creating tokens and offering them to investors in exchange for established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Investors buy these tokens with the hope that their value will increase as the project develops or that they will gain utility within the ecosystem.
Historical Context of ICO Regulations
The first notable ICO was conducted by Mastercoin (now OmniLayer) in 2013; however, it was Ethereum's 2014 launch that truly popularized this fundraising model. The explosive growth of ICOs between 2017 and 2018 saw hundreds of projects raising millions rapidly but also drew attention from regulators worldwide due to concerns over fraud and lack of oversight.
Initially operating in legal gray areas due to unclear regulations across jurisdictions, many countries struggled to establish frameworks suitable for this novel form of fundraising. This ambiguity led to numerous scams and failed projects tarnishing industry reputation while prompting calls for clearer rules.
Key Regulatory Challenges Facing ICOs
- Securities Law Classification
One primary concern is whether issued tokens should be classified as securities under existing laws—a question central to many jurisdictions including the United States. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), through its Howey Test analysis, has indicated that some tokens meet criteria similar to securities because they involve investment contracts with expectations of profit derived from efforts by others.
This classification subjects token offerings to stringent securities regulations—including registration requirements—and necessitates compliance with disclosure obligations designed primarily for traditional financial instruments.
- Commodity Regulation
Beyond securities law considerations, agencies like the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) have stepped into regulating certain aspects related to derivatives or futures contracts tied directly or indirectly to cryptocurrencies issued via ICOs.
- Anti-Money Laundering & Know Your Customer Policies
Many countries have implemented AML/KYC policies aimed at preventing illicit activities such as money laundering or terrorist financing through cryptocurrency transactions involving ICO funds. These measures often require identity verification processes before participating in token sales—a challenge given some projects' initial anonymity focus.
- International Guidelines & FATF Recommendations
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an international body promoting global standards against money laundering and terrorism financing, has issued guidelines emphasizing transparency requirements for virtual asset service providers—including those involved in token offerings—to curb misuse while fostering innovation responsibly.
Recent Developments Shaping Regulatory Approaches
Several recent events highlight how regulators are actively shaping policies around cryptocurrencies:
SEC Delays Litecoin ETF Approval: In May 2025, the SEC postponed approving a Litecoin-based exchange-traded fund (ETF). This move underscores ongoing concerns about market manipulation risks associated with crypto ETFs despite growing institutional interest[2].
Mainstream Acceptance Through Corporate Listings: Galaxy Digital’s debut on Nasdaq after navigating regulatory hurdles exemplifies increasing acceptance of crypto-focused firms within traditional financial markets[1].
Expansion into Derivatives Markets: Coinbase’s acquisition of Deribit—a derivatives trading platform—for nearly $3 billion demonstrates how regulated derivatives markets are becoming integral parts of crypto ecosystems[3].
Regulatory Scrutiny Over Meme Coins: The SEC launched investigations into meme coins linked with high-profile figures like Donald Trump amid reports of investor losses[4]. Such probes reflect efforts toward greater oversight over unregulated speculative assets posing consumer protection risks.
Fundraising Successes Highlight Industry Growth: Notably, Sam Altman’s World Network blockchain project raised $135 million privately—showcasing continued investor confidence despite regulatory uncertainties[5].
Potential Impacts & Risks Due To Lack Of Clear Regulations
Uncertainty around regulation can lead to several adverse outcomes:
Market Volatility: Fluctuations driven by regulatory announcements can cause sharp price swings affecting investor confidence.
Increased Fraud & Scams: Without robust legal frameworks enforcement becomes challenging; fraudulent schemes may proliferate damaging industry credibility.
Legal Compliance Challenges: Companies conducting token sales risk penalties if they inadvertently violate laws—especially when operating across multiple jurisdictions.
Public Perception Deterioration: Negative news related to regulatory crackdowns can diminish mainstream trust necessary for broader adoption.
Navigating Future Regulatory Trends
As governments worldwide grapple with balancing innovation against consumer protection concerns,
stakeholders must stay informed about evolving rules:
Emphasizing Transparency & Due Diligence — Projects should prioritize clear disclosures regarding token functions,regulatory status,and compliance measures.
Engaging With Regulators — Active dialogue between industry playersand authorities helps shape practical policies conduciveto sustainable growth.
Adopting Best Practices — Implementing AML/KYC procedures,security audits,and legal reviews reduces risk exposure.
Semantic Keywords & Related Terms
To optimize understanding:
- Cryptocurrency regulation
- Token classification laws
- Blockchain compliance standards
- Crypto market oversight
- Digital asset regulation
- Investor protection laws
- Security vs utility tokens
By understanding these interconnected elements—and recognizing ongoing developments—the industry can better navigate complex legal environments while fostering responsible innovation.
Final Thoughts
Regulations significantly influence how ICOs operate today—from their legality under securities law to international anti-money laundering standards—and continue evolving rapidly amid technological advancements and market expansion efforts. For investors seeking opportunities within this space—or entrepreneurs aiming to launch compliant projects—it remains crucially important to monitor policy changes closely and adhere strictly to applicable legal frameworks ensuring long-term sustainability amidst an ever-changing landscape


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-29 03:44
What regulations affect ICOs?
Regulations Affecting ICOs: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the regulatory landscape surrounding Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) is essential for investors, entrepreneurs, and regulators alike. As a pioneering method of fundraising in the cryptocurrency space, ICOs have experienced rapid growth and significant scrutiny. This article provides an in-depth look at how regulations influence ICOs, recent developments shaping the industry, and potential implications for stakeholders.
What Are ICOs and How Do They Work?
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are a form of crowdfunding that allows blockchain projects to raise capital by issuing new digital tokens. Unlike traditional funding methods such as IPOs or bond sales, ICO tokens are typically created on existing blockchain platforms like Ethereum. These tokens can represent various assets—such as utility rights within a platform, ownership stakes, or other utilities—depending on the project's design.
The process involves a project team creating tokens and offering them to investors in exchange for established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Investors buy these tokens with the hope that their value will increase as the project develops or that they will gain utility within the ecosystem.
Historical Context of ICO Regulations
The first notable ICO was conducted by Mastercoin (now OmniLayer) in 2013; however, it was Ethereum's 2014 launch that truly popularized this fundraising model. The explosive growth of ICOs between 2017 and 2018 saw hundreds of projects raising millions rapidly but also drew attention from regulators worldwide due to concerns over fraud and lack of oversight.
Initially operating in legal gray areas due to unclear regulations across jurisdictions, many countries struggled to establish frameworks suitable for this novel form of fundraising. This ambiguity led to numerous scams and failed projects tarnishing industry reputation while prompting calls for clearer rules.
Key Regulatory Challenges Facing ICOs
- Securities Law Classification
One primary concern is whether issued tokens should be classified as securities under existing laws—a question central to many jurisdictions including the United States. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), through its Howey Test analysis, has indicated that some tokens meet criteria similar to securities because they involve investment contracts with expectations of profit derived from efforts by others.
This classification subjects token offerings to stringent securities regulations—including registration requirements—and necessitates compliance with disclosure obligations designed primarily for traditional financial instruments.
- Commodity Regulation
Beyond securities law considerations, agencies like the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) have stepped into regulating certain aspects related to derivatives or futures contracts tied directly or indirectly to cryptocurrencies issued via ICOs.
- Anti-Money Laundering & Know Your Customer Policies
Many countries have implemented AML/KYC policies aimed at preventing illicit activities such as money laundering or terrorist financing through cryptocurrency transactions involving ICO funds. These measures often require identity verification processes before participating in token sales—a challenge given some projects' initial anonymity focus.
- International Guidelines & FATF Recommendations
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an international body promoting global standards against money laundering and terrorism financing, has issued guidelines emphasizing transparency requirements for virtual asset service providers—including those involved in token offerings—to curb misuse while fostering innovation responsibly.
Recent Developments Shaping Regulatory Approaches
Several recent events highlight how regulators are actively shaping policies around cryptocurrencies:
SEC Delays Litecoin ETF Approval: In May 2025, the SEC postponed approving a Litecoin-based exchange-traded fund (ETF). This move underscores ongoing concerns about market manipulation risks associated with crypto ETFs despite growing institutional interest[2].
Mainstream Acceptance Through Corporate Listings: Galaxy Digital’s debut on Nasdaq after navigating regulatory hurdles exemplifies increasing acceptance of crypto-focused firms within traditional financial markets[1].
Expansion into Derivatives Markets: Coinbase’s acquisition of Deribit—a derivatives trading platform—for nearly $3 billion demonstrates how regulated derivatives markets are becoming integral parts of crypto ecosystems[3].
Regulatory Scrutiny Over Meme Coins: The SEC launched investigations into meme coins linked with high-profile figures like Donald Trump amid reports of investor losses[4]. Such probes reflect efforts toward greater oversight over unregulated speculative assets posing consumer protection risks.
Fundraising Successes Highlight Industry Growth: Notably, Sam Altman’s World Network blockchain project raised $135 million privately—showcasing continued investor confidence despite regulatory uncertainties[5].
Potential Impacts & Risks Due To Lack Of Clear Regulations
Uncertainty around regulation can lead to several adverse outcomes:
Market Volatility: Fluctuations driven by regulatory announcements can cause sharp price swings affecting investor confidence.
Increased Fraud & Scams: Without robust legal frameworks enforcement becomes challenging; fraudulent schemes may proliferate damaging industry credibility.
Legal Compliance Challenges: Companies conducting token sales risk penalties if they inadvertently violate laws—especially when operating across multiple jurisdictions.
Public Perception Deterioration: Negative news related to regulatory crackdowns can diminish mainstream trust necessary for broader adoption.
Navigating Future Regulatory Trends
As governments worldwide grapple with balancing innovation against consumer protection concerns,
stakeholders must stay informed about evolving rules:
Emphasizing Transparency & Due Diligence — Projects should prioritize clear disclosures regarding token functions,regulatory status,and compliance measures.
Engaging With Regulators — Active dialogue between industry playersand authorities helps shape practical policies conduciveto sustainable growth.
Adopting Best Practices — Implementing AML/KYC procedures,security audits,and legal reviews reduces risk exposure.
Semantic Keywords & Related Terms
To optimize understanding:
- Cryptocurrency regulation
- Token classification laws
- Blockchain compliance standards
- Crypto market oversight
- Digital asset regulation
- Investor protection laws
- Security vs utility tokens
By understanding these interconnected elements—and recognizing ongoing developments—the industry can better navigate complex legal environments while fostering responsible innovation.
Final Thoughts
Regulations significantly influence how ICOs operate today—from their legality under securities law to international anti-money laundering standards—and continue evolving rapidly amid technological advancements and market expansion efforts. For investors seeking opportunities within this space—or entrepreneurs aiming to launch compliant projects—it remains crucially important to monitor policy changes closely and adhere strictly to applicable legal frameworks ensuring long-term sustainability amidst an ever-changing landscape
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is an Open Interest Chart?
An open interest chart is a vital tool in financial trading that visually represents the total number of outstanding contracts—such as futures or options—that remain open at any given time. Unlike price charts, which track the movement of asset prices, open interest charts focus on market participation and commitment levels. They display how many contracts are active, providing traders with insights into market sentiment and potential future movements.
Open interest is calculated by summing all new contracts created minus those closed or settled within a specific period. When plotted over time, this data forms an open interest chart that helps traders identify trends in market activity. For example, rising open interest often indicates increasing participation and can signal the continuation of current price trends. Conversely, declining open interest might suggest waning momentum or impending reversals.
Understanding these dynamics allows traders to interpret whether a market is strengthening or weakening based on contract activity rather than just price action alone. As such, an open interest chart becomes an essential component for technical analysis in various markets including cryptocurrencies, commodities, stocks, and forex.
Why Traders Use Open Interest Charts
Traders rely on open interest charts because they provide context beyond simple price movements. While price charts show what has happened recently with an asset’s value, open interest reveals how many participants are actively engaged in the market at any moment.
High levels of open interest generally indicate strong investor confidence and liquidity—meaning there are enough buyers and sellers to facilitate smooth trading without large spreads or slippage. This liquidity makes it easier for traders to enter or exit positions efficiently.
Moreover, changes in open interest can serve as early signals for upcoming volatility or trend shifts. For instance:
- Increasing Open Interest + Rising Prices: Often suggests a bullish trend where new money flows into the market.
- Increasing Open Interest + Falling Prices: Might indicate bearish sentiment with more traders betting against the asset.
- Decreasing Open Interest: Could imply profit-taking or closing out positions ahead of potential reversals.
By combining these observations with other indicators like volume and technical patterns, traders can develop more accurate strategies tailored to current market conditions.
How Open Interest Affects Market Sentiment
Market sentiment—the overall attitude of investors toward a particular security—is significantly influenced by changes in open interest levels. When many traders commit capital through new contracts (reflected as rising open interest), it typically signifies confidence that current trends will continue.
For example:
In cryptocurrency markets like Bitcoin futures trading near $95,000 (as observed in April 2025), surges in open interest often accompany bullish runs fueled by institutional inflows such as ETFs.
Conversely, if after a rally investors start closing their positions en masse—leading to decreasing/open-interest decline—it may signal skepticism about further gains and possible reversal points.
Open interests also help distinguish between different types of trader behavior: whether participants are entering new trades (indicating strength) or simply unwinding existing ones (suggesting caution). This understanding aids investors not only in gauging immediate sentiment but also predicting longer-term trend sustainability.
The Relationship Between Price Movements & Open Interest
The interplay between price action and changes in open interests offers valuable clues about future movements:
- Rising Price + Increasing Open Interest: Indicates fresh buying pressure; likely continuation upward.
- Rising Price + Decreasing Open Interest: Suggests short-term momentum but possibly weakening conviction; caution advised.
- Falling Price + Increasing Open Interest: Reflects growing short-selling activity; potential for further declines.
- Falling Price + Decreasing Open Interest: Implies profit-taking; may precede stabilization or reversal phases.
This relationship helps differentiate between healthy trending markets versus consolidations where volume might be low despite significant moves elsewhere on the chart.
In recent years—particularly within crypto markets—these signals have become even more relevant due to heightened volatility driven by macroeconomic factors like ETF inflows into Bitcoin futures during April 2025[1].
Recent Trends & Developments
The use ofopeninterest data has gained prominence across various financial sectors:
In cryptocurrency markets such as Bitcoin derivatives trading near record highs amid ETF inflows[1], analysts monitor increases in both volume and openness to predict breakout scenarios.
Traders now combine multiple indicators—including volume profiles alongside OI—to enhance predictive accuracy when assessing potential breakouts versus false signals[2].
Furthermore,, understanding how regulatory developments impact openness is crucial since policy shifts can cause sudden drops—as seen when regulatory crackdowns lead to decreased crypto derivatives activity[3].
These evolving practices underscore the importance of integrating real-time data analysis into comprehensive trading strategies aimed at managing risk effectively while maximizing returns over time.
Practical Tips for Using Open Interests Effectively
To leverage this indicator optimally:
Always analyze alongside other technical tools like RSI (Relative Strength Index), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), and candlestick patterns.
Watch for divergence between price movement and changeable OI levels—a divergence often precedes significant reversals.
Consider contract expiration dates which naturally cause fluctuations; high turnover around expiry periods could distort true sentiment signals if not contextualized properly.[4]
By applying disciplined analysis methods rooted firmly within sound research principles—and staying updated on recent developments—you enhance your ability to make informed decisions grounded on solid evidence rather than speculation alone.
Risks & Limitations
While valuable, relying solely on anopeninterest chart carries risks:
It can be manipulated by large players who artificially inflate contract numbers before executing strategic moves—a form known as "spoofing."
Sudden regulatory actions may drastically alter openness metrics overnight,[3] making historical comparisons less reliable during turbulent periods.
Low liquidity environments tend to produce noisy data that misrepresents actual trader commitment levels.[5]
Therefore,, it's essential always to interpret OI data within broader contextual frameworks involving multiple indicators rather than viewing it as standalone evidence.
How To Access & Interpret Data
Most modern trading platforms provide real-time access tomarket depth reports showing currentopen interests across various assets.. These platforms allow users touse customizable charts displaying historical trends alongside live updates., enabling timely decision-making basedon evolving conditions..
Interpreting this data involves looking at both absolute figures—the total numberof outstanding contracts—and relative changes over specific periods.. Recognizing patterns suchas sustained increases signaling accumulation—or sharp drops indicating liquidation—is keyto effective utilization.
Final Thoughts
Anopeninterest chart offers deep insights into underlyingmarket dynamics beyond mere price fluctuations.. By understanding its significanceand learning howto interpret its signals accurately,, traders gain a competitive edgein anticipating future moves., especially when combinedwith other analytical tools.. Asmarkets evolve—with increased participation from institutional playersand rapid technological advancements—the importanceof masteringthis indicator continuesgrowing., makingit indispensablefor serious investors aimingfor consistent successin volatile environments.
Note: Staying informed about recent developments—from ETF inflows impacting Bitcoin's futures landscapeto regulatory shifts affecting derivatives—is crucial for maintaining effective strategies usingopeninterest data..


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-20 05:20
What’s an open interest chart?
What Is an Open Interest Chart?
An open interest chart is a vital tool in financial trading that visually represents the total number of outstanding contracts—such as futures or options—that remain open at any given time. Unlike price charts, which track the movement of asset prices, open interest charts focus on market participation and commitment levels. They display how many contracts are active, providing traders with insights into market sentiment and potential future movements.
Open interest is calculated by summing all new contracts created minus those closed or settled within a specific period. When plotted over time, this data forms an open interest chart that helps traders identify trends in market activity. For example, rising open interest often indicates increasing participation and can signal the continuation of current price trends. Conversely, declining open interest might suggest waning momentum or impending reversals.
Understanding these dynamics allows traders to interpret whether a market is strengthening or weakening based on contract activity rather than just price action alone. As such, an open interest chart becomes an essential component for technical analysis in various markets including cryptocurrencies, commodities, stocks, and forex.
Why Traders Use Open Interest Charts
Traders rely on open interest charts because they provide context beyond simple price movements. While price charts show what has happened recently with an asset’s value, open interest reveals how many participants are actively engaged in the market at any moment.
High levels of open interest generally indicate strong investor confidence and liquidity—meaning there are enough buyers and sellers to facilitate smooth trading without large spreads or slippage. This liquidity makes it easier for traders to enter or exit positions efficiently.
Moreover, changes in open interest can serve as early signals for upcoming volatility or trend shifts. For instance:
- Increasing Open Interest + Rising Prices: Often suggests a bullish trend where new money flows into the market.
- Increasing Open Interest + Falling Prices: Might indicate bearish sentiment with more traders betting against the asset.
- Decreasing Open Interest: Could imply profit-taking or closing out positions ahead of potential reversals.
By combining these observations with other indicators like volume and technical patterns, traders can develop more accurate strategies tailored to current market conditions.
How Open Interest Affects Market Sentiment
Market sentiment—the overall attitude of investors toward a particular security—is significantly influenced by changes in open interest levels. When many traders commit capital through new contracts (reflected as rising open interest), it typically signifies confidence that current trends will continue.
For example:
In cryptocurrency markets like Bitcoin futures trading near $95,000 (as observed in April 2025), surges in open interest often accompany bullish runs fueled by institutional inflows such as ETFs.
Conversely, if after a rally investors start closing their positions en masse—leading to decreasing/open-interest decline—it may signal skepticism about further gains and possible reversal points.
Open interests also help distinguish between different types of trader behavior: whether participants are entering new trades (indicating strength) or simply unwinding existing ones (suggesting caution). This understanding aids investors not only in gauging immediate sentiment but also predicting longer-term trend sustainability.
The Relationship Between Price Movements & Open Interest
The interplay between price action and changes in open interests offers valuable clues about future movements:
- Rising Price + Increasing Open Interest: Indicates fresh buying pressure; likely continuation upward.
- Rising Price + Decreasing Open Interest: Suggests short-term momentum but possibly weakening conviction; caution advised.
- Falling Price + Increasing Open Interest: Reflects growing short-selling activity; potential for further declines.
- Falling Price + Decreasing Open Interest: Implies profit-taking; may precede stabilization or reversal phases.
This relationship helps differentiate between healthy trending markets versus consolidations where volume might be low despite significant moves elsewhere on the chart.
In recent years—particularly within crypto markets—these signals have become even more relevant due to heightened volatility driven by macroeconomic factors like ETF inflows into Bitcoin futures during April 2025[1].
Recent Trends & Developments
The use ofopeninterest data has gained prominence across various financial sectors:
In cryptocurrency markets such as Bitcoin derivatives trading near record highs amid ETF inflows[1], analysts monitor increases in both volume and openness to predict breakout scenarios.
Traders now combine multiple indicators—including volume profiles alongside OI—to enhance predictive accuracy when assessing potential breakouts versus false signals[2].
Furthermore,, understanding how regulatory developments impact openness is crucial since policy shifts can cause sudden drops—as seen when regulatory crackdowns lead to decreased crypto derivatives activity[3].
These evolving practices underscore the importance of integrating real-time data analysis into comprehensive trading strategies aimed at managing risk effectively while maximizing returns over time.
Practical Tips for Using Open Interests Effectively
To leverage this indicator optimally:
Always analyze alongside other technical tools like RSI (Relative Strength Index), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), and candlestick patterns.
Watch for divergence between price movement and changeable OI levels—a divergence often precedes significant reversals.
Consider contract expiration dates which naturally cause fluctuations; high turnover around expiry periods could distort true sentiment signals if not contextualized properly.[4]
By applying disciplined analysis methods rooted firmly within sound research principles—and staying updated on recent developments—you enhance your ability to make informed decisions grounded on solid evidence rather than speculation alone.
Risks & Limitations
While valuable, relying solely on anopeninterest chart carries risks:
It can be manipulated by large players who artificially inflate contract numbers before executing strategic moves—a form known as "spoofing."
Sudden regulatory actions may drastically alter openness metrics overnight,[3] making historical comparisons less reliable during turbulent periods.
Low liquidity environments tend to produce noisy data that misrepresents actual trader commitment levels.[5]
Therefore,, it's essential always to interpret OI data within broader contextual frameworks involving multiple indicators rather than viewing it as standalone evidence.
How To Access & Interpret Data
Most modern trading platforms provide real-time access tomarket depth reports showing currentopen interests across various assets.. These platforms allow users touse customizable charts displaying historical trends alongside live updates., enabling timely decision-making basedon evolving conditions..
Interpreting this data involves looking at both absolute figures—the total numberof outstanding contracts—and relative changes over specific periods.. Recognizing patterns suchas sustained increases signaling accumulation—or sharp drops indicating liquidation—is keyto effective utilization.
Final Thoughts
Anopeninterest chart offers deep insights into underlyingmarket dynamics beyond mere price fluctuations.. By understanding its significanceand learning howto interpret its signals accurately,, traders gain a competitive edgein anticipating future moves., especially when combinedwith other analytical tools.. Asmarkets evolve—with increased participation from institutional playersand rapid technological advancements—the importanceof masteringthis indicator continuesgrowing., makingit indispensablefor serious investors aimingfor consistent successin volatile environments.
Note: Staying informed about recent developments—from ETF inflows impacting Bitcoin's futures landscapeto regulatory shifts affecting derivatives—is crucial for maintaining effective strategies usingopeninterest data..
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is the Chikou Span? A Complete Explanation
Understanding technical analysis tools is essential for traders and investors aiming to make informed decisions. Among these tools, the Ichimoku Cloud stands out for its comprehensive approach to market analysis, with the Chikou Span being a vital component. This article provides an in-depth look at what the Chikou Span is, how it functions within the Ichimoku system, and its relevance in both stock and cryptocurrency markets.
The Role of the Chikou Span in Technical Analysis
The Chikou Span, often called the Lagging Span, serves as a confirmation tool within the Ichimoku Cloud framework. Its primary purpose is to help traders identify trend direction and potential reversals by comparing current prices with past prices. Unlike leading indicators that predict future movements or oscillators that measure momentum, lagging indicators like the Chikou Span analyze historical data to validate current trends.
In practice, this means plotting a security’s closing price 26 periods behind its current position. If this lagging line remains above previous prices over time, it suggests sustained upward momentum; if below, it indicates downward pressure. When combined with other components of the Ichimoku system—such as Tenkan-sen (Conversion Line) or Kijun-sen (Base Line)—the Chikou Span enhances overall market insight.
How Is The Chikou Span Calculated?
The calculation of the Chikou Span is straightforward but crucial for accurate interpretation. It involves taking today's closing price and plotting it 26 periods back on your chart. For example:
- If today’s closing price is $100,
- You would plot $100 on your chart 26 days ago (or 26 candlesticks if using daily data).
This simple shift creates a visual representation that allows traders to compare past prices directly with current levels without complex formulas or additional calculations.
Interpreting The Chikou Span: What Do Different Positions Mean?
The position of the Chikou Span relative to past prices offers valuable insights into market sentiment:
- Above previous prices: Indicates bullish momentum; recent closes are higher than those from 26 periods ago.
- Below previous prices: Signals bearish sentiment; recent closes are lower than those from 26 periods ago.
- Crossing over: When this line crosses above or below historical price levels—especially when combined with other signals—it can suggest potential trend reversals.
For example:
- A rising Chikou span crossing above past prices may confirm an emerging uptrend.
- Conversely, crossing below could warn of a downtrend forming.
Traders often look for these crossovers as part of their decision-making process alongside other elements like cloud support/resistance levels.
Historical Background and Development
The Ichimoku Cloud was developed by Japanese journalist Goichi Hosoda during the late 1960s as an all-in-one trading system designed for quick decision-making without relying on multiple separate indicators. Its name translates roughly as "one glance" cloud because it provides a comprehensive view at a glance through five key components—including Tenkan-sen, Kijun-sen, Senkou Spans A & B (Leading Spans), and notably—the Chikou Span.
Since its inception decades ago, this method has gained worldwide popularity among professional traders due to its ability to depict trend strength and potential reversal points effectively across various markets—from stocks to forex and cryptocurrencies.
Practical Applications in Stock Trading
In stock markets today, many traders incorporate Ichimoku components—including the Chikoudo span—to enhance their technical analysis toolkit. It helps identify long-term trends by confirming whether recent price action aligns with historical movement patterns captured by lagging lines like Chiukō span.
For instance:
- When stock prices are above all cloud boundaries AND Chiukō spans remain above past lows—this typically signals strong bullish conditions.
- Conversely,if stock prices fall below key support levels while Chiukō spans stay beneath prior lows—it suggests bearish dominance or possible trend exhaustion.
Using these signals together improves confidence in trade entries/exits while reducing false positives common when relying solely on single indicators.
Application in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency trading has seen rapid growth over recent years—with high volatility making reliable analysis essential. Traders have adapted traditional tools like Ichimoku Cloud because they provide clear visual cues amidst turbulent price swings typical of digital assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum.
In crypto markets:
- The Lagging span can help confirm whether recent surges are sustainable.
- Crossings between Chiukō spans and historical lows/highs serve as early warning signs for reversals amid volatile conditions.
However—as cryptocurrencies tend toward extreme volatility—the effectiveness of lagging indicators like Chiukō should be complemented with volume analysis or other momentum tools for better accuracy.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
While useful—like any indicator—theChikuo span isn’t perfect:
- Lag Effect: Since it's based on past data (26 periods behind), it may not react quickly enough during sudden market moves.
- False Signals: In highly volatile environments such as crypto markets or during news events—crossovers might generate misleading signals.
- Market Conditions: During sideways consolidation phases—or choppy ranges—the indicator's readings can become ambiguous.
Therefore—and especially when trading high-volatility assets—it’s advisable always to combine Lagging Spans with other technical tools such as volume profiles or oscillators like RSI/MACD.
How To Use The Chikou Spread Effectively
To maximize utility:
- Confirm trend direction via position relative to prior candles
- Watch for crossovers indicating possible reversals
- Use alongside cloud support/resistance zones
- Combine with volume confirmation where applicable
By integrating these strategies into your trading plan—and understanding both strengths & limitations—you’ll improve your chances of making more accurate predictions about future market movements.
Final Thoughts on The Importance Of The Lagging Indicator
TheChikuo span remains an integral part of modern technical analysis due primarily to its simplicity yet powerful confirmation capabilities within broader systems likeIchimoku Cloud . Whether you're analyzing stocks or cryptocurrencies , understanding how this indicator works will enhance your abilityto interpret long-term trends accurately .
While no single tool guarantees success — combiningLagging Spanswith other analytical methods will give you more robust insights into market dynamics . As always — continuous learningand practical experienceare key ingredientsfor successful trading.
Note: Always remember that no indicator should be used in isolation; effective risk management practices remain essential regardlessof which analytical techniques you employ.


kai
2025-05-20 03:02
What’s Chikou Span?
What is the Chikou Span? A Complete Explanation
Understanding technical analysis tools is essential for traders and investors aiming to make informed decisions. Among these tools, the Ichimoku Cloud stands out for its comprehensive approach to market analysis, with the Chikou Span being a vital component. This article provides an in-depth look at what the Chikou Span is, how it functions within the Ichimoku system, and its relevance in both stock and cryptocurrency markets.
The Role of the Chikou Span in Technical Analysis
The Chikou Span, often called the Lagging Span, serves as a confirmation tool within the Ichimoku Cloud framework. Its primary purpose is to help traders identify trend direction and potential reversals by comparing current prices with past prices. Unlike leading indicators that predict future movements or oscillators that measure momentum, lagging indicators like the Chikou Span analyze historical data to validate current trends.
In practice, this means plotting a security’s closing price 26 periods behind its current position. If this lagging line remains above previous prices over time, it suggests sustained upward momentum; if below, it indicates downward pressure. When combined with other components of the Ichimoku system—such as Tenkan-sen (Conversion Line) or Kijun-sen (Base Line)—the Chikou Span enhances overall market insight.
How Is The Chikou Span Calculated?
The calculation of the Chikou Span is straightforward but crucial for accurate interpretation. It involves taking today's closing price and plotting it 26 periods back on your chart. For example:
- If today’s closing price is $100,
- You would plot $100 on your chart 26 days ago (or 26 candlesticks if using daily data).
This simple shift creates a visual representation that allows traders to compare past prices directly with current levels without complex formulas or additional calculations.
Interpreting The Chikou Span: What Do Different Positions Mean?
The position of the Chikou Span relative to past prices offers valuable insights into market sentiment:
- Above previous prices: Indicates bullish momentum; recent closes are higher than those from 26 periods ago.
- Below previous prices: Signals bearish sentiment; recent closes are lower than those from 26 periods ago.
- Crossing over: When this line crosses above or below historical price levels—especially when combined with other signals—it can suggest potential trend reversals.
For example:
- A rising Chikou span crossing above past prices may confirm an emerging uptrend.
- Conversely, crossing below could warn of a downtrend forming.
Traders often look for these crossovers as part of their decision-making process alongside other elements like cloud support/resistance levels.
Historical Background and Development
The Ichimoku Cloud was developed by Japanese journalist Goichi Hosoda during the late 1960s as an all-in-one trading system designed for quick decision-making without relying on multiple separate indicators. Its name translates roughly as "one glance" cloud because it provides a comprehensive view at a glance through five key components—including Tenkan-sen, Kijun-sen, Senkou Spans A & B (Leading Spans), and notably—the Chikou Span.
Since its inception decades ago, this method has gained worldwide popularity among professional traders due to its ability to depict trend strength and potential reversal points effectively across various markets—from stocks to forex and cryptocurrencies.
Practical Applications in Stock Trading
In stock markets today, many traders incorporate Ichimoku components—including the Chikoudo span—to enhance their technical analysis toolkit. It helps identify long-term trends by confirming whether recent price action aligns with historical movement patterns captured by lagging lines like Chiukō span.
For instance:
- When stock prices are above all cloud boundaries AND Chiukō spans remain above past lows—this typically signals strong bullish conditions.
- Conversely,if stock prices fall below key support levels while Chiukō spans stay beneath prior lows—it suggests bearish dominance or possible trend exhaustion.
Using these signals together improves confidence in trade entries/exits while reducing false positives common when relying solely on single indicators.
Application in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency trading has seen rapid growth over recent years—with high volatility making reliable analysis essential. Traders have adapted traditional tools like Ichimoku Cloud because they provide clear visual cues amidst turbulent price swings typical of digital assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum.
In crypto markets:
- The Lagging span can help confirm whether recent surges are sustainable.
- Crossings between Chiukō spans and historical lows/highs serve as early warning signs for reversals amid volatile conditions.
However—as cryptocurrencies tend toward extreme volatility—the effectiveness of lagging indicators like Chiukō should be complemented with volume analysis or other momentum tools for better accuracy.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
While useful—like any indicator—theChikuo span isn’t perfect:
- Lag Effect: Since it's based on past data (26 periods behind), it may not react quickly enough during sudden market moves.
- False Signals: In highly volatile environments such as crypto markets or during news events—crossovers might generate misleading signals.
- Market Conditions: During sideways consolidation phases—or choppy ranges—the indicator's readings can become ambiguous.
Therefore—and especially when trading high-volatility assets—it’s advisable always to combine Lagging Spans with other technical tools such as volume profiles or oscillators like RSI/MACD.
How To Use The Chikou Spread Effectively
To maximize utility:
- Confirm trend direction via position relative to prior candles
- Watch for crossovers indicating possible reversals
- Use alongside cloud support/resistance zones
- Combine with volume confirmation where applicable
By integrating these strategies into your trading plan—and understanding both strengths & limitations—you’ll improve your chances of making more accurate predictions about future market movements.
Final Thoughts on The Importance Of The Lagging Indicator
TheChikuo span remains an integral part of modern technical analysis due primarily to its simplicity yet powerful confirmation capabilities within broader systems likeIchimoku Cloud . Whether you're analyzing stocks or cryptocurrencies , understanding how this indicator works will enhance your abilityto interpret long-term trends accurately .
While no single tool guarantees success — combiningLagging Spanswith other analytical methods will give you more robust insights into market dynamics . As always — continuous learningand practical experienceare key ingredientsfor successful trading.
Note: Always remember that no indicator should be used in isolation; effective risk management practices remain essential regardlessof which analytical techniques you employ.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Assessing Materiality of Subsequent Events: A Complete Guide for Accountants and Auditors
Understanding the significance of subsequent events in financial reporting is essential for maintaining transparency and accuracy in financial statements. This guide explores how professionals can effectively evaluate the materiality of these events, especially amid recent developments in the crypto and investment sectors.
What Are Subsequent Events in Financial Reporting?
Subsequent events are occurrences that happen after a company's balance sheet date but before its financial statements are finalized and issued. These events can influence the interpretation of a company's financial position or performance. They are classified into two categories:
- Adjusting Events: These require modifications to the financial statements because they provide additional evidence about conditions existing at the balance sheet date. For example, discovering an error or recognizing new information about an asset's impairment.
- Non-Adjusting Events: These do not lead to adjustments but must be disclosed if they are material enough to influence users' decisions. An example includes a major lawsuit filed after year-end.
The importance of correctly identifying and classifying subsequent events lies in ensuring that stakeholders receive accurate, complete information that reflects current realities.
How to Assess Materiality of Subsequent Events
Evaluating whether a subsequent event is material involves several critical steps designed to determine its impact on financial reports:
Identify Whether an Event Has Occurred
The first step is detecting any significant event post-balance sheet date through ongoing review processes, management inquiries, or external information sources such as news reports or regulatory filings.
Evaluate Its Impact on Financial Statements
Once identified, assess whether this event could alter the understanding of a company's assets, liabilities, income, or cash flows—especially if it affects key figures like liquidity ratios or debt levels.
Consider Quantitative Factors
Quantitative assessment involves measuring how much an event could change reported figures—such as dollar amounts—that might influence decision-making by investors or creditors.
Assess Qualitative Factors
Qualitative considerations include evaluating aspects like:
- The nature of the transaction (e.g., fraud vs legitimate business activity)
- The potential reputational impact
- Regulatory implications
- Industry-specific risks (notably relevant for volatile sectors like cryptocurrencies)
Compare with Historical Data
Comparing recent events with historical trends helps determine their unusualness or significance within broader operational contexts.
Determine Stakeholder Impact
Finally, consider whether disclosure would influence stakeholder decisions—such as investment choices—or alter market perceptions significantly enough to warrant detailed reporting.
Recent Developments Shaping Materiality Assessment
The landscape surrounding subsequent event assessments has evolved considerably due to rapid changes within certain industries:
Crypto Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets have experienced extreme fluctuations recently — including crashes like FTX’s collapse in 2022 — which have led to substantial subsequent events affecting asset valuations and liquidity positions for involved entities. Such volatility underscores why auditors need heightened vigilance when assessing crypto-related assets’ fair value post-year-end.
Regulatory Changes
Governments worldwide continue updating regulations concerning digital currencies and investments; these shifts often trigger material subsequent events requiring disclosure due to their potential impact on compliance costs and operational risk profiles.
Evolving Auditing Standards
International standards bodies such as IAASB have issued updated guidelines emphasizing comprehensive evaluation methods that incorporate both quantitative data (financial impacts) and qualitative factors (industry risks). Staying aligned with these standards ensures auditors maintain high-quality assessments amid complex environments like crypto markets.
Potential Consequences When Materiality Is Misjudged
Incorrectly assessing what constitutes a material subsequent event can lead to serious repercussions:
Loss of Investor Confidence: Incomplete disclosures may cause stakeholders to question management’s transparency.
Legal Risks: Failure to properly disclose significant developments might result in regulatory penalties or lawsuits.
Reputational Damage: Auditors who overlook critical updates risk damaging their professional credibility; firms may face scrutiny from oversight bodies if they neglect evolving standards.
Key Dates That Shape Current Practices
Several pivotal moments highlight how regulatory guidance influences assessment procedures:
In 2019, SEC issued specific guidance on disclosing significant subsequent events impacting investor decision-making.
The IAASB’s updated guidelines from 2020 emphasize integrating both qualitative insights alongside quantitative analysis during audits related particularly to high-risk industries such as cryptocurrency trading platforms.
Understanding How To Stay Compliant
For accountants and auditors aiming for compliance while managing emerging risks associated with volatile sectors:
- Regularly review updates from standard-setting organizations.*
- Incorporate industry-specific risk factors into your assessment procedures.*
- Maintain thorough documentation supporting your judgment regarding what qualifies as materially impactful.*
- Engage multidisciplinary teams—including legal counsel—to interpret complex situations involving new regulations.*
Why Accurate Assessment Matters More Than Ever Today
In today’s fast-changing economic environment—marked by technological innovation and increased market volatility—the ability to accurately evaluate the materiality of subsequent events is vital for safeguarding stakeholder interests while upholding professional integrity within accounting practices.
By applying structured evaluation techniques rooted in current standards—and remaining vigilant about sector-specific developments—professionals can ensure timely disclosures that reflect true economic realities without exposing themselves—or their clients—to unnecessary legal exposure or reputational harm.
Keywords: materiality assessment, subsequent events disclosure, audit procedures crypto sector , regulatory compliance accounting , investor confidence finance , high-risk industries audit standards


Lo
2025-05-19 15:29
How to assess materiality of subsequent events?
Assessing Materiality of Subsequent Events: A Complete Guide for Accountants and Auditors
Understanding the significance of subsequent events in financial reporting is essential for maintaining transparency and accuracy in financial statements. This guide explores how professionals can effectively evaluate the materiality of these events, especially amid recent developments in the crypto and investment sectors.
What Are Subsequent Events in Financial Reporting?
Subsequent events are occurrences that happen after a company's balance sheet date but before its financial statements are finalized and issued. These events can influence the interpretation of a company's financial position or performance. They are classified into two categories:
- Adjusting Events: These require modifications to the financial statements because they provide additional evidence about conditions existing at the balance sheet date. For example, discovering an error or recognizing new information about an asset's impairment.
- Non-Adjusting Events: These do not lead to adjustments but must be disclosed if they are material enough to influence users' decisions. An example includes a major lawsuit filed after year-end.
The importance of correctly identifying and classifying subsequent events lies in ensuring that stakeholders receive accurate, complete information that reflects current realities.
How to Assess Materiality of Subsequent Events
Evaluating whether a subsequent event is material involves several critical steps designed to determine its impact on financial reports:
Identify Whether an Event Has Occurred
The first step is detecting any significant event post-balance sheet date through ongoing review processes, management inquiries, or external information sources such as news reports or regulatory filings.
Evaluate Its Impact on Financial Statements
Once identified, assess whether this event could alter the understanding of a company's assets, liabilities, income, or cash flows—especially if it affects key figures like liquidity ratios or debt levels.
Consider Quantitative Factors
Quantitative assessment involves measuring how much an event could change reported figures—such as dollar amounts—that might influence decision-making by investors or creditors.
Assess Qualitative Factors
Qualitative considerations include evaluating aspects like:
- The nature of the transaction (e.g., fraud vs legitimate business activity)
- The potential reputational impact
- Regulatory implications
- Industry-specific risks (notably relevant for volatile sectors like cryptocurrencies)
Compare with Historical Data
Comparing recent events with historical trends helps determine their unusualness or significance within broader operational contexts.
Determine Stakeholder Impact
Finally, consider whether disclosure would influence stakeholder decisions—such as investment choices—or alter market perceptions significantly enough to warrant detailed reporting.
Recent Developments Shaping Materiality Assessment
The landscape surrounding subsequent event assessments has evolved considerably due to rapid changes within certain industries:
Crypto Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets have experienced extreme fluctuations recently — including crashes like FTX’s collapse in 2022 — which have led to substantial subsequent events affecting asset valuations and liquidity positions for involved entities. Such volatility underscores why auditors need heightened vigilance when assessing crypto-related assets’ fair value post-year-end.
Regulatory Changes
Governments worldwide continue updating regulations concerning digital currencies and investments; these shifts often trigger material subsequent events requiring disclosure due to their potential impact on compliance costs and operational risk profiles.
Evolving Auditing Standards
International standards bodies such as IAASB have issued updated guidelines emphasizing comprehensive evaluation methods that incorporate both quantitative data (financial impacts) and qualitative factors (industry risks). Staying aligned with these standards ensures auditors maintain high-quality assessments amid complex environments like crypto markets.
Potential Consequences When Materiality Is Misjudged
Incorrectly assessing what constitutes a material subsequent event can lead to serious repercussions:
Loss of Investor Confidence: Incomplete disclosures may cause stakeholders to question management’s transparency.
Legal Risks: Failure to properly disclose significant developments might result in regulatory penalties or lawsuits.
Reputational Damage: Auditors who overlook critical updates risk damaging their professional credibility; firms may face scrutiny from oversight bodies if they neglect evolving standards.
Key Dates That Shape Current Practices
Several pivotal moments highlight how regulatory guidance influences assessment procedures:
In 2019, SEC issued specific guidance on disclosing significant subsequent events impacting investor decision-making.
The IAASB’s updated guidelines from 2020 emphasize integrating both qualitative insights alongside quantitative analysis during audits related particularly to high-risk industries such as cryptocurrency trading platforms.
Understanding How To Stay Compliant
For accountants and auditors aiming for compliance while managing emerging risks associated with volatile sectors:
- Regularly review updates from standard-setting organizations.*
- Incorporate industry-specific risk factors into your assessment procedures.*
- Maintain thorough documentation supporting your judgment regarding what qualifies as materially impactful.*
- Engage multidisciplinary teams—including legal counsel—to interpret complex situations involving new regulations.*
Why Accurate Assessment Matters More Than Ever Today
In today’s fast-changing economic environment—marked by technological innovation and increased market volatility—the ability to accurately evaluate the materiality of subsequent events is vital for safeguarding stakeholder interests while upholding professional integrity within accounting practices.
By applying structured evaluation techniques rooted in current standards—and remaining vigilant about sector-specific developments—professionals can ensure timely disclosures that reflect true economic realities without exposing themselves—or their clients—to unnecessary legal exposure or reputational harm.
Keywords: materiality assessment, subsequent events disclosure, audit procedures crypto sector , regulatory compliance accounting , investor confidence finance , high-risk industries audit standards
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is Know Your Customer (KYC)?
Understanding KYC in Financial Services
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a fundamental regulatory requirement within the financial services industry. It involves verifying the identity of clients to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and identity theft. The process requires financial institutions to collect personal information from their customers—such as full name, date of birth, residential address, and official identification documents like passports or driver’s licenses—and then authenticate this data through various verification methods.
The primary goal of KYC is to ensure that financial entities understand who their customers are. This understanding helps institutions assess potential risks associated with each client and maintain compliance with legal standards designed to combat financial crimes. As digital banking continues to expand globally, the importance of robust KYC procedures has grown exponentially.
Historical Context and Evolution
Although the concept of verifying customer identities has existed for decades, recent technological advancements have transformed how KYC processes are implemented. Traditionally reliant on manual document checks at bank branches or offices, today’s systems leverage automation and digital tools for faster onboarding and ongoing monitoring.
The rise of online banking platforms during the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift toward remote verification methods such as video calls or biometric authentication. Regulatory bodies worldwide have responded by updating frameworks—like Europe’s Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD5)—to strengthen requirements around customer due diligence (CDD). These updates aim not only to improve security but also facilitate smoother user experiences without compromising compliance standards.
Key Components of KYC Procedures
Effective KYC involves several critical steps:
- Customer Identification: Collecting basic personal details including name, date of birth, address.
- Document Verification: Confirming authenticity through official IDs like passports or driver’s licenses.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential threats based on customer profiles and transaction patterns.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously reviewing account activity for suspicious behavior post-verification.
Financial institutions often employ advanced technologies such as biometric scans—fingerprints or facial recognition—and machine learning algorithms that analyze transaction data in real-time. These tools enhance accuracy while reducing manual effort.
Regulatory Frameworks Supporting KYC Compliance
Various authorities enforce regulations requiring strict adherence to KYC protocols:
- In the United States, agencies like FinCEN mandate comprehensive anti-money laundering measures.
- The European Union enforces directives such as AMLD5 that impose detailed customer due diligence rules across member states.
- Other countries have similar laws tailored to local contexts but aligned with international standards set by organizations like FATF (Financial Action Task Force).
These regulations aim not only at preventing illicit activities but also at fostering transparency within global financial markets.
Recent Innovations in KYC Technology
Technological progress continues shaping modern KYC practices:
- Digital Transformation – Remote onboarding via video conferencing reduces physical visits while maintaining verification integrity.
- Blockchain & Cryptocurrency Regulation – As cryptocurrencies gain popularity, regulators develop guidelines ensuring crypto exchanges comply with AML/KYC norms.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning – AI-driven systems analyze vast datasets swiftly; they can flag anomalies indicative of fraud or money laundering attempts more effectively than traditional methods.
Such innovations help balance stringent security requirements with user convenience—a crucial factor in competitive markets where seamless customer experience influences loyalty and trust.
Challenges Faced by Financial Institutions
Despite technological advances, implementing effective KYC processes presents several challenges:
Customer Experience: Overly complex procedures may frustrate users leading to drop-offs during onboarding stages.Compliance Costs: Developing compliant systems requires significant investment in technology infrastructure and staff training—costs often passed onto consumers indirectly.Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting sensitive personal information raises questions about data security; breaches could damage reputation severely.Regulatory Overreach: Excessively broad rules might hinder innovation especially concerning emerging sectors like blockchain-based finance solutions.
Balancing these factors demands strategic planning from banks and regulators alike—to uphold security without sacrificing usability or stifling innovation.
The Impact on Customer Trust & Business Operations
A well-executed Know Your Customer process enhances trust between clients and service providers by demonstrating commitment to security standards. Customers tend to favor institutions that prioritize privacy protections alongside compliance efforts because it reassures them their data is handled responsibly.
From an operational perspective, thorough identity verification reduces risks associated with fraudulent accounts or transactions—saving costs related to fraud management later down the line. Additionally,
a transparent approach fosters regulatory confidence which can facilitate smoother cross-border transactions—a vital aspect for multinational corporations operating across different jurisdictions.
Future Trends in Know Your Customer Practices
As technology evolves further,
the future landscape of KYC will likely feature increased automation using artificial intelligence coupled with biometric authentication techniques such as facial recognition or fingerprint scanning integrated into mobile apps seamlessly.
Moreover,
regulators may introduce more standardized global frameworks for crypto-related activities ensuring consistent compliance levels worldwide.
Finally,
privacy-preserving technologies like zero-knowledge proofs could become mainstream—they allow verification without exposing sensitive data—addressing privacy concerns while maintaining rigorous anti-fraud measures.
Final Thoughts on Implementing Effective KYC Strategies
In summary,
Know Your Customer remains a cornerstone element within global financial regulation aimed at safeguarding economies from illicit activities while enhancing consumer trust through secure processes.
While challenges persist—including balancing stringent controls against user experience—the integration of innovative technologies promises more efficient solutions moving forward.
Financial institutions must stay adaptable by continuously updating their systems aligned with evolving regulations—and prioritize responsible handling of personal data—to succeed in an increasingly digital world.
This comprehensive overview underscores why robust KYC practices are essential—not just for regulatory compliance but also for building resilient financial ecosystems capable of thwarting emerging threats effectively.
Keywords: Know Your Customer,KYCCustomer VerificationAnti-Money LaunderingDigital BankingBiometric AuthenticationAML RegulationsFinancial Crime PreventionBlockchainCrypto ComplianceAI in FinanceData Privacy


kai
2025-05-15 01:40
What is Know Your Customer (KYC)?
What is Know Your Customer (KYC)?
Understanding KYC in Financial Services
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a fundamental regulatory requirement within the financial services industry. It involves verifying the identity of clients to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and identity theft. The process requires financial institutions to collect personal information from their customers—such as full name, date of birth, residential address, and official identification documents like passports or driver’s licenses—and then authenticate this data through various verification methods.
The primary goal of KYC is to ensure that financial entities understand who their customers are. This understanding helps institutions assess potential risks associated with each client and maintain compliance with legal standards designed to combat financial crimes. As digital banking continues to expand globally, the importance of robust KYC procedures has grown exponentially.
Historical Context and Evolution
Although the concept of verifying customer identities has existed for decades, recent technological advancements have transformed how KYC processes are implemented. Traditionally reliant on manual document checks at bank branches or offices, today’s systems leverage automation and digital tools for faster onboarding and ongoing monitoring.
The rise of online banking platforms during the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift toward remote verification methods such as video calls or biometric authentication. Regulatory bodies worldwide have responded by updating frameworks—like Europe’s Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD5)—to strengthen requirements around customer due diligence (CDD). These updates aim not only to improve security but also facilitate smoother user experiences without compromising compliance standards.
Key Components of KYC Procedures
Effective KYC involves several critical steps:
- Customer Identification: Collecting basic personal details including name, date of birth, address.
- Document Verification: Confirming authenticity through official IDs like passports or driver’s licenses.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential threats based on customer profiles and transaction patterns.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously reviewing account activity for suspicious behavior post-verification.
Financial institutions often employ advanced technologies such as biometric scans—fingerprints or facial recognition—and machine learning algorithms that analyze transaction data in real-time. These tools enhance accuracy while reducing manual effort.
Regulatory Frameworks Supporting KYC Compliance
Various authorities enforce regulations requiring strict adherence to KYC protocols:
- In the United States, agencies like FinCEN mandate comprehensive anti-money laundering measures.
- The European Union enforces directives such as AMLD5 that impose detailed customer due diligence rules across member states.
- Other countries have similar laws tailored to local contexts but aligned with international standards set by organizations like FATF (Financial Action Task Force).
These regulations aim not only at preventing illicit activities but also at fostering transparency within global financial markets.
Recent Innovations in KYC Technology
Technological progress continues shaping modern KYC practices:
- Digital Transformation – Remote onboarding via video conferencing reduces physical visits while maintaining verification integrity.
- Blockchain & Cryptocurrency Regulation – As cryptocurrencies gain popularity, regulators develop guidelines ensuring crypto exchanges comply with AML/KYC norms.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning – AI-driven systems analyze vast datasets swiftly; they can flag anomalies indicative of fraud or money laundering attempts more effectively than traditional methods.
Such innovations help balance stringent security requirements with user convenience—a crucial factor in competitive markets where seamless customer experience influences loyalty and trust.
Challenges Faced by Financial Institutions
Despite technological advances, implementing effective KYC processes presents several challenges:
Customer Experience: Overly complex procedures may frustrate users leading to drop-offs during onboarding stages.Compliance Costs: Developing compliant systems requires significant investment in technology infrastructure and staff training—costs often passed onto consumers indirectly.Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting sensitive personal information raises questions about data security; breaches could damage reputation severely.Regulatory Overreach: Excessively broad rules might hinder innovation especially concerning emerging sectors like blockchain-based finance solutions.
Balancing these factors demands strategic planning from banks and regulators alike—to uphold security without sacrificing usability or stifling innovation.
The Impact on Customer Trust & Business Operations
A well-executed Know Your Customer process enhances trust between clients and service providers by demonstrating commitment to security standards. Customers tend to favor institutions that prioritize privacy protections alongside compliance efforts because it reassures them their data is handled responsibly.
From an operational perspective, thorough identity verification reduces risks associated with fraudulent accounts or transactions—saving costs related to fraud management later down the line. Additionally,
a transparent approach fosters regulatory confidence which can facilitate smoother cross-border transactions—a vital aspect for multinational corporations operating across different jurisdictions.
Future Trends in Know Your Customer Practices
As technology evolves further,
the future landscape of KYC will likely feature increased automation using artificial intelligence coupled with biometric authentication techniques such as facial recognition or fingerprint scanning integrated into mobile apps seamlessly.
Moreover,
regulators may introduce more standardized global frameworks for crypto-related activities ensuring consistent compliance levels worldwide.
Finally,
privacy-preserving technologies like zero-knowledge proofs could become mainstream—they allow verification without exposing sensitive data—addressing privacy concerns while maintaining rigorous anti-fraud measures.
Final Thoughts on Implementing Effective KYC Strategies
In summary,
Know Your Customer remains a cornerstone element within global financial regulation aimed at safeguarding economies from illicit activities while enhancing consumer trust through secure processes.
While challenges persist—including balancing stringent controls against user experience—the integration of innovative technologies promises more efficient solutions moving forward.
Financial institutions must stay adaptable by continuously updating their systems aligned with evolving regulations—and prioritize responsible handling of personal data—to succeed in an increasingly digital world.
This comprehensive overview underscores why robust KYC practices are essential—not just for regulatory compliance but also for building resilient financial ecosystems capable of thwarting emerging threats effectively.
Keywords: Know Your Customer,KYCCustomer VerificationAnti-Money LaunderingDigital BankingBiometric AuthenticationAML RegulationsFinancial Crime PreventionBlockchainCrypto ComplianceAI in FinanceData Privacy
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
